Rich Communication Services (RCS) is a communication protocol between mobile telephone carriers and between phone and carrier, aiming at replacing SMS messages with a text-message system that is richer, provides phonebook polling (for service discovery), and can transmit in-call multimedia. It is part of the broader IP Multimedia Subsystem. Google has added support for end-to-end encryption for all chats using RCS in their own app, Google Messages. End-to-end encryption is not a feature of RCS specified by GSMA, instead deferring to the individual messaging clients to establish encryption.[1][2][3][4]
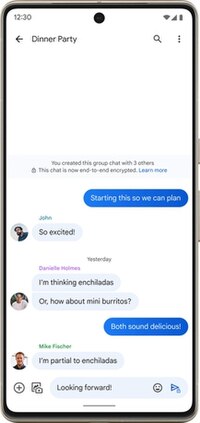 A thread of conversation and media in the Google Messages application on Android | |
| Developer | GSMA |
|---|---|
| Type | Instant messaging |
| Launch date | September 15, 2008 |
| Platform(s) | various Android smartphones, iPhone in 2024 |
| Operating system(s) | Android 5 and later, iOS in 2024 |
| Status | Active |
| Website | www |
It is also marketed as Advanced Messaging,[5] and was marketed as chat features,[6] joyn, SMSoIP,[7] Message+, and SMS+.[8]
In early 2020, it was estimated that RCS was available from 88 operators in 59 countries with approximately 390 million users per month.[9] By November 2020, RCS was available globally in Google Messages on Android, provided directly by Google if the operator does not provide RCS.[10] By 2023, there were 800 million active RCS users on Google's platform and 1.2 billion handsets worldwide supporting RCS.[11]
History
The Rich Communication Suite industry initiative[12] was formed by a group of industry promoters in 2007. In February 2008 the GSM Association (GSMA) officially became the project home of RCS and an RCS steering committee was established by the organization, officially announced as Rich Communications Suite on September 15, 2008.[13]
The steering committee specified the definition, testing, and integration of the services in the application suite known as RCS.[14][15][16] Three years later, the RCS project released a new specification – RCS-e (e = "enhanced"), which included various iterations of the original RCS specifications. The GSMA program is now called Rich Communication Services.[17]
The GSMA published the Universal Profile in November 2016.[18] The Universal Profile is a single GSMA specification for advanced communications. Carriers that deploy the Universal Profile guarantee interconnection with other carriers. As of early 2017[update], there were 47 mobile network operators, 11 manufacturers, and 2 OS providers (Google and Microsoft) that had announced their support of the Universal Profile.[19] Google's Jibe Cloud platform is an implementation of the RCS Universal Profile, designed to help carriers launch RCS quickly and scale easily.[20]
Samsung was one of the first major device original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to support RCS. Samsung RCS capable devices have been commercially launched in Europe since 2012 and in the United States since 2015.
Google supports RCS on Android devices with its Android SMS app Google Messages, beginning with Lollipop across Android devices.[21][22] In April 2018, it was reported that Google would be transferring the team that was working on its Google Allo messaging service to work on a wider RCS implementation.[23][24][25] In June 2019, Google announced that it would begin to deploy RCS on an opt-in basis via the Messages app, with service compliant with the Universal Profile and hosted by Google rather than the user's carrier, if the carrier does not provide RCS. The rollout of this functionality began in France and the United Kingdom.[23][24][26]
In response to concerns over the lack of end-to-end encryption in RCS, Google stated that it would only retain message data in transit until it is delivered to the recipient.[27] In November 2020, Google later announced that it would begin to roll out end-to-end encryption for one-on-one conversations between Messages users, using RCS but not part of the GSMA's RCS specifications, beginning with the beta version of the app.[28] In December 2020, Samsung updated its One UI Messages app to also allow users to opt into RCS.[29] Google added end-to-end encryption to their Messages app using the Signal Protocol as the default option for one-on-one RCS conversations starting in June 2021. Google stated it would like to collaborate with other companies to make end to end encryption over RCS compatible with other apps.[30][31][1][32] In December 2022, end-to-end encryption was added to group chats in the Google Messages app for beta users and was made available to all users in August 2023. Additionally, Google enabled RCS in Messages by default to encourage end-to-end encryption adoption.[3][4][33]
In October 2019, the four major U.S. carriers announced an agreement to form the Cross-Carrier Messaging Initiative to jointly implement RCS using a newly developed app. This service was to be compatible with the Universal Profile.[34] However, this carrier-made app never came to fruition. And later, both T-Mobile and AT&T signed deals with Google to adopt Google's Messages app.[35][36][37]
In September 2022, Apple CEO Tim Cook said the company had no plans to support RCS on its devices or any interoperability with iMessage.[38] However, in November 2023, an Apple spokesperson announced that Apple plans to introduce RCS support in 2024. The decision came after the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology proposed new regulation which could have required Apple to support RCS.[39][40] Apple stated it will not support Google's end-to-end encryption extension over RCS, but would work with GSMA to create an RCS encryption standard.[40]
RCS specifications
RCS Universal Profile
The GSMA's Universal Profile is a globally agreed-upon standard for implementing RCS. The profile allows subscribers of different carriers and nations to communicate with each other.[41] Universal Profile became the dominant RCS specification since its introduction.
