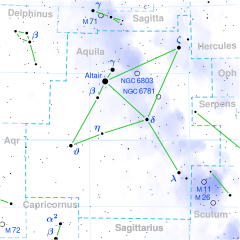
Beta Aquilae, Latinized from β Aquilae, is a triple star[12] system in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. It is visible to the naked eye as a point-like source with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.87.[2] Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is located at a distance of approximately 44.7 light-years from the Sun.[1] It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −40 km/s.[6]
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aquila |
| Right ascension | 19h 55m 18.79256s[1] |
| Declination | +06° 24′ 24.3425″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.87 + 12.0[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | G9.5 IV[3] + M2.5 V[4] |
| U−B color index | 0.48[5] |
| B−V color index | 0.86[5] |
| R−I color index | 0.49 |
| Variable type | Suspected |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −40.3±0.09[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 45.27[1] mas/yr Dec.: −481.91[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 73.00 ± 0.20 mas[1] |
| Distance | 44.7 ± 0.1 ly (13.70 ± 0.04 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +3.03[7] |
| Details[8] | |
| A | |
| Mass | 1.26±0.18[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 3.064±0.020 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 5.60±0.17 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.54±0.14 cgs |
| Temperature | 5,071±37 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.19±0.05 dex |
| Rotation | 5.08697±0.00031 d[10] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 22.28 km/s |
| Age | 9.6–11.4[11] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| ARICNS | data |
Its two components are designated Beta Aquilae A (formally named Alshain /ælˈʃeɪn/, the traditional name for the system)[13][14] and B.
Nomenclature

β Aquilae (Latinised to Beta Aquilae) is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as Beta Aquilae A and B derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).[15]
The system bore the traditional name Alshain derived from the Perso-Arabic term الشاهين, aš-šāhīn, meaning "the (peregrine) falcon", perhaps by folk etymology from the Persian šāhīn tarāzū (or possibly šāhīn tara zed; see Gamma Aquilae), the Persian name for the asterism α, β and γ Aquilae.[citation needed] In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[16] to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN decided to attribute proper names to individual stars rather than entire multiple systems.[17] It approved the name Alshain for the component Beta Aquilae A on 21 August 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[14]
In the catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Al Achsasi al Mouakket, this star was designated Unuk al Ghyrab (عنق ألغراب - únuq al-ghuraab), which was translated into Latin as Collum Corvi, meaning the crow's neck.[18]
In Chinese, 河鼓 (Hé Gŭ), meaning River Drum, refers to an asterism consisting of Beta Aquilae, Altair and Gamma Aquilae.[19] Consequently, the Chinese name for Beta Aquilae itself is 河鼓一 (Hé Gŭ yī, English: the First Star of River Drum).[20]
Namesake
USS Alshain (AKA-55) was a United States navy ship.
Properties
The primary, component A, is of magnitude 3.71 and spectral class G8IV. It has a very low level of surface magnetic activity and may be in a state similar to a Maunder minimum.[21] The activity shows a cycle of 969±27 d.[10] Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor points by which other stars are classified.[22] This is an aging subgiant star that has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core and is evolving into a giant.[10] It has a mass 26% greater than the Sun's,[9] a luminosity six times that of the Sun, and a radius about thrice solar.[8]
The 12th magnitude secondary companion, designated component B, is a double-lined spectroscopic binary[23] which is 13 arcseconds away in the sky. It has a stellar classification of M2.5 V,[4] matching a class M red dwarf.
In culture
In the Chinese folk tale The Cowherd and the Weaver Girl, Beta and Gamma Aquilae are children of Niulang (牛郎, The Cowherd, Altair) and Zhinü (織女, The Princess, Vega).
The Koori people of Victoria knew Beta and Gamma Aquilae as the black swan wives of Bunjil (Altair), the wedge-tailed eagle.[24]
References
External links
- Kaler, James B., "ALSHAIN (Beta Aquilae)", Stars, University of Illinois, retrieved 2018-03-03
- ARICNS
- Beta Aquilae by Professor Jim Kaler.
- Image β Aquilae