The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N.[1] Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.

The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at which, on the Northern Hemisphere's winter solstice (which is the shortest day of the year), the Sun will not rise all day, and on the Northern Hemisphere's summer solstice (which is the longest day of the year), the Sun will not set. These phenomena are referred to as polar night and midnight sun respectively, and the further north one progresses, the more pronounced these effects become. For example, in the Russian port city of Murmansk, three degrees above the Arctic Circle, the Sun does not rise above the horizon for 40 successive days in midwinter.[2][3][4]
The position of the Arctic Circle is not fixed and currently runs 66°33′49.9″ north of the Equator.[5] Its latitude depends on the Earth's axial tilt, which fluctuates within a margin of more than 2° over a 41,000-year period, owing to tidal forces resulting from the orbit of the Moon.[6] Consequently, the Arctic Circle is currently drifting northwards at a speed of about 14.5 m (48 ft) per year.
Etymology
The word arctic comes from the Greek word ἀρκτικός (arktikos: "near the Bear, northern")[7] and that from the word ἄρκτος (arktos: "bear").[8]
Midnight sun and polar night
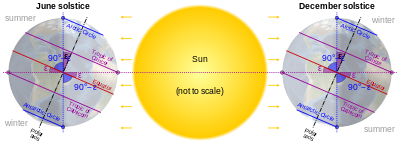
The Arctic Circle is the southernmost latitude in the Northern Hemisphere at which the center of the Sun can remain continuously above or below the horizon for twenty-four hours; as a result, at least once each year at any location within the Arctic Circle the center of the Sun is visible at local midnight, and at least once the center is not visible at local noon.[9]
Directly on the Arctic Circle these events occur, in principle, exactly once per year: at the June and December solstices, respectively. However, because of atmospheric refraction and mirages, and also because the sun appears as a disk and not a point, part of the midnight sun is visible, on the night of the northern summer solstice, at a latitude of about 50 minutes of arc (′) (90 km (56 mi)) south of the Arctic Circle. Similarly, on the day of the northern winter solstice, part of the sun may be seen up to about 50′ north of the Arctic Circle. That is true at sea level; those limits increase with elevation above sea level, although in mountainous regions there is often no direct view of the true horizon.

Human habitation

The largest communities north of the Arctic Circle are situated in Russia, Norway, and Sweden: Murmansk (population 295,374) and Norilsk (178,018) in Russia; Tromsø (75,638) in Norway, Vorkuta (58,133) in Russia, Bodø (52,357), and Harstad (24,703) in Norway; and Kiruna, Sweden (22,841). Rovaniemi (62,667) in Finland is the largest settlement in the immediate vicinity of the Arctic Circle, lying 6 km (4 mi) south of the line. Salekhard (51,186) in Russia is the only city in the world located directly on the Arctic Circle.[10]
In contrast, the largest North American community north of the Arctic Circle, Sisimiut (Greenland), has approximately 5,600 inhabitants. In the United States, Utqiaġvik, Alaska (formerly known as Barrow), is the largest settlement north of the Arctic Circle with about 5,000 inhabitants. The largest such community in Canada is Inuvik in the Northwest Territories, with 3,137 inhabitants.
Geography
The Arctic Circle is roughly 16,000 km (9,900 mi) in circumference.[11] The area north of the Circle is about 20,000,000 km2 (7,700,000 sq mi) and covers roughly 4% of Earth's surface.[12]
The Arctic Circle passes through the Arctic Ocean, the Scandinavian Peninsula, North Asia, Northern America, and Greenland. The land within the Arctic Circle is divided among eight countries: Norway, Sweden, Finland, Russia, the United States (Alaska), Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut), Denmark (Greenland), and Iceland (where it passes through the small offshore island of Grímsey).
Climate
The climate north of the Arctic Circle is generally cold, but the coastal areas of Norway have a generally mild climate as a result of the Gulf Stream, which makes the ports of northern Norway and northwest Russia ice-free all year long. In the interior, summers can be quite warm, while winters are extremely cold. For example, summer temperatures in Norilsk, Russia will sometimes reach as high as 30 °C (86 °F), while the winter temperatures frequently fall below −50 °C (−58 °F).
Sites along the Arctic Circle
Starting at the prime meridian and heading eastwards, the Arctic Circle passes through:
- Northern Polar Circle Globe on Vikingen island marking the Arctic Circle in Norway
- Arctic Circle sign by the Inland Line railway, Sweden
- The white borderline of the Arctic Circle at the Santa Claus Village in Rovaniemi, Finland
- Arctic Circle sign in the Republic of Karelia, Russia
- Arctic Circle sign by the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Russia
- A sign in the Sakha Republic (Yakutia), Russia
- Arctic Circle marker on island of Grímsey in Iceland
See also
References
External links


- Terra Incognita: Exploration of the Canadian Arctic—Historical essay about early expeditions to the Canadian Arctic, illustrated with maps, photographs and drawings
- Temporal Epoch Calculations ©2006 by James Q. Jacobs Download: Epoch v2009.xls (modify D4)
- Useful constants" See: Obliquity of the ecliptic



