- Version 1.0 (November 2016)[42]
- Includes core features such as capability discovery which will be interoperable between regions, chat, group chat, file transfer, audio messaging, video share, multi-device, enriched calling, location share and live sketching.
- Version 2.0 (July 2017)[42]
- Includes Messaging as a Platform, APIs, plug-in integration and improved authentication and app security.
- Version 2.1 (December 2017)[42]
- Version 2.2 (May 2018)[42]
- Version 2.3 (December 2018)[42]
- Version 2.4 (October 2019)[42]
- Removes plug-in integration and includes integrated seamless web-view.
Historical RCS Specifications
Before Universal Profile RCS, there was a variety of proprietary RCS specifications that did not allow RCS messaging between carriers.[43] RCS combines different services defined by 3GPP and Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) with an enhanced phonebook. Another phone's capabilities and presence information can be discovered and displayed by a mobile phone.RCS reuses 3GPP specified IMS core system as the underlying service platform taking care of issues such as authentication, authorization, registration, charging and routing.
Release 1 Version 1.0 (December 15, 2008)
- Offered the first definitions for the enrichment of voice and chat with content sharing, driven from an RCS enhanced address book (EAB).
Release 2 Version 1.0 (August 31, 2009)
- Added broadband access to RCS features: enhancing the messaging and enabling sharing of files.
Release 3 Version 1.0 (February 25, 2010)
- Focused on the broadband device as a primary device.
Release 4 Version 1.0 (February 14, 2011)
- Included support for LTE.
Release 5 Version 1.0 (April 19, 2012)
- RCS 5.0 was completely backwards-compatible with RCS-e V1.2 specifications and also includes features from RCS 4 and new features such as IP video call, IP voice call and Geo-location exchange. RCS5.0 supported both OMA CPM and OMA SIMPLE IM. RCS 5.0 included the following features.
- Standalone Messaging
- 1-2-1 Chat
- Group Chat
- File Transfer
- Content Sharing
- Social Presence Information
- IP Voice call (IR.92 and IR.58)
- IP Video call (IR.94)
- Geolocation Exchange
- Capability Exchange based on Presence or SIP OPTIONS
Release 5.1
- 5.1 was completely backwards compatible with the RCS-e V1.2 and RCS 5.0 specifications. It introduced additional new features such as Group Chat Store & Forward, File Transfer in Group Chat, File Transfer Store & Forward, and Best Effort Voice Call, as well as lessons-learnt and bug fixes from the V1.2 interoperability testing efforts. RCS 5.1 supported both OMA CPM and OMA SIMPLE IM.
- Version 1.0 (August 13, 2012)
- Version 2.0 (May 3, 2013)
- Version 3.0 (September 09, 2013)
- Version 4.0 (November 28, 2013)
Release 5.2 Version 5.0 (May 7, 2014)
- Improved central message store and introduced service extension tags into the specification. It also introduced a number of incremental improvements and bug fixes to RCS 5.1 V4.0 that improved the user experience and resolve issues that were noticed in deployed RCS networks.
