The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) is the modern archaeological designation for a particular Middle Bronze Age civilisation of southern Central Asia, also known as the Oxus Civilization. The civilisation's urban phase or Integration Era,[1] was dated in 2010 by Sandro Salvatori to c. 2400–1950 BC,[2][3] but a different view is held by Nadezhda A. Dubova and Bertille Lyonnet, c. 2250–1700 BC.[3][4]
The extent of the BMAC (according to the Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture) Female statuette, an example of a "Bactrian princess"; late 3rd–early 2nd millennium BC; steatite or chlorite and alabaster; 9 × 9.4 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York City) | |
| Location | Southern Central Asia, mainly in modern-day Turkmenistan, northern Afghanistan, and southern Uzbekistan |
|---|---|
| Region | Margiana, Bactria |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | Viktor Sarianidi (late 1960s to 1979) |
| Condition | Ruins |
Though it may be called the "Oxus civilization", apparently centred on the upper Amu Darya (Oxus River) in Bactria, most of the BMAC's urban sites are actually located in Margiana (modern Turkmenistan) on the Murghab river delta, and in the Kopet Dagh mountain range. There are a few later (c. 1950–1450 BC) sites in northern Bactria, currently known as southern Uzbekistan,[5] but they are mostly graveyards belonging to the BMAC-related Sapalli culture.[6][7][8] A single BMAC site, known as Dashli, lies in southern Bactria, current territory of northern Afghanistan.[9] Sites found further east, in southwestern Tajikistan, though contemporary with the main BMAC sites in Margiana, are only graveyards, with no urban developments associated with them.[10]
The civilisation was named BMAC by the Soviet archaeologist Viktor Sarianidi in 1976, during the period (1969–1979) when he was excavating in northern Afghanistan.[11] Sarianidi's excavations from the late 1970s onward revealed numerous monumental structures in many sites, fortified by impressive walls and gates. Reports on the BMAC were mostly confined to Soviet journals.[12] A journalist from The New York Times wrote in 2001 that during the years of the Soviet Union, the findings were largely unknown to the West until Sarianidi's work began to be translated in the 1990s.[13] However, some publications by Soviet authors, like Masson, Sarianidi, Atagarryev, and Berdiev, had been available to the West, translated in the first half of 1970s, slightly before Sarianidi labelled the findings as BMAC.[14][15][16][17]
Origin and chronology
Italian archaeologists, like Massimo Vidale and Dennys Frenez, support Sandro Salvatori's hypothesis that Namazga V is the beginning of the ultimate urban phase called BMAC, belonging to the Integration Era (c. 2400–1950 BC).[18] On the other hand, Russian and French archaeologists Nadezhda Dubova and Bertille Lyonnet consider there was a gap between the end of Namazga III phase and the beginning of BMAC in Margiana, and that most of the sites both in Margiana and Bactria were founded on virgin soil only around 2250 BC lasting until 1700 BC.[19]
Etymology
The region was first named Bakhdi in Old Persian, which then formed the Persian satrapy of Marguš (perhaps from the Sumerian term Marhasi),[20] the capital of which was Merv, in modern-day southeastern Turkmenistan. It was then called Bāxtriš in Middle Persian, and Baxl in New Persian. The region was also mentioned in ancient Sanskrit texts as बाह्लीक or Bāhlīka. The modern term Bactria is derived from the Ancient Greek: Βακτριανή (Romanized Greek term: Baktrianē) (modern Balkh), which came from the Old Persian term.
