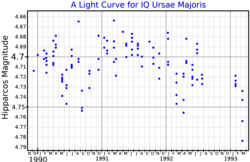
83 Ursae Majoris is a candidate binary star[11] system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It is a semiregular variable star, and it has been given the variable star designation IQ Ursae Majoris. It ranges in brightness from apparent visual magnitude 4.69 to 4.75.[3] Percy and Au (1994) identified it as a small amplitude red variable with an irregular behavior, having a characteristic time scale of 20 days.[12] Based upon an annual parallax shift of 6.23±0.22 mas,[2] it is located roughly 520 light years from the Sun. The distance derived from its Gaia Early Data Release 3 parallax is 179 pc.[13] The system is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −18.6[6] km/s.
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Ursa Major |
| Right ascension | 13h 40m 44.27335s[2] |
| Declination | +54° 40′ 53.8891″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.69 - 4.75[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M2 III[4] |
| B−V color index | +1.630±0.006[5] |
| Variable type | SRb[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −18.61±0.20[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −19.06[2] mas/yr Dec.: −10.56[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 6.23 ± 0.22 mas[2] |
| Distance | 520 ± 20 ly (161 ± 6 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.39[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.1[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 80[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,250[9] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.62[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,579[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.07[7] dex |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
The visible component is an evolved red giant with a stellar classification of M2 III.[4] It is a marginal barium star, showing an enhanced abundance of s-process elements in its outer atmosphere. This material may have been acquired during a previous mass transfer from a now white dwarf companion, or self-enriched by a dredge-up during the asymptotic giant branch process.[14]