Release 5.3 Version 6.0 (February 28, 2015)
Release 6.0 Version 7.0 (March 21, 2016)
- Support for Visual Voice Mail and more
Release 7.0 Version 8.0 (June 28, 2017)
- Support for Chatbots, SMS fallback features and more
Release 8.0 Version 9.0 (May 16, 2018)
- Support for additional Chatbots features and vCard 4.0
RCS-e (enhanced)
- Initial Version (May 2011)
- Version 1.2 (November 28, 2011)
- Version 1.2.2 (July 4, 2012)
Joyn
The GSMA defined a series of specific implementations of the RCS specifications. The RCS specifications often defined a number of options for implementing individual communications features, resulting in challenges in delivering interoperable services between carriers. The RCS specifications aimed to define a more specific implementation that promotes standardization and simplify interconnection between carriers.
- Joyn Hot Fixes (July 15, 2013) - based upon the RCS 1.2.2 specification (previously known as RCS-e), this includes 1:1 chat, group chat, MSRP file sharing and video sharing (during a circuit-switched call).[44] Services based upon this specification were live in Spain, France and Germany.
- Joyn Blackbird Drop 1 (June 19, 2013) - based upon the RCS 5.1 specification, this extends the Joyn Hot Fixes service to include HTTP file sharing, location sharing, group file sharing, and other capabilities such as group chat store and forward. Joyn Blackbird Drop 1 was backwards compatible with Joyn Hot Fixes.[45] Vodafone Spain's network is accredited for Joyn Blackbird Drop 1, and Telefónica and Orange Spain have also been involved in interoperability testing with vendors of Joyn Blackbird Drop 1 clients. A number of client vendors were accredited to Joyn Blackbird Drop 1.
- Joyn Blackbird Drop 2 (September 26, 2013) - also based upon the RCS 5.1 specification, this primarily added IP voice and video calling.[46]
- Joyn Crane (August 18, 2015) [47]
RCS Business Messaging
RCS Business Messaging (RBM) is the B2C (A2P in telecoms terminology) version of RCS. This is supposed to be an answer to third-party messaging apps (or OTTs) absorbing mobile operators' messaging traffic and associated revenues. While RCS is designed to win back Person-to-Person (P2P) traffic, RBM is intended to retain and grow this A2P traffic.[48][49] RCS offers "rich" features similar to those of messaging apps, but delivered (in theory) via the preloaded SMS messaging app - for example Google Messages or Samsung Messages. By making these features available in a B2C setting, RBM is expected to attract marketing and customer service spend from enterprises, thanks to improved customer engagement and interactive features that facilitate new use cases.[50][51] This was the primary reason for the development of RCS by the GSMA.
RBM includes features not available to ordinary users, including predefined quick-reply suggestions, rich cards, carousels, and branding. This last feature is intended to increase consumer confidence and reduce fraud through the implementation of a verified sender system.[52] These additional features are only available with the use of a messaging-as-a-platform (MaaP) server integrated with the operator's network. The MaaP controls the verified sender details, unlocking RBM features, while also segregating P2P and A2P RCS messages, aiding monetisation of the latter (SMS currently suffers from grey routes, where A2P messages are sent over P2P connections, which are cheaper or often free).[53]
Status
According to GSMA PR in 2012, Rich Communication Services (RCS) carriers from around the globe supporting the RCS standard included AT&T, Bell Mobility, Bharti Airtel, Deutsche Telekom, Jio, KPN, KT Corporation, LG U+, Orange, Orascom Telecom, Rogers Communications, SFR, SK Telecom, Telecom Italia, Telefónica, Telia Company, Telus, Verizon and Vodafone.[54]
Universal Profile is currently backed by "a large and growing ecosystem" (68 supporters in 2019). Universal Profile support is optional in 4G, but mandatory in 5G networks and devices.[55]
- 55 operators: Advanced Info Service, América Móvil, AT&T Mobility, Axiata, Beeline, Base, Bell Mobility, Bharti Airtel, China Telecom, China Unicom, Claro Americas, Deutsche Telekom, Etisalat, Globe Telecom, Ice, Indosat Ooredoo, Jio, KDDI, KPN, M1 Limited, MegaFon, Millicom, MTN Group, MTS (network provider), NTT Docomo, Optus, Orange S.A., Personal, Proximus, Rogers Communications, Singtel, Smart Communications, SLTMobitel, Sprint Corporation, T-Mobile US, Telcel, Tele2, Telefónica, Telenor, Telia Company, Telkomsel, Telstra, Telus, TIM, Turkcell, Verizon Communications, VEON, and Vodafone.