Early Food-Producing Era
There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the well-watered northern foothills of the Kopet Dag during the Neolithic period at Jeitun (or Djeitun). In this region, mud brick houses were first occupied during the Early Food-Producing Era, also known as Jeitun Neolithic, from c. 7200 to 4600 BC.[21] The inhabitants were farmers with origins in southwest Asia, who kept herds of goats and sheep and grew wheat and barley.[22] Jeitun has given its name to the whole Neolithic period in the northern foothills of the Kopet Dag. At the late Neolithic site of Chagylly Depe, farmers increasingly grew the kinds of crops that are typically associated with irrigation in an arid environment, such as hexaploid bread wheat, which became predominant during the Chalcolithic period.[23] This region is dotted with the multi-period hallmarks characteristic of the ancient Near East, similar to those southwest of the Kopet Dag in the Gorgan Plain in Iran.[24]
Regionalization Era
The Regionalization Era begins in Anau IA with a pre-Chalcolithic phase also in the Kopet Dag piedmont region from 4600 to 4000 BC, then the Chalcolithic period develops from 4000 to 2800 BC in Namazga I-III, Ilgynly Depe, and Altyn Depe.[21] During this Copper Age, the population of the region grew. Archaeologist Vadim Mikhaĭlovich Masson, who led the South Turkmenistan Complex Archaeological Expedition of 1946, saw signs that people migrated to the region from central Iran at this time, bringing metallurgy and other innovations, but thought that the newcomers soon blended with the Jeitun farmers.[25] (Vadim was the son of archaeologist Mikhail Masson, who had previously already started work in this same area.) By contrast, a re-excavation of Monjukli Depe in 2010 found a distinct break in settlement history between the late neolithic and early chalcolithic eras there.[26][27]

Major chalcolithic settlements sprang up at Kara-Depe and Namazga-Depe. In addition, there were smaller settlements at Anau, Dashlyji, and Yassy-depe. Settlements similar to the early level at Anau also appeared further east– in the ancient delta of the river Tedzen, the site of the Geoksiur Oasis. About 3500 BC, the cultural unity of the area split into two pottery styles: colourful in the west (Anau, Kara-Depe and Namazga-Depe) and more austere in the east at Altyn-Depe and the Geoksiur Oasis settlements. This may reflect the formation of two tribal groups. It seems that around 3000 BC, people from Geoksiur migrated into the Murghab delta (where small, scattered settlements appeared) and reached further east into the Zerafshan Valley in Transoxiana. In both areas pottery typical of Geoksiur was in use. In Transoxiana they settled at Sarazm near Pendjikent. To the south the foundation layers of Shahr-i Shōkhta on the bank of the Helmand River in south-eastern Iran contained pottery of the Altyn-Depe and Geoksiur type. Thus the farmers of Iran, Turkmenistan and Afghanistan were connected by a scattering of farming settlements.[25]
Late Regionalization Era
In Kopet Dag region, at Altyn Depe, the Namazga III phase lasted (c. 3200–2800 BC) and showed a late Chalcolithic culture, at the beginning of Late Regionalization Era.[28]In the Early Bronze Age, at the end of Late Regionalization Era (2800 to 2400 BC),[21] the culture of the Kopet Dag oases in Altyn-Depe site developed a proto-urban society. This corresponds to phase IV at Namazga-Depe. Altyn-Depe was a major centre even then. Pottery was wheel-turned. Grapes were grown.[citation needed]
Integration Era: Oxus Civilization
The height of the urban development was reached in the Middle Bronze Age, also known as Integration Era, mainly in three regions, Kopet Dag piedmont, Margiana, and southern Bactria, as well as some cemetery remains recently found in southwestern Tajikistan.
Kopet Dag, Namazga V phase
BMAC's urban period begins in the Kopet Dag piedmont, as per Massimo Vidale, corresponding to Namazga-Depe level V (c. 2400-2000 BC).[21][25] Namazga Depe reaching c. 52 hectares and holding maybe 17–20,000 inhabitants, and Altyn Depe with its maximum size of c. 25 hectares and 7–10,000 inhabitants, were the two big cities in Kopet Dag piedmont.[29] This urban development is considered to have lasted, not from 2400 BC, but from c. 2250 to 1700 BC by Lyonnet and Dubova's recent publication.[3]
Margiana, Kelleli phase
Identification of the first large settling in Margiana was possible through excavations at Kelleli 3 and 4, and these are the type sites of Kelleli phase.[30] Massimo Vidale (2017) considers that the Kelleli phase was characterised by the appearance of the first palatial compounds from 2400 to 2000 BC.[21] Kelleli is located around 40 km northwest of Gonur; featuring Kelleli 3 with four hectares, characterised by towers in a double perimetral wall, four equal entrances, and houses in the southwest of the site. Kelleli 4 settlement is around three hectares, with the same characteristics in its wall.[31] Sandro Salvatori (1998) commented that Kelleli phase began sightly later than Namazga V period.[32]
