Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P.,[2] commonly referred to as Blue Origin[3] is an American aerospace manufacturer, defense contractor,[4][5] launch service provider and space technologies[6] company headquartered in Kent, Washington, United States. The company makes rocket engines for United Launch Alliance (ULA)'s Vulcan rocket and manufactures their own rockets, spacecraft, satellites,[7] and heavy-lift launch vehicles. The company is the second provider of lunar lander services for NASA's Artemis program and was awarded a $3.4 billion contract.[8] The four rocket engines the company has in production are the BE-3U, BE-3PM, BE-4 and the BE-7.[9]
 | |
| Blue Origin | |
| Company type | Limited partnership |
| Industry | Aerospace and launch service provider |
| Founded | September 8, 2000 |
| Founder | Jeff Bezos |
| Headquarters | Kent, Washington, United States |
Number of locations | 10 (5 production facilities & 5 field offices) |
Area served | United States of America |
Key people | Dave Limp (CEO) |
| Products | Spacecrafts, rockets, heavy-lift launch vehicles and lunar growth technology |
| Owner | Jeff Bezos |
Number of employees | 11,000 (2023)[1] |
| Subsidiaries |
|
| ASN | 55244 |
| Website | blueorigin.com |
The organization was awarded the Robert J. Collier Trophy in 2016 for demonstrating rocket booster reusability with their New Shepard Rocket Program.[10] The award is administered by the U.S. National Aeronautic Association (NAA) and is presented to those who have made "the greatest achievement in aeronautics or astronautics in America, with respect to improving the performance, efficiency, and safety of air or space vehicles, the value of which has been thoroughly demonstrated by actual use during the preceding year."[11]
History
The company was founded in 2000 by Jeff Bezos, the founder of Amazon.[12][13] Rob Meyerson joined the company in 2003 and served as the CEO before leaving the company in 2018.[14] Bob Smith served as CEO from 2018 to 2023.[15] The current CEO is Dave Limp.[16] Little is known about the company's activities in its early years. In 2006, the company purchased land for its New Shepard missions 30 miles North of Van Horn, Texas, United States called Launch Site One (LS1). In November 2006, the first test vehicle was launched, the Goddard rocket, which reached an altitude of 285 feet.[17]
After initiating the development of an orbital rocket system prior to 2012, and stating in 2013 on their website that the first stage would perform a powered vertical landing and be reusable, the company publicly announced their orbital launch vehicle intentions in September 2015. In January 2016, the company indicated that the new rocket would be many times larger than New Shepard. The company publicly released the high-level design of the vehicle and announced its name in September 2016 as "New Glenn". The New Glenn heavy-lift launch vehicle can be configured in both two-stage and three-stage variants. New Glenn is planned to launch in Q3 of 2024.[18]
On July 20, 2021, New Shepard performed its first crewed mission to sub-orbital space called Blue Origin NS-16. The flight lasted approximately 10 minutes and crossed the Kármán line. The passengers were Jeff Bezos, his brother Mark Bezos, Wally Funk, and Oliver Daemen, after the unnamed auction winner (later revealed to have been Justin Sun) dropped out due to a scheduling conflict. Subsequent New Shepard passenger and cargo missions were: Blue Origin NS-17, Blue Origin NS-18, Blue Origin NS-19, Blue Origin NS-20, Blue Origin NS-21 and Blue Origin NS-23.[19]
