In archaeogenetics, the term Western Hunter-Gatherer (WHG), West European Hunter-Gatherer, Western European Hunter-Gatherer, Villabruna cluster, or Oberkassel cluster (c. 15,000~5,000 BP) is the name given to a distinct ancestral component of modern Europeans, representing descent from a population of Mesolithic hunter-gatherers who scattered over Western, Southern and Central Europe, from the British Isles in the west to the Carpathians in the east, following the retreat of the ice sheet of the Last Glacial Maximum.[2]
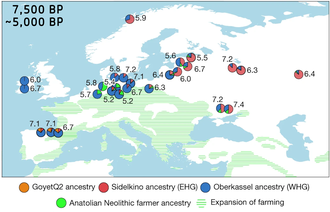
Genetic ancestry of hunter-gatherers in Europe between 14 ka and 9 ka, with the main area of Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG) in blue. Individual numbers correspond to calibrated sample dates.[1] |
Along with the Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers (SHG) and Eastern Hunter-Gatherers (EHG), the WHGs constituted one of the three main genetic groups in the postglacial period of early Holocene Europe.[3] The border between WHGs and EHGs ran roughly from the lower Danube, northward along the western forests of the Dnieper towards the western Baltic Sea.[2]
SHGs were in turn a nearly equal mix of WHGs and EHGs. Once the main population throughout Europe, the WHGs were largely displaced by successive expansions of Early European Farmers (EEFs) during the early Neolithic, but experienced a resurgence during the Middle Neolithic. During the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, Western Steppe Herders (WSHs) from the Pontic–Caspian steppe embarked on a massive expansion, which further displaced the WHGs. Among modern-day populations, WHG ancestry is most common among populations of the eastern Baltic.[4]
Research
Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG) are recognised as a distinct ancestral component contributing to the ancestry of most modern Europeans.[5] Most Europeans can be modeled as a mixture of WHG, EEF, and WSH from the Pontic–Caspian steppe.[6] WHGs also contributed ancestry to other ancient groups such as Early European Farmers (EEF), who were, however, mostly of Anatolian descent.[5] With the Neolithic expansion, EEF came to dominate the gene pool in most parts of Europe, although WHG ancestry had a resurgence in Western Europe from the Early Neolithic to the Middle Neolithic.[7]
Expansion into continental Europe (14,000 BP)
WHGs themselves are believed to have formed around 14,000 years ago, during the Bølling-Allerød interstadial, at the time of the first major warming period after the Ice Age. They represent a major population shift within Europe at the end of the Ice Age, probably a population expansion into continental Europe, from Southeastern European or West Asian refugia.[8] It is thought that their ancestors separated from eastern Eurasians around 40,000 BP, and from Ancient North Eurasians (ANE) prior to 24,000 BP (the estimated age date of the Mal'ta boy). This date was subsequently put further back in time by the findings of the Yana Rhinoceros Horn Site to around 38kya, shortly after the divergence of West-Eurasian and East-Eurasian lineages.[5][9] Vallini et al. 2022 argues that the dispersal and split patterns of West Eurasian lineages was not earlier than c. 38,000 years ago, with older Initial Upper Paleolithic European specimens, such as Zlaty Kun, Peștera cu Oase and Bacho Kiro, being unrelated to Western Hunter-gatherers but closer to Ancient East Eurasians or basal to both.[10] The WHG displayed higher affinity for ancient and modern Middle Eastern populations when compared against earlier Paleolithic Europeans such as Gravettians. The affinity for ancient Middle Eastern populations in Europe increased after the Last Glacial Maximum, correlating with the expansion of WHG (Villabruna or Oberkassel) ancestry. There is also evidence for bi-directional geneflow between WHG and Middle Eastern populations as early as 15,000 years ago. WHG associated remains belonged primarily to the human Y-chromosome haplogroups I-M170 with a lower frequency of C-F3393 (specifically the clade C-V20/C1a2), which has been found commonly among earlier Paleolithic European remains such as Kostenki-14 and Sungir. The paternal haplogroup C-V20 can still be found in men living in modern Spain, attesting to this lineage's longstanding presence in Western Europe. Their mitochondrial chromosomes belonged primarily to haplogroup U5.[11][12]

