Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a white solid that appears in form of tabular crystals.[2]
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1H-1,3-Benzimidazole | |||
| Other names 1H-Benzo[d]imidazole | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| 109682 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.075 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 3106 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H6N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 118.139 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 170 to 172 °C (338 to 342 °F; 443 to 445 K) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.8 (for benzimidazole) and 5.6 (for the conjugate acid)[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 | |||
| Warning | |||
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Preparation
Benzimidazole was discovered during research on vitamin B12. The benzimidazole nucleus was found to be a stable platform on which drugs could be developed.[3] Benzimidazole is produced by condensation of o-phenylenediamine with formic acid,[4] or the equivalent trimethyl orthoformate:
- C6H4(NH2)2 + HC(OCH3)3 → C6H4N(NH)CH + 3 CH3OH
2-Substituted derivatives are obtained when the condensation is conducted with aldehydes in place of formic acid, followed by oxidation.[5]
Reactions
Benzimidazole is a base:
- C6H4N(NH)CH + H+ → [C6H4(NH)2CH]+
It can also be deprotonated with stronger bases:
- C6H4N(NH)CH + LiH → Li [C6H4N2CH] + H2
The imine can be alkylated and also serves as a ligand in coordination chemistry. The most prominent benzimidazole complex features N-ribosyl-dimethylbenzimidazole, as found in vitamin B12.[6]
N,N'-Dialkylbenzimidazolium salts are precursors to certain N-heterocyclic carbenes.[7][8]
Applications
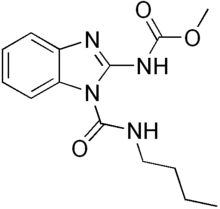
Benzimidazole derivatives are among the most frequently used ring systems for small molecule drugs listed by the United States Food and Drug Administration.[9] Many pharmaceutical agents belong to the benzimidazole class of compounds. For example:
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers such as azilsartan, candesartan, and telmisartan.
- Anthelmintic agents such as albendazole, ciclobendazole, fenbendazole, flubendazole, mebendazole, oxfendazole, oxibendazole, triclabendazole, and thiabendazole. These drugs work by binding tubulin, a vital part of the cytoskeleton and mitotic spindle. Benzimidazoles are selectively toxic towards parasitic nematodes, selectively binding and depolymerising their tubulins.[10]
- Antihistamines such as astemizole, bilastine, clemizole, emedastine, mizolastine, and oxatomide.
- Benzimidazole fungicides such as benomyl, carbendazim, fuberidazole, and thiabendazole. These drugs selectively bind to and depolymerise fungal tubulin.[10]
- Benzimidazole opioids such as bezitramide, brorphine, clonitazene, etodesnitazene, etonitazene, etonitazepipne, etonitazepyne, isotonitazene, metodesnitazene, and metonitazene.
- Proton-pump inhibitors such as dexlansoprazole, esomeprazole, ilaprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole, and tenatoprazole.
- Typical antipsychotics such as benperidol, clopimozide, droperidol, neflumozide, and oxiperomide, and pimozide.
- Other notable pharmaceutical agents which contain a benzimidazole group include abemaciclib, bendamustine, dabigatran, daridorexant, and glasdegib.
In printed circuit board manufacturing, benzimidazole can be used as an organic solderability preservative.[citation needed]
See also
- Benzimidazoline
- Polybenzimidazole, a high performance fiber
References
Further reading
- Grimmett, M. R. (1997). Imidazole and benzimidazole synthesis. Boston: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-303190-7.