The Sefid-Rud (Persian: سفیدرود, lit. 'white river', Gilaki: اسپي بيه, Espī bīeh) (also known as Sepid-Rud) is a river, approximately 670 kilometres (416 mi) long, rising in the Alborz mountain range of northwestern Iran and flowing generally northeast to empty into the Caspian Sea at Rasht.
| Sefid-Rud Sepid-Rud, Ghezel Owzan, Qizil Owzan, Qizil Ozen | |
|---|---|
 | |
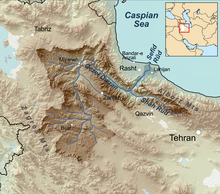 Sefīd-Rūd drainage basin | |
| Native name | Espī bīeh (Gilaki) |
| Location | |
| Country | Iran |
| Provinces | Gilan |
| City | Rasht |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Alborz Mountains |
| Mouth | Caspian Sea |
| Length | 670 km (420 mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Qizil Owzan |
| • right | Shahrood |
Names
Other names and transcriptions include Sepīd-Rūd, Sefidrud, Sefidrood, Sepidrood, and Sepidrud. Above Manjil, "Long Red River".[1][2]
William Smith equated the river with the Amardus (Ancient Greek: Ἀμάρδος) or Mardus (Μάρδος) river of antiquity.[3][4]
The river is historically famous for its abundant fish, especially the Caspian trout, Salmo trutta caspius.[5]
Geography
The Sefid-Rud has cut a water gap through the Alborz mountain range, the Manjil gap,[6] capturing its two headwater tributaries, the Qizil Üzan and Shahrood rivers. It then widens the valley between the Talesh Hills and the main Alborz range. The gap provides a major route between Tehran and Gīlān Province with its Caspian lowlands.[6]
In the wide valley before the Sefid-Rud enters the Caspian Sea, a number of transportation and irrigation canals have been cut; the two biggest are the Khomam and the Now.[7]
Dam and reservoir
The Sefid-Rud was dammed in 1962 by the Shahbanu Farah Dam (later renamed Manjil Dam),[8] which created a 1.86 cubic kilometres (0.45 cu mi) reservoir and allowed the irrigation of an additional 2,380 km2 (919 sq mi).[8] The reservoir mediates some flooding and significantly increased rice production in the Sefid Rud delta.[9][10] The hydroelectric component of the dam generates 87,000 kilowatts.[8] The completion of the dam had a negative impact on the river's fisheries, through reduced stream flow (due to diversion), increased water temperature, and decreased food availability, especially for sturgeon but also for the Caspian trout.[11]

History

The river was known in antiquity as Mardos (Greek: Μαρδος; Latin: Mardus) and Amardos (Greek: Αμαρδος; Latin: Amardus).[2] In the Hellenistic period, the north side of the Sefid (then Mardus) was occupied by the Cadusii mountain tribe .[12]
David Rohl proposes identification of Sefid-Rud with the Biblical Pishon river.[citation needed]
Gallery
Notes
External links
- "Sefid Rood Watershed" Economic potentials of Kurdistan Province in the fields of Water, Agriculture and Natural Resources Ministry of Interior, Islamic Republic of Iran