In a genetic study published in Nature in March 2023, the authors found that the ancestors of the WHGs were populations associated with the Epigravettian culture, which largely replaced populations associated with the Magdalenian culture about 14,000 years ago (the ancestors of the Magdalenian-associated individuals were the populations associated with the western Gravettian, Solutrean and Aurignacian cultures).[11][13] In the study, WHG ancestry is renamed 'Oberkassel ancestry', first found north of the Alps in two 14,000 year-old individuals at the eponymous site at Oberkassel, who can be modeled as an admixture of Villabruna ancestry (itself modeled as an admixture between a lineage related to the Věstonice cluster and a lineage ancestral to the Kostenki-14 and Goyet Q116-1 individuals), and Goyet-Q2 ancestry related to individuals found in Europe prior to the Last Glacial Maximum. The study states that all of the individuals of the Oberkassel cluster could be modeled as c. 75% Villabruna and 25% Goyet-Q2 ancestry or, alternatively, as c. 90% Villabruna and 10% Fournol ancestry, a newly identified cluster described as a sister lineage of the Goyet Q116-1 ancestry found in individuals associated with the Gravettian culture of southwestern Europe.[11] The study suggests that Oberkassel ancestry was mostly already formed before expanding, possibly around the west side of the Alps, to Western and Central Europe and Britain, where sampled WHG individuals are genetically homogeneous. This is in contrast to the arrival of Villabruna and Oberkassel ancestry to Iberia, which seems to have involved repeated admixture events with local populations carrying high levels of Goyet-Q2 ancestry. This, and the survival of specific Y-DNA haplogroup C1 clades previously observed among early European hunter-gatherers, suggests relatively higher genetic continuity in southwest Europe during this period.[11]
There are indications that the WHG carried "risk alleles for diabetes and Alzheimer's disease".[14]

Interaction with other populations

The WHG were also found to have contributed ancestry to populations on the borders of Europe such as early Anatolian farmers and Ancient Northwestern Africans,[16] as well as other European groups such as Eastern Hunter-Gatherers.[17] The relationship of WHGs to the EHGs remains inconclusive.[17] EHGs are modeled to derive varying degrees of ancestry from a WHG-related lineage, ranging from merely 25% to up to 91%, with the remainder being linked to geneflow from Paleolithic Siberians (ANE) and perhaps Caucasus hunter-gatherers. Another lineage known as the Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers (SHGs) were found to be a mix of EHGs and WHGs.[a][19][20]
People of the Mesolithic Kunda culture and the Narva culture of the eastern Baltic were a mix of WHG and EHG,[21] showing the closest affinity with WHG. Samples from the Ukrainian Mesolithic and Neolithic were found to cluster tightly together between WHG and EHG, suggesting genetic continuity in the Dnieper Rapids for a period of 4,000 years. The Ukrainian samples belonged exclusively to the maternal haplogroup U, which is found in around 80% of all European hunter-gatherer samples.[22]
People of the Pit–Comb Ware culture (CCC) of the eastern Baltic were closely related to EHG.[23] Unlike most WHGs, the WHGs of the eastern Baltic did not receive European farmer admixture during the Neolithic. Modern populations of the eastern Baltic thus harbor a larger amount of WHG ancestry than any other population in Europe.[21]
SHGs have been found to contain a mix of WHG components who had likely migrated into Scandinavia from the south, and EHGs who had later migrated into Scandinavia from the northeast along the Norwegian coast. This hypothesis is supported by evidence that SHGs from western and northern Scandinavia had less WHG ancestry (ca 51%) than individuals from eastern Scandinavia (ca. 62%). The WHGs who entered Scandinavia are believed to have belonged to the Ahrensburg culture. EHGs and WHGs displayed lower allele frequencies of SLC45A2 and SLC24A5, which cause depigmentation, and OCA/Herc2, which causes light eye color, than SHGs.[24]