- 12 OEMs: TCL (Alcatel Mobile), Asus, General Mobile, HTC, Huawei, Intex Technologies, Lava International, LG Electronics, Lenovo (Motorola), Samsung Electronics, Sony and ZTE.[56]
- 2 mobile OS providers: Google and Apple in 2024.[39]
| Operator | Country | Launch date | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Movistar |  Spain Spain | June 2012 | [58] Branded as joyn. |
| MetroPCS |  United States United States | November 2012 | [58] Branded as joyn. |
| KT |  South Korea South Korea | December 2012 | [58][59] Branded as joyn. Discontinued in 2016. |
| LG U+ |  South Korea South Korea | December 2012 | [58][59] Branded as joyn. Discontinued in 2016. |
| SK Telecom |  South Korea South Korea | December 2012 | [58][59] Branded as joyn. |
| Deutsche Telekom |  Germany Germany | February 2013 | [58] Branded as Message+[60] |
| Telcel |  Mexico Mexico | February 2013 | [58] Branded as joyn. |
| Claro | Multiple markets | May 2013 | [58] Branded as joyn. |
| Sprint |  United States United States | October 2013 | Launched as a separate application |
| U.S. Cellular |  United States United States | October 2018 | Universal Profile [61] |
| Telekom |  Romania Romania | June 2014 | [62][63] Branded as joyn. |
| Slovak Telekom |  Slovakia Slovakia | June 2014 | [62][63] Branded as joyn. |
| O2 |  Germany Germany | 2015 | [64] Branded as Message+Call. |
| SFR |  France France | May 2015 | [65][66] Initially branded as joyn, now RCS.[67] |
| T-Mobile US |  United States United States | July 2015 - September 2023 | [68] Branded as Advanced Messaging. In June 2023, T-Mobile US converted to Google Jibe for RCS services.[69] |
| AT&T |  United States United States | November 2015 - June 2023 | Branded as Advanced Messaging and Video Call.[70][71] In June 2023, AT&T converted to Google Jibe for RCS services.[72] |
| MTS |  Russia Russia | December 2015 | [73] Branded as MTS Connect. |
| Airtel |  India India | February 2016 | |
| Jio |  India India | September 2016 | [74] Branded as Jio4GVoice. |
| Rogers Wireless |  Canada Canada | December 2016 | Universal Profile. |
| Fido Solutions |  Canada Canada | December 2016 | Universal Profile. |
| Telenor | Multiple markets | February 2017 | Universal Profile.[75] |
| Celcom |  Malaysia Malaysia | May 2017 | Universal Profile. |
| Vodafone | Multiple markets | 2012-2017 | [76] Universal Profile.[77] [58][78][79][80][81] First Branded as joyn. Since November 2013 Message+. |
| Telstra |  Australia Australia | October 2017 | Branded as Telstra Messaging.[82] Universal Profile v2.[83] |
| Telia Company |  Sweden Sweden | December 2017 | Branded as SMS+.[84] |
| Telia Company |  Norway Norway | February 2018 | Branded as SMS+.[84] |
| Globe Telecom |  Philippines Philippines | February 2018 | Universal Profile |
| NTT Docomo |  Japan Japan | May 2018 | Branded as +Message.[85] |
| KDDI |  Japan Japan | May 2018 | Branded as +Message.[85] |
| SoftBank Corp. |  Japan Japan | May 2018 | Branded as +Message.[85] |
| Rakuten Mobile |  Japan Japan | April 2020 | As part of Link application.[86] |
| Freedom Mobile |  Canada Canada | October 2018 | Universal Profile. |
| Verizon |  United States United States | December 2018 | Branded as Chat and launched as part of Android's default Messenger app with initial rollout for Pixel 3 phones. By 2022, Google's Messages app with RCS became the default messaging app for Android phones on Verizon.[87] In February 2024, Verizon announced a conversion to Google Jibe for RCS services.[88] |
| Google Fi Wireless |  United States United States | January 2019 | Universal Profile. |
| Google (Note: Not a carrier) | 🌐 Global | November 2019 | In Google's Messages app, if a carrier does not provide Universal Profile RCS, Google provides RCS.[10] |
| Telekom Albania |  Albania Albania | Universal Profile. | |
| Bell |  Canada Canada | Universal Profile. | |
| China Mobile |  China China | Universal Profile. | |
| Orange | Multiple markets | 2012-2019[89] | Branded as Chat Messages in Romania,[90] joyn elsewhere.[58][62][63] [91] Since July 2018 branded as Chat - Universal profile in Slovakia. [92] Service in France was interrupted as of 14 November 2017. |
| Boost |  United States United States | Universal Profile. | |