Margiana, Gonur phase
Gonur phase was considered, by Sarianidi, as a southward movement of the previous Kelleli phase people.[32] In the ancient region of Margiana, the site Gonur Depe is the largest of all settlements in this period and is located at the delta of Murghab river in southern Turkmenistan, with an area of around 55 hectares. An almost elliptical fortified complex, known as Gonur North includes the so-called "Monumental Palace", other minor buildings, temples and ritual places, together with the "Royal Necropolis", and water reservoirs, all dated by Italian archaeologists from around 2400 to 1900 BC.[33] However French and Russian scholars like Lyonnet and Dubova date it to c. 2250-1700 BC.[3]
Southern Bactria
In southern Bactria, northern Afghanistan, the site Dashly 3 is regarded to be also from Middle Bronze Age to Late Bronze Age (2300–1700 BC) occupation,[34] but its beginning is probably later than 2300 BC, although earlier than 2000 BC, if new datings for BMAC by Lyonnet and Dubova are taken into account.[35] The old Dashly 3 complex, sometimes identified as a palace, is a fortified rectangular 88 m x 84 m compound. The square building had massive double outer walls and in the middle of each wall was a protruding salient composed of a T-shaped corridor flanked by two L-shaped corridors.[36]
Southwestern Tajikistan
New archaeological research has recently found at three ancient cemeteries in southwestern Tajikistan called Farkhor, Gelot (in Kulob District), and Darnajchi, ceramics influenced by Namazga IV and Namazga V transitional period from Early to Middle Bronze Age, which can suggest a presence of BMAC inhabitants in this region earlier considered out of their influx.[37] Gelot's grave N6-13 was dated to 2203–2036 cal BC (2 sigma), and Darnajchi's grave N2-2 as 2456-2140 cal BC (2 sigma).[38] Farkhor's cemetery is located on the right bank of Panj river, very near the Indus Civilization's site Shortughai.[39]
Material culture

Agriculture and economy
The inhabitants of the BMAC were sedentary people who practised irrigation farming of wheat and barley. With their impressive material culture including monumental architecture, bronze tools, ceramics, and jewellery of semiprecious stones, the complex exhibits many of the hallmarks of civilisation. The complex can be compared to proto-urban settlements in the Helmand basin at Mundigak in western Afghanistan and Shahr-e Sukhteh in eastern Iran, or at Harappa and Mohenjo-daro in the Indus Valley.[40]
Models of two-wheeled carts from c. 3000 BC found at Altyn-Depe are the earliest evidence of wheeled transport in Central Asia, though model wheels have come from contexts possibly somewhat earlier. Judging by the type of harness, carts were initially pulled by oxen or a bull. However, camels were domesticated within the BMAC. A model of a cart drawn by a camel of c. 2200 BC was found at Altyn-Depe.[41]
Art
Fertility goddesses, named "Bactrian princesses", made from limestone, chlorite and clay reflect agrarian Bronze Age society, while the extensive corpus of metal objects point to a sophisticated tradition of metalworking.[42] Wearing large stylised dresses, as well as headdresses that merge with the hair, "Bactrian princesses" embody the ranking goddess, character of the central Asian mythology that plays a regulatory role, pacifying the untamed forces.[citation needed]
- Female figurine of the "Bactrian princess" type; between 3rd millennium and 2nd millennium BC; chlorite mineral group (dress and headdresses) and limestone (face and neck); height: 17.3 cm, width: 16.1 cm; Louvre
- Axe with eagle-headed demon & animals; late 3rd millennium-early 2nd millennium BC; gilt silver; length: 15 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York City)
- Camel figurine; late 3rd–early 2nd millennium BCE; copper alloy; 8.89 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Axe head; late 3rd–early 2nd millennium BC; copper alloy; height: 2.8 cm, length: 7.2 cm, thickness: 1.8 cm, weight: 82.5 g; Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Female figurine of the "Bactrian princess" type; between 3rd millennium and 2nd millennium BC; grey chlorite (dress and headdresses) and calcite (face); Barbier-Mueller Museum (Geneva, Switzerland)
- Female figurine of the "Bactrian princess" type; between 3rd millennium and 2nd millennium BC; grey chlorite (dress and headdresses) and calcite (face); Barbier-Mueller Museum
- Beaker with birds on the rim; late 3rd–early 2nd millennium BC; electrum; height: 12 cm, width: 13.3 cm, depth: 4.5 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Handled weight; late 3rd–early 2nd millennium BC; chlorite; 25.08 x 19.69 x 4.45 cm; Los Angeles County Museum of Art (USA)