The DNA of eleven WHGs from the Upper Palaeolithic and Mesolithic in Western Europe, Central Europe and the Balkans was analyzed, with regards to their Y-DNA haplogroups and mtDNA haplogroups. The analysis suggested that WHGs were once widely distributed from the Atlantic coast in the West, to Sicily in the South, to the Balkans in the Southeast, for more than six thousand years.[25] The study also included an analysis of a large number of individuals of prehistoric Eastern Europe. Thirty-seven samples were collected from Mesolithic and Neolithic Ukraine (9500-6000 BC). These were determined to be an intermediate between EHG and SHG, although WHG ancestry in this population increased during the Neolithic. Samples of Y-DNA extracted from these individuals belonged exclusively to R haplotypes (particularly subclades of R1b1) and I haplotypes (particularly subclades of I2). mtDNA belonged almost exclusively to U (particularly subclades of U5 and U4).[25] A large number of individuals from the Zvejnieki burial ground, which mostly belonged to the Kunda culture and Narva culture in the eastern Baltic, were analyzed. These individuals were mostly of WHG descent in the earlier phases, but over time EHG ancestry became predominant. The Y-DNA of this site belonged almost exclusively to haplotypes of haplogroup R1b1a1a and I2a1. The mtDNA belonged exclusively to haplogroup U (particularly subclades of U2, U4 and U5).[25] Forty individuals from three sites of the Iron Gates Mesolithic in the Balkans were also analyzed. These individuals were estimated to be of 85% WHG and 15% EHG descent. The males at these sites carried exclusively haplogroup R1b1a and I (mostly subclades of I2a) haplotypes. mtDNA belonged mostly to U (particularly subclades of U5 and U4).[25] People of the Balkan Neolithic were found to harbor 98% Anatolian ancestry and 2% WHG ancestry. By the Chalcolithic, people of the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture were found to harbor about 20% hunter-gatherer ancestry, which was intermediate between EHG and WHG. People of the Globular Amphora culture were found to harbor ca. 25% WHG ancestry, which is significantly higher than Middle Neolithic groups of Central Europe.[25]
Replacement by Neolithic farmers

A seminal 2014 study first identified the contribution of three main components to modern European lineages: the Western Hunter Gatherers (WHG, in proportions of up to 50% in Northern Europeans), the Ancient North Eurasians (ANE, Upper Palaeolithic Siberians later associated with the later Indo-European expansion, present in proportions up to 20%), and finally the Early European Farmers (EEF, agriculturists of mainly Near Eastern origin who migrated to Europe from circa 8,000 BP, now present in proportions from around 30% in the Baltic region to around 90% in the Mediterranean). The Early European Farmer (EEF) component was identified based on the genome of a woman buried c. 7,000 years ago in a Linear Pottery culture grave in Stuttgart, Germany.[27]
This 2014 study found evidence for genetic mixing between WHG and EEF throughout Europe, with the largest contribution of EEF in Mediterranean Europe (especially in Sardinia, Sicily, Malta and among Ashkenazi Jews), and the largest contribution of WHG in Northern Europe and among Basque people.[28]
Since 2014, further studies have refined the picture of interbreeding between EEF and WHG. In a 2017 analysis of 180 ancient DNA datasets of the Chalcolithic and Neolithic periods from Hungary, Germany and Spain, evidence was found of a prolonged period of interbreeding. Admixture took place regionally, from local hunter-gatherer populations, so that populations from the three regions (Germany, Iberia and Hungary) were genetically distinguishable at all stages of the Neolithic period, with a gradually increasing ratio of WHG ancestry of farming populations over time. This suggests that after the initial expansion of early farmers, there were no further long-range migrations substantial enough to homogenize the farming population, and that farming and hunter-gatherer populations existed side by side for many centuries, with ongoing gradual admixture throughout the 5th to 4th millennia BC (rather than a single admixture event on initial contact).[29] Admixture rates varied geographically; in the late Neolithic, WHG ancestry in farmers in Hungary was at around 10%, in Germany around 25% and in Iberia as high as 50%.[30]
Analysis of remains from the Grotta Continenza in Italy showed that out of six remains, three buried between c. 10,000 BC and 7000 BC belonged to I2a-P214; and two-times the maternal haplogroups U5b1 and one U5b3.[31][32] Around 6000 BC, the WHGs of Italy were almost completely genetically replaced by EEFs (two G2a2) and one Haplogroup R1b, although WHG ancestry slightly increased in subsequent millennia.[33]
Neolithic individuals in the British Isles were close to Iberian and Central European Early and Middle Neolithic populations, modeled as having about 75% ancestry from EEF with the rest coming from WHG in continental Europe. They subsequently replaced most of the WHG population in the British Isles without mixing much with them.[34]
The WHG are estimated to have contributed between 20-30% ancestry to Neolithic EEF groups throughout Europe. Specific adaptions against local pathogens may have been introduced via the Mesolithic WHG admixture into Neolithic EEF populations.[35]
A study on Mesolithic hunter-gatherers from Denmark found that they were related to contemporary Western hunter-gatherers, and are associated with the Maglemose, Kongemose and Ertebølle cultures. They displayed "genetic homogeneity from around 10,500 to 5,900 calibrated years before present", until "Neolithic farmers with Anatolian-derived ancestry arrived". The transition to the Neolithic period was "very abrupt and resulted in a population turnover with limited genetic contribution from local hunter-gatherers. The succeeding Neolithic population has been associated with the Funnelbeaker culture.[36]
Physical appearance