| COSMOTE |  Greece Greece | Branded as Message+[93] | |
| Telekom |  Hungary Hungary | Universal Profile. | |
| Vodacom |  South Africa South Africa | Universal Profile. | |
| Telkom Mobile |  South Africa South Africa | Universal Profile.[94] | |
| Illinois Valley Cellular |  United States United States | Universal Profile. | |
| Tiercel Wireless |  United States United States | Universal Profile. | |
| TracFone Wireless |  United States United States | Universal Profile. | |
| T-Mobile US |  United States United States | May 2020 | Universal Profile[95] |
| Swisscom |  Switzerland Switzerland | April 2020 | Branded as Message+ [96] Discontinued in 2023. |
| Proximus |  Belgium Belgium | August 2020[97] | |
| MTS |  Russia Russia | October 2020 | Only for Samsung smartphones and only for Moscow customers,[98] MTS Connect still works for all MTS customers |
| Base |  Belgium Belgium | February 2021[89] |
Interconnect and hubs
Like SMS, RCS requires national and international interconnects to enable roaming. As with SMS, this will be accomplished with hubbing - where third-party providers complete agreements with individual operators to interwork their systems. Each subsequent operator that connects to a hub is therefore connected automatically to all other connected operators. This eliminates the need to each operator to connect to all the others to which they may need to send messages.[99] RCS hubs are provided by stakeholders with a vested interest in increasing RCS use. These include traditional SMS hub providers (e.g. Global Message Services and Sinch), software and hardware vendors (e.g. Interop Technologies, Mavenir, and ZTE), and also Google via its Jibe Cloud platform.[100]
Accreditation
The RCS interop and testing (IOT) accreditation process[101] was started by the GSMA in order to improve the quality of testing, increase transparency, drive scale, minimize complexity and accelerate time-to-market (TTM) of joyn services. Companies need to undertake the IOT process from the GSMA to apply for a license to use the service mark joyn.
"Accredited" means that the device, client or network has undertaken a series of test cases (150 to 300) in a specific set of conditions, provided test results and traces that have been analysed by the GSMA RCS IOT team and any IOT issues arising resolved with the submitter.[102]
"Accreditation Ready" is the designation awarded to a hosted RCS service that has undertaken the same series of test cases as the mobile network operator, provided test results and traces that have been analysed by the GSMA RCS IOT team and any IoT issues arising resolved with the submitter.[102]
A list of RCS AS providers and their GSMA RCS Accreditation status can be found here:[103]
Reception
In 2018, Amnesty International researcher Joe Westby criticized RCS for not allowing end-to-end encryption, because it is treated as a service of carriers and thus subject to lawful interception.[104][105]
The Verge in 2019 criticized the inconsistent support of RCS in the United States, with carriers not supporting RCS in all markets, not certifying service on all phones, or not yet supporting the Universal Profile. Concerns were shown over Google's decision to run its own RCS service due to the possibility of antitrust scrutiny, but it was acknowledged that Google had to do so in order to bypass the carriers' inconsistent support of RCS, as it wanted to have a service more comparable to Apple's iMessage service available on Android.[27][106]
Ars Technica in 2019 criticized Google's move to launch a direct-to-consumer RCS service, considering it a contradiction of RCS being native to the carrier to provide features reminiscent of messaging apps, counting it as being among various past and unsuccessful attempts by Google to develop an in-house messaging service (including Google Talk, Google+ Messenger, Hangouts, and Allo), and noting limitations: such as its dependencies on phone numbers as the identity (whereas email-based accounts are telco-agnostic), not being capable of being readily synchronized between multiple devices, and the aforementioned lack of end-to-end encryption.[107]




