- Female figurine of the "Bactrian princess" type; 2500–1500; chlorite (dress and headdresses) and limestone (head, hands and a leg); height: 13.33 cm; Los Angeles County Museum of Art (USA)
- Vessel with guilloche pattern; 2000–1500; chlorite; 3.33 x 6.67 x 3.81 cm; Los Angeles County Museum of Art
- Female figurine of the "Bactrian princess" type; 2nd millennium BC; chlorite and calcite; Louvre
- Seated Goddess, an example of a "Bactrian princess", Bronze Age Bactria, Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex, circa 2000 BC. chlorite and limestone. Central Asian art, Miho Museum, Japan.[43][44]
Architecture

Sarianidi regards Gonur as the "capital" of the complex in Margiana throughout the Bronze Age. The palace of north Gonur measures 150 metres by 140 metres, the temple at Togolok 140 metres by 100 metres, the fort at Kelleli 3 125 metres by 125 metres, and the house of a local ruler at Adji Kui 25 metres by 25 metres. Each of these formidable structures has been extensively excavated. While they all have impressive fortification walls, gates, and buttresses, it is not always clear why one structure is identified as a temple and another as a palace.[46] Mallory points out that the BMAC fortified settlements such as Gonur and Togolok resemble the qila, the type of fort known in this region in the historical period. They may be circular or rectangular and have up to three encircling walls. Within the forts are residential quarters, workshops and temples.[47]
The people of the BMAC culture were very proficient at working in a variety of metals including bronze, copper, silver, and gold. This is attested through the many metal artefacts found throughout the sites.[45]
Extensive irrigation systems have been discovered at the Geoksiur Oasis.[25]
Writing
The discovery of a single tiny stone seal (known as the "Anau seal") with geometric markings from the BMAC site at Anau in Turkmenistan in 2000 led some to claim that the Bactria-Margiana complex had also developed writing, and thus may indeed be considered a literate civilisation. It bears five markings which are similar to Chinese "small seal" characters. The only match to the Anau seal is a small jet seal of almost identical shape from Niyä (near modern Minfeng) along the southern Silk Road in Xinjiang, originally thought to be from the Western Han dynasty but now thought to date to 700 BC.[48]
Archaeological interactions with neighbouring cultures
BMAC materials have been found in the Indus Valley civilisation, on the Iranian Plateau, and in the Persian Gulf.[46] Finds within BMAC sites provide further evidence of trade and cultural contacts. They include an Elamite-type cylinder seal and a Harappan seal stamped with an elephant and Indus script found at Gonur-depe.[49] The relationship between Altyn-Depe and the Indus Valley seems to have been particularly strong. Among the finds there were two Harappan seals and ivory objects. The Harappan settlement of Shortugai in Northern Afghanistan on the banks of the Amu Darya probably served as a trading station.[25]
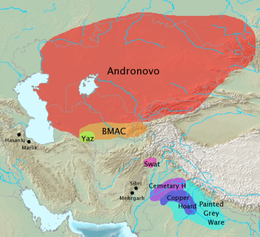
There is evidence of sustained contact between the BMAC and the Eurasian steppes to the north, intensifying c. 2000 BC. In the delta of the Amu Darya where it reaches the Aral Sea, its waters were channelled for irrigation agriculture by people whose remains resemble those of the nomads of the Andronovo culture. This is interpreted as nomads settling down to agriculture, after contact with the BMAC, known as the Tazabagyab culture.[50] About 1900 BC, the walled BMAC centres decreased sharply in size. Each oasis developed its own types of pottery and other objects. Also pottery of the Tazabagyab-Andronovo culture to the north appeared widely in the Bactrian and Margian countryside. Many BMAC strongholds continued to be occupied and Tazabagyab-Andronovo coarse incised pottery occurs within them (along with the previous BMAC pottery) as well as in pastoral camps outside the mudbrick walls. In the highlands above the Bactrian oases in Tajikistan, kurgan cemeteries of the Vaksh and Bishkent type appeared with pottery that mixed elements of the late BMAC and Tazabagyab-Andronovo traditions.[51] In southern Bactrian sites like Sappali Tepe too, increasing links with the Andronovo culture are seen. During the period 1700 – 1500 BCE, metal artefacts from Sappali Tepe derive from the Tazabagyab-Andronovo culture.[52]
New research in the Murghab region, in excavations at defensive walls of Adji Kui 1, showed pastoralists present, and living on the edge of the town, as early as the second half of the Middle Bronze Age (c. 2210-1960 BC), coexisting with the BMAC population that lived in the 'citadel.'[53]
Relationship with Indo-Iranians
The Bactria–Margiana complex has attracted attention as a candidate for those looking for the material counterparts to the Indo-Iranians (Aryans), a major linguistic branch that split off from the Proto-Indo-Europeans.