According to David Reich, DNA analysis has shown that Western Hunter Gatherers were typically dark skinned, dark haired, and blue eyed.[39] The dark skin was due to their Out-of-Africa origin (all Homo sapiens populations having had initially dark skin), while the blue eyes were the result of a variation in their OCA2 gene, which caused iris depigmentation.[40]
Archaeologist Graeme Warren has said that their skin color ranged from olive to black, and speculated that they may have had some regional variety of eye and hair colors.[41] This is strikingly different from the distantly related Eastern Hunter-Gatherers (EHG)—who have been suggested to be light-skinned, brown-eyed or blue eyed and dark-haired or light-haired.[42]
Two WHG skeletons with incomplete SNPs, La Braña and Cheddar Man, are predicted to have had dark or dark to black skin, whereas two other WHG skeletons with complete SNPs, "Sven" and Loschbour man, are predicted to have had dark or intermediate-to-dark and intermediate skin, respectively.[43][24][b] Spanish biologist Carles Lalueza-Fox said the La Braña-1 individual had dark skin, "although we cannot know the exact shade."[45]
According to a 2020 study, the arrival of Early European Farmers (EEFs) from western Anatolia from 8500 to 5000 years ago, along with Western Steppe Herders during the Bronze Age, caused a rapid evolution of European populations towards lighter skin and hair.[40] Admixture between hunter-gatherer and agriculturist populations was apparently occasional, but not extensive.[46]

Some authors have expressed caution regarding skin pigmentation reconstructions: Quillen et al. (2019) acknowledge studies that generally show that "lighter skin color was uncommon across much of Europe during the Mesolithic", including studies regarding the “dark or dark to black” predictions for the Cheddar Man, but warn that "reconstructions of Mesolithic and Neolithic pigmentation phenotype using loci common in modern populations should be interpreted with some caution, as it is possible that other as yet unexamined loci may have also influenced phenotype."[47]
Geneticist Susan Walsh at Indiana University–Purdue University Indianapolis, who worked on Cheddar Man project, said that "we simply don't know his skin colour".[48] German biochemist Johannes Krause stated that we do not know whether the skin color of Western European hunter-gatherers was more similar to the skin color of people from present-day Central Africa or people from the Arab region. It is only certain that they did not carry any known mutation responsible for the light skin in subsequent populations of Europeans.[49]
A 2024 research into the genomic ancestry and social dynamics of the last hunter-gatherers of Atlantic France has stated that "phenotypically, we find some diversity during the Late Mesolithic in France", at which two of the WHG's sequenced in the study "likely had pale to intermediate skin pigmentation", but "most individuals carry the dark skin and blue eyes characteristic of WHGs" of the studied samples.[50]