The company primarily employs an incremental approach from sub-orbital to orbital flight,[20] with each developmental step building on its prior work. The company moved into the orbital spaceflight technology development business in 2014, initially as a rocket engine supplier via a contractual agreement to build the BE-4 rocket engine, for major US launch system operator United Launch Alliance (ULA). United Launch Alliance (ULA) has said that the first flight of its Vulcan Centaur heavy-lift launch vehicle is scheduled to launch in Q4 of 2023. The heavy-lift launch vehicles main power is supported by two BE-4 engines. On June 7, 2023, United Launch Alliance (ULA) performed a Flight Readiness Firing of the Vulcan Centaur rocket at launch pad 41 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Cape Canaveral, Florida, United States. The two BE-4 rocket engines worked as expected.[21]
Launch vehicles


New Shepard
New Shepard is a fully reusable suborbital launch vehicle developed for space tourism. The vehicle is named after Alan Shepard, the first American astronaut in space. The vehicle is capable of vertical takeoff and landings and can carry humans and customer payloads to the edge of space.[22]
The New Shepard launch vehicle is a rocket that consists of a booster rocket and a crew capsule. The capsule can be configured to house up to six passengers, cargo, or a combination of both. The booster rocket is powered by one BE-3PM engine, which sends the capsule to an apogee (Sub-Orbital) of 100.5 kilometres (62.4 mi) and flies above the Kármán line, where passengers and cargo can experience a few minutes of weightlessness before the capsule returns to Earth.[23][24]
The launch vehicle is designed to be fully reusable, with the capsule returning to Earth via three parachutes and a solid rocket motor. The booster lands vertically on the same launchpad it took off from. The company has successfully launched and landed the New Shepard launch vehicle 22 times with 1 partial failure deemed successful and 1 failure. The launch vehicle has a length of 15.0 metres (49.2 ft), a diameter of 3.7 metres (12 ft) and a launch mass of 75 short tons (150,000 lb; 68,000 kg). The BE-3PM engine produces 490 kN of thrust at takeoff. New Shepard allows the company to significantly reduce the cost of space tourism, making the experience more accessible to the general public.[25][26]
New Glenn
New Glenn is a heavy-lift launch vehicle in development stage, and is expected to be ready for Launch in Q3 of 2024. The launch date has been set back because of numerous delays. Named after NASA astronaut John Glenn, design work on the vehicle began in early 2012. Illustrations of the vehicle, and the high-level specifications, were initially publicly unveiled in September 2016. The full vehicle was first unveiled on a launch pad on February 21, 2024.[27] The rocket will have a diameter of 7 meters (23 ft), and its first stage will be powered by seven BE-4 engines. The 7 meter-diameter fairing is claimed to have twice the payload volume of "any commercial launch system" and to be the biggest payload fairing in the world.[28]
Like the New Shepard, New Glenn's first stage is also designed to be reusable. In 2021, the company initiated conceptual design work on approaches to potentially make the second stage reusable as well, with the project codenamed "Project Jarvis".[29]
NASA announced on February 9, 2023, that it had selected the New Glenn heavy-lift launch vehicle for the launch of two Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers (ESCAPADE) spacecraft. The New Glenn heavy-lift launch vehicle will launch ESCAPADE[30][31] in Q3 of 2024 with the ESCAPADE spacecraft entering Mars's orbit approximately one year after launch.
In 2024, Blue Origin received funding from the USSF to assess New Glenn's ability to launch national security payloads.[32]
Blue Moon
In May 2019, Jeff Bezos announced plans for a crew-carrying lunar lander known as Blue Moon.[33] The standard version of the lander is intended to transport 3.6 t (7,900 lb) to the lunar surface, whereas a stretched tank variant could land up to 6.5 t (14,000 lb) on the Moon, both are vehicles designed to make a soft landing on the Moon's surface.