For example, Sarianidi advocated identifying the complex as Indo-Iranian, describing it as the result of a migration from southwestern Iran. Bactria–Margiana material has been found at Susa, Shahdad, and Tepe Yahya in Iran.[citation needed] In contrast, Lamberg-Karlovsky did not see this as evidence that the complex originated in southeastern Iran. "The limited materials of this complex are intrusive in each of the sites on the Iranian Plateau as they are in sites of the Arabian peninsula."[citation needed]
Mallory/Adams (1997) associated the Andronovo, BMAC and Yaz cultures with Indo-Iranian migrations, writing,
It has become increasingly clear that if one wishes to argue for Indo-Iranian migrations from the steppe lands south into the historical seats of the Iranians and Indo-Aryans that these steppe cultures were transformed as they passed through a membrane of Central Asian urbanism. The fact that typical steppe wares are found on BMAC sites and that intrusive BMAC material is subsequently found further to the south in Iran, Afghanistan, Nepal, India and Pakistan, may suggest then the subsequent movement of Indo-Iranian-speakers after they had adopted the culture of the BMAC.[54]
Anthony (2007) sees the culture as begun by farmers in the Near Eastern Neolithic tradition, but infiltrated by Indo-Iranian speakers from the Andronovo culture in its late phase, creating a hybrid. In this perspective, Proto-Indo-Aryan developed within the composite culture before moving south into the Indian subcontinent.[51]
Possible evidence for a BMAC substratum in Indo-Iranian
As argued by Michael Witzel[55] and Alexander Lubotsky,[56] there is a proposed substratum in Proto-Indo-Iranian which can be plausibly identified with the original language of the BMAC. Moreover, Lubotsky points out a larger number of words apparently borrowed from the same language, which are only attested in Indo-Aryan and therefore evidence of a substratum in Vedic Sanskrit. He explains this by proposing that Indo-Aryan speakers probably formed the vanguard of the movement into south-central Asia and many of the BMAC loanwords which entered Iranian may have been mediated through Indo-Aryan.[56]: 306 Michael Witzel points out that the borrowed vocabulary includes words from agriculture, village and town life, flora and fauna, ritual and religion, so providing evidence for the acculturation of Indo-Iranian speakers into the world of urban civilisation.[55]
Horses
In excavations at Gonur Depe, at a brick-lined burial pit, grave number 3200 of the Royal necropolis, a horse skeleton was found in period I, dated around 2200 BCE along with a four-wheeled wooden wagon with bronze rims.[57] Archaeologist Julio Bendezu-Sarmiento, mentioning N. A. Dubova's (2015) article, comments that this was an "almost complete skeleton of a foal" resting on the wagon with "wheels circled by bronze bands" and radiocarbon-dated to 2250 BCE.[58] So he considers this horse and the wagon are "one and a half century prior" to similar burials of Sintashta culture.[58] A stone statuette that seems to be a horse with saddle was found in burial number 3210 also in the Royal necropolis and was reported by Sarianidi in 2005, and in burial 3310 parts of a stallion's body were found, the stallion lacked its head, rump, and tail, and was considered as a cult burial of a domestic horse by archaeologist Sarianidi in his 2008 publication.[57]
Genetics


In 2019, Narasimhan and co-authors analysed BMAC skeletons from the Bronze Age sites of Bustan, Dzharkutan, Gonur Tepe, and Sappali Tepe. The male specimens belonged primarily to haplogroup J, specifically J* (3/26), J1 (1/26), J2 (7/26), as well as G (2/26), L (2/26), R2 (3/26), R1b (1/26), R* (2/26), H1a (1/26), P (1/26), Q (1/26), T (1/26) and E1b1b (1/26).[60][61]