The lander will use the BE-7 hydrolox engine.[34] On May 19, 2023 NASA contracted Blue Origin to develop, test and deploy its Blue Moon landing system for the agency's Artemis V mission, which explores the Moon and prepares future manned missions to Mars. The project includes an unmanned test mission followed by a manned Moon landing in 2029. The contract value is $3.4 billion.[35][36]
Rocket engines

BE-1
Blue Origin's first engine was a "simple, single-propellant engine" called the Blue Engine-1 (BE-1) which used peroxide propellant and generated only 8.9 kN (2,000 lbf) of thrust.[37]
BE-2
The Blue Engine-2 (BE-2) which was a bipropellant engine using kerosene and peroxide, producing 140 kN (31,000 lbf) thrust.[37]
BE-3 (BE-3U and BE-3PM)
The BE-3 is a family of rocket engines made by Blue Origin with two variants, the BE-3U and BE-3PM. The rocket engine is a liquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen (LH2/LOX) cryogenic engine that can produce 490 kN (110,000 lbf) and 710 kN (160,000 lbf) of thrust, respectively. Early thrust chamber testing began at NASA Stennis[38] in 2013.[39] By late 2013, the BE-3 had been successfully tested on a full-duration sub-orbital burn, with simulated coast phases and engine relights, "demonstrating deep throttle, full power, long-duration and reliable restart all in a single-test sequence."[40] NASA has released a video of the test.[39] As of December 2013[update], the engine had demonstrated more than 160 starts and 9,100 seconds (2.5 h) of operation at the company's test facility near Van Horn, Texas.[40][41]
- The BE-3U is an open expander cycle variant of the BE-3. Two of these engines will be used to power the New Glenn heavy-lift launch vehicle's second stage. The amount of thrust the BE-3U produces is 710 kilonewtons (160,000 lbf).[42]
- The BE-3PM, uses a pump-fed engine design, with a combustion tap-off cycle to take a small amount of combustion gases from the main combustion chamber to power the engine's turbopumps. One engine is used to power the Propulsive Module (PM) of New Shepard. The amount of thrust the BE-3PM produces is 490 kilonewtons (110,000 lbf).[42] The rocket engine can be throttled down to as low as 110 kN (25,000 lbf) for use in controlled vertical landings.
BE-4
The BE-4 is a liquid oxygen/liquified natural gas (LOX/LNG) rocket engine that can produce 2,400 kN (550,000 lbf) of thrust.[43]
In late 2014, the company signed an agreement with United Launch Alliance (ULA) to develop the BE-4 engine, for ULA's upgraded Atlas V and Vulcan Centaur rockets replacing the RD-180 Russian-made rocket engine. The newly developed heavy-lift launch vehicle will use two of the 2,400 kN (550,000 lbf) BE-4 engines on each first stage. The engine development program for the BE-4 began in 2011.[44]
On October 31, 2022, a Twitter post by the official Blue Origin account announced that the first two BE-4 engines had been delivered to ULA and were in the process of being integrated on a Vulcan rocket. In a later tweet, ULA CEO Tory Bruno said that one of the engines had already been installed on the booster, and that the other would be joining it momentarily.[45] On June 7, 2023, the two BE-4 rocket engines performed as expected when ULA performed a Flight Readiness Firing of the Vulcan Rocket at launch pad 41 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Cape Canaveral, Florida.[46][47]
Vulcan Centaur launched for the first time on January 8, 2024, successfully carrying Astrobotic Technology's Peregrine lunar lander, the first mission on NASA's Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program using the BE-4 engine.[48]
BE-7
The BE-7 engine is a liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen dual expander cycle engine currently under development, designed for use on Blue Moon.[49] The engine produces 44 kN (10,000 lbf) of thrust. Its first ignition tests were performed in June 2019, with thrust chamber assembly testing continuing through 2023.[50]
Pusher escape motor
The company partnered with Aerojet Rocketdyne to develop a pusher launch escape system for the New Shepard suborbital crew capsule. Aerojet Rocketdyne provides the Crew Capsule Escape Solid Rocket Motor (CCE SRM) while the thrust vector control system that steers the capsule during an abort is designed and manufactured by Blue Origin.[51][52]
Facilities

The company has facilities across the United States which include five main locations and five field offices:[53]
- Kent, Washington (headquarters)
- Van Horn, Texas
- Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida
- Huntsville, Alabama
- Marshall Space Flight Center, Alabama
- Arlington, Virginia
- Denver, Colorado
- Los Angeles, California
- Phoenix, Arizona
- Washington, DC
The company’s headquarters is in Kent, Washington. Rocket development takes place at its Headquarters. The company has continued to expand its Seattle-area offices and rocket production facilities since 2016, purchasing an adjacent 11,000 m2 (120,000 sq ft)-building.[54] In 2017, the company filed permits to build a new 21,900 m2 (236,000 sq ft) warehouse complex and an additional 9,560 m2 (102,900 sq ft) of office space.[55] The company established a new headquarters and R&D facility, called the O'Neill Building on June 6, 2020.[56][57]
Launch Site One (LSO)
Corn Ranch, commonly referred to as Launch Site One (LSO) is the company's launch site 30 miles north of Van Horn, Texas.[58] The launch facility is located at 31.422927°N 104.757152°W.[59]
In addition to the sub-orbital launch pad, Launch Site One (LSO) includes a number of rocket engine test stands and engine test cells are at the site to support the hydrolox, methalox and storable propellant engines that are used. There are three test cells for testing the BE-3 and BE-4 engines. The test cells support full-thrust and full-duration burns, and one supports short-duration, high-pressure preburner tests.
Blue Engine
Engine production is located in Huntsville, Alabama, at a 600,000sqft facility called, "Blue Engine". The companies website states that, "The world-class engine manufacturing facility in The Rocket City conduct[s] high rate production of the BE-4 and BE-3U engines.
The company is planning a third major expansion in Huntsville and the company was approved for the sale of 14.83 acres adjacent to its already sprawling campus at the price of $1.427 million.[60]
Orbital Launch Site (OLS)
The Orbital Launch Site (OLS) at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, develops rockets and does extensive testing. The company converted Launch Complex 36 (LC-36) to launch its New Glenn into orbit[61] at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The facility was initially completed in 2020 and is being used for the construction of New Glenn prototypes, rocket testing, and designs.[62]
The companies facility is situated on 306 acres of land assembled from former Launch Complexes 11, 36A, and 36B. The land parcel used to build a rocket engine test stand for the BE-4 engine, a launch mount, called the Orbital Launch Site, (hence its name) and a reusable booster refurbishment facility for the New Glenn launch vehicle, which is expected to land on a drone ship and return to Port Canaveral for refurbishment. Manufacturing of "large elements, such as New Glenn's first and second stages as well as the payload fairings and other large components will be made nearby in Exploration Park, which is near the entrance to the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex on Merritt Island, Florida.[63]
Other projects
Blue Ring (Space Truck Vehicle)
The Blue Ring vehicle was announced in October 2023 by Blue Origin. It will have its own engine and is meant to handle orbital logistics and delivery. In March 2024, in partnership with the United States Space Force, it was announced that the Blue Ring’s capabilities will be tested soon on a mission called DarkSky-1.[64]
Orbital Reef (commercial space station)
The company and its partners Sierra Space, Boeing, Redwire Space and Genesis Engineering Solutions won a $130 million award to jump-start the design of their Orbital Reef commercial space station. The project is envisioned as an expandable business park, with Boeing's Starliner and Sierra Space's Dream Chaser transporting passengers to and from low Earth orbit (LEO) for tourism, research and in-space manufacturing projects.[65]
Orbital Reef’s design will be modular in nature, to provide the greatest amount of customization and compatibility. It will reportedly be designed to accept docking from almost every in operation spacecraft like SpaceX Dragon 2, Soyuz (spacecraft), Dream Chaser, and Boeing Starliner. The initial modules will be: Life, Node, Core, and Research Modules.[66]
In 2024 NASA increased funding for Orbital Reef by $42 million, bringing the total award to $172 million.[67]
Nuclear rocket program
NASA plans to test spacecraft, engines and other propellent systems powered by nuclear fission no later than 2027 as part of the agency's effort to demonstrate more efficient methods of traveling through outer space for space exploration.[68] One benefit to using nuclear fission as a propellent for spacecraft is that nuclear-based systems can have less mass than solar cells which means a spacecraft could be much smaller while absorbing and using the same amount of energy more efficiently. Nuclear fission concepts that can power both life support and propulsion systems could greatly reduce the cost and flight time during space exploration.[69]
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency awarded General Atomics, Lockheed Martin and Blue Origin contracts to fund and build nuclear spacecraft under the agency's Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations program or DRACO program. The company was awarded $2.9 million to develop spacecraft component designs.[70]
In partnership with Blue Origin, Ultra Safe Nuclear Corp., GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, GE Research, Framatome and Materion, USNC-Tech won a $5 million contract from NASA and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) to develop a long range nuclear propulsion system called the Power Adjusted Demonstration Mars Engine, or PADME.[71]
Space Technology
NASA awarded $35 million to the company in 2023 for the company's work on lunar regrowth to be used for solar powered systems on the moon. The company's website states that "Blue Alchemist is a proposed end-to-end, scalable, autonomous, and commercial solution that produces solar cells from lunar regolith, which is the dust and crushed rock abundant on the surface of the Moon. Based on a process called molten regolith electrolysis, the breakthrough would bootstrap unlimited electricity and power transmission cables anywhere on the surface of the Moon. This process also produces oxygen as a useful byproduct for propulsion and life support."