The BMAC population largely derived from preceding local Copper Age peoples who were in turn related to Neolithic farmers from the Iranian plateau and to a lesser extent early Anatolian farmers, as well as hunter-gatherers from Western Siberia (WSHG). The samples extracted from the BMAC sites did not have derived any part of their ancestry from the Yamnaya people, who are associated with Proto-Indo-Europeans, although some peripheral samples did already carry significant Yamnaya-like Western Steppe Herders ancestry, inline with the southwards expansion of Western Steppe Herders from the Sintashta and Andronovo cultures towards Southern Central Asia at c. 2100 BCE.[62][63] Succeeding cultures, specifically the Yaz culture, was characterised by a combination of BMAC and Yamnaya/WSH ancestries, and associated with early Indo-Iranians.[64] Narasimshan et al. (2019) found no essential genetic contributions from the BMAC in later South Asians, suggesting that the Steppe-related ancestry was mediated via other groups.[60]
Genetic data on Iron Age samples from modern-day Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan confirm the admixture between local BMAC groups and Andronovo-related populations, at the end of Oxus Civilization. These Southern Central Asian Iron Age population derived around 57% of their ancestry from Western Steppe Herders (Andronovo) and c. 43% from the BMAC culture population. Modern day Tajiks and Yaghnobis were found to be direct descendants of the Bronze and Iron Age Central Asian populations, deriving ancestry from both the Yamnaya-like Western Steppe Herders and BMAC groups, and showing genetic continuity to historical Indo-Iranians.[65] These Iron Age Central Asians also displayed a higher genetic affinity to present-day Europeans than present-day Uzbeks, which harbour an additional componet derived from an East Asian-like source "through several admixture events over the past ~2,000 years", absent from Iron Age Uzbeks and modern Europeans.[63]
Sites
In Afghanistan

- Dashli, Jowzjan Province
- Khush Tepe (Tepe Fullol)
In Turkmenistan
In Uzbekistan
- Ayaz Kala
- Djarkutan
- Koi Krylgan Kala
- Sappali tepe
- Toprak-Kala
See also
References
Sources
- Francfort, H.P. (1991), "Note on some Bronze Age Petroglyphs of Upper Indus and Central Asia", Pakistan Archaeology, 26: 125–135
- Francfort, H.P. (1994), "The central Asian Dimension of the Symbolic System in Bactria and Margia", Antiquity, vol. 28, no. 259, pp. 406–418
- Kohl, Philip L. (2007). The Making of Bronze Age Eurasia. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1139461993.
- Mallory, J. P.; Adams, D. Q. (1997). "BMAC". Encyclopedia of Indo-European culture. London: Fitzroy Dearborn. ISBN 1-884964-98-2.
- Parpola, Asko (2015). The Roots of Hinduism: The Early Aryans and the Indus Civilization. Oxford University Press Incorporated. ISBN 978-0190226923.
Further reading
- Aruz, Joan (ed), Art of the First Cities: The Third Millennium B.C. from the Mediterranean to the Indus, pp. 347–375, 2003, Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York, N.Y.), google books (fully online)
- Edwin Bryant (2001). The Quest for the Origins of Vedic Culture: The Indo-Aryan Migration Debate. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-516947-6.
- CNRS, L'archéologie de la Bactriane ancienne, actes du colloque Franco-soviétique n° 20. Paris: Editions du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, 1985, ISBN 2-222-03514-7
- Fussman, G.; et al. (2005). Aryas, Aryens et Iraniens en Asie Centrale. Paris: de Boccard. ISBN 2-86803-072-6.
- Lubotsky, A. (2001). "Indo-Iranian substratum" (PDF). In Carpelan, Christian (ed.). Early Contacts between Uralic and Indo-European. Helsinki: Suomalais-Ugrilainen Seura. ISBN 952-5150-59-3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 April 2008.
- Sarianidi, V. I. (1994). "Preface". In Hiebert, F. T. (ed.). Origins of the Bronze Age Oasis Civilization of Central Asia. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-87365-545-1.
- Sarianidi, V. I. (1995). "Soviet Excavations in Bactria: The Bronze Age". In Ligabue, G.; Salvatori, S. (eds.). Bactria: An ancient oasis civilization from the sands of Afghanistan. Venice: Erizzo. ISBN 88-7077-025-7.
- Forizs, L. (2016, 2003) Apāṁ Napāt, Dīrghatamas and Construction of the Brick Altar. Analysis of RV 1.143 in the homepage of Laszlo Forizs
External links