Gary Lai, chief architect of the New Shepard rocket said during the pathfinder awards at the Seattle Museum of Flight that [The company] "aims to be the first company that harvests natural resources from the moon to use here on Earth,” He also mentioned that the company is building a novel approach to extract outer space's vast resources.
Blue Origin flight data
1 2 3 4 5 6 2005 2010 2015 2020
| 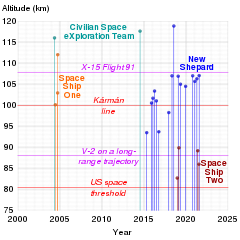 |
In the chart below, ♺ means "Flight Proven Booster"
| Flight No. | Date | Vehicle | Apogee | Outcome | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | March 5, 2005 | Charon | 315 ft (0.05 mi) | Success | Test Flight |
| 2 | November 13, 2006 | Goddard | 279 ft (0.05 mi) | Success | First rocket-powered test flight[72] |
| 3 | March 22, 2007 | Goddard ♺[73] | N/A | Success | Test Flight |
| 4 | April 19, 2007 | Goddard ♺[74] | N/A | Success | Test Flight |
| 5 | May 6, 2011 | PM2 (Propulsion Module)[75] | N/A | Success | Test Flight |
| 6 | August 24, 2011 | PM2 (Propulsion Module) ♺ | N/A | Failure | Test Flight |
| 7 | October 19, 2012 | New Shepard capsule | N/A | Success | Pad escape test flight[76] |
| 8 | April 29, 2015 | New Shepard 1 | 307,000 ft (58 mi) | Partial success | Flight to altitude 93.5 km, capsule recovered, booster crashed on landing[77] |
| 9 | November 23, 2015 | New Shepard 2 | 329,839 ft (62 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital spaceflight and landing[78] |
| 10 | January 22, 2016 | New Shepard 2 ♺ | 333,582 ft (63 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital spaceflight and landing of a reused booster[79] |
| 11 | April 2, 2016 | New Shepard 2 ♺ | 339,178 ft (64 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital spaceflight and landing of a reused booster[80] |
| 12 | June 19, 2016 | New Shepard 2 ♺ | 331,501 ft (63 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital spaceflight and landing of a reused booster: The fourth launch and landing of the same rocket. The company published a live webcast of the takeoff and landing.[81] |
| 13 | October 5, 2016 | New Shepard 2 ♺ | Booster:307,458 ft (58 mi) Capsule:23,269 ft (4 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital spaceflight and landing of a reused booster. Successful test of the in-flight abort system. The fifth and final launch and landing of the same rocket (NS2).[82] |
| 14 | December 12, 2017 | New Shepard 3 | Booster:322,032 ft(61 mi) Capsule:322,405 ft(61 mi) | Success | Flight to just under 100 km and landing. The first launch of NS3 and a new Crew Capsule 2.0.[83] |
| 15 | April 29, 2018 | New Shepard 3 ♺ | 351,000 ft (66 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital spaceflight and landing of a reused booster.[84] |
| 16 | July 18, 2018 | New Shepard 3 ♺ | 389,846 ft (74 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital spaceflight and landing of a reused booster, with the Crew Capsule 2.0–1 RSS H.G.Wells, carrying a mannequin. Successful test of the in-flight abort system at high altitude. Flight duration was 11 minutes.[85] |
| 17 | January 23, 2019 | New Shepard 3 ♺ | 351,000 ft (66 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital flight, delayed from December 18, 2018. Eight NASA research and technology payloads were flown.[86][87] |
| 18 | May 2, 2019 | New Shepard 3 ♺ | 346,000 ft (65 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital flight. Max Ascent Velocity: 2,217 mph (3,568 km/h),[88] duration: 10 minutes, 10 seconds. Payload: 38 microgravity research payloads (nine sponsored by NASA). |
| 19 | December 11, 2019 | New Shepard 3 ♺ | 343,000 ft (64 mi) | Success | Sub-orbital flight, Payload: Multiple commercial, research (8 sponsored by NASA) and educational payloads, including postcards from Club for the Future.[89][90][91] |
| 20 | October 13, 2020 | New Shepard 3 ♺ | 346,000 ft (65 mi) | Success | 7th flight of the same capsule/booster. Onboard 12 payloads include Space Lab Technologies, Southwest Research Institute, postcards and seeds for Club for the Future, and multiple payloads for NASA including SPLICE to test future lunar landing technologies in support of the Artemis program[92] |
| 21 | January 14, 2021 | New Shepard 4 | 350,858 ft (66 mi) | Success | Uncrewed qualification flight for NS4 rocket and "RSS First Step" capsule and maiden flight for NS4.[93] |
| 22 | April 14, 2021 | New Shepard 4 ♺ | 348,753 ft (66 mi) | Success | 2nd flight of NS4 with Astronaut Rehearsal. Gary Lai, Susan Knapp, Clay Mowry, and Audrey Powers, all Blue Origin personnel, are "stand-in astronauts". Lai and Powers briefly get in.[94] |
| 23 | July 20, 2021 | New Shepard 4 ♺ | 351,210 ft (66 mi) | Success | First crewed flight (NS-16). Crew: Jeff Bezos, Mark Bezos, Wally Funk, and Oliver Daemen.[95] |
| 24 | August 26, 2021[96] | New Shepard 3 ♺ | 347,434 ft (66 mi) | Success | Payload mission consisting of 18 commercial payloads inside the crew capsule, a NASA lunar landing technology demonstration installed on the exterior of the booster and an art installation installed on the exterior of the crew capsule.[97] |
| 25 | October 13, 2021 | New Shepard 4 ♺ | 341,434 ft (66 mi) | Success | Second crewed flight (NS-18). Crew: Audrey Powers, Chris Boshuizen, Glen de Vries, and William Shatner.[98] |
| 26 | December 11, 2021 | New Shepard 4 ♺ | 351,050 ft (66 mi) | Success | Third crewed flight (NS-19). Crew: Laura Shepard Churchley, Michael Strahan, Dylan Taylor, Evan Dick, Lane Bess, and Cameron Bess.[99] |
| 27 | March 31, 2022 | New Shepard 4 ♺ | 351,050 ft (66 mi) | Success | Fourth crewed flight (NS-20). Crew: Marty Allen, Sharon Hagle, Marc Hagle, Jim Kitchen, George Nield, and Gary Lai.[100] |
| 28 | June 4, 2022 | New Shepard 4 ♺ | 351,050 ft (66 mi) | Success | Fifth crewed flight (NS-21). Crew: Evan Dick, Katya Echazarreta, Hamish Harding, Victor Correa Hespanha, Jaison Robinson, and Victor Vescovo.[101] |
| 29 | August 4, 2022 | New Shepard 4 ♺ | 351,050 ft (66 mi) | Success | Sixth crewed flight (NS-22). Crew: Coby Cotton, Mário Ferreira, Vanessa O'Brien, Clint Kelly III, Sara Sabry, and Steve Young.[102] |
| 30 | September 12, 2022 | New Shepard 3 ♺ | 37,402 ft (7 mi) | Failure | Uncrewed flight with commercial payloads onboard (NS-23). A booster failure triggered the launch escape system during flight, and the capsule landed successfully. The Blue Origin incident investigation found that a thermal-structural failure occurred on the BE-3 nozzle leading to the launch failure.[103] |
| 31 | December 19, 2023 | New Shepard 4 ♺ | 107.060 km (66.5242 mi) | Success | Successful Return to Flight mission (NS-24) following failure of NS-23 more than a year prior. 33 payloads and 38,000 Club for the Future postcards from students around the world.[104] |
NASA partnerships and funding
The company has contracted to do work for NASA on several development efforts. The company was awarded $3.7 million in funding by NASA in 2009 via a Space Act Agreement[105][106] under the first Commercial Crew Development (CCDev) program for development of concepts and technologies to support future human spaceflight operations.[107][108] NASA co-funded risk-mitigation activities related to ground testing of (1) an innovative 'pusher' escape system, that lowers cost by being reusable and enhances safety by avoiding the jettison event of a traditional 'tractor' Launch Escape System, and (2) an innovative composite pressure vessel cabin that both reduces weight and increases safety of astronauts.[105] This was later revealed to be a part of a larger system, designed for a bionic capsule, that would be launched atop an Atlas V rocket.[109] On November 8, 2010, it was announced that the company had completed all milestones under its CCDev Space Act Agreement.[110]
In April 2011, The company received a commitment from NASA for $22 million of funding under the CCDev phase 2 program.[111] Milestones included (1) performing a Mission Concept Review (MCR) and System Requirements Review (SRR) on the orbital Space Vehicle, which utilizes a bionic shape to optimize its launch profile and atmospheric reentry, (2) further maturing the pusher escape system, including ground and flight tests, and (3) accelerating development of its BE-3 LOX/LH2 440 kN (100,000 lbf) engine through full-scale thrust chamber testing.[112]
In 2012, NASA's Commercial Crew Program released its follow-on CCiCap solicitation for the development of crew delivery to ISS by 2017. The company did not submit a proposal for CCiCap, but reportedly continued work on its development program with private funding.[113] The company had a failed attempt to lease a different part of the Space Coast, when they submitted a bid in 2013 to lease Launch Complex 39A (LC39A) at the Kennedy Space Center – on land to the north of, and adjacent to, Cape Canaveral AFS – following NASA's decision to lease the unused complex out as part of a bid to reduce annual operation and maintenance costs. The companies bid was for shared and non-exclusive use of the LC39A complex such that the launchpad was to have been able to interface with multiple vehicles, and costs for using the launch pad were to have been shared across multiple companies over the term of the lease. One potential shared user in the companies proposed plan was United Launch Alliance (ULA). Commercial use of the LC39A launch complex was awarded to SpaceX, which submitted a bid for exclusive use of the launch complex to support their crewed missions.[114]
The company completed work for NASA on several small development contracts, receiving total funding of $25.7 million by 2013.[105][111] In September 2013 – before completion of the bid period, and before any public announcement by NASA of the results of the process – Florida Today reported that the company had filed a protest with the U.S. General Accounting Office (GAO) "over what it says is a plan by NASA to award an exclusive commercial lease to SpaceX for use of mothballed space shuttle launch pad 39A".[115] NASA had originally planned to complete the bid award and have the pad transferred by October 1, 2013, but the protest delayed a decision until the U.S. General Accounting Office (GAO) reached a decision on the protest.[115][116] SpaceX said that they would be willing to support a multi-user arrangement for pad 39A.[117] In December 2013, the U.S. General Accounting Office (GAO) denied the companies protest and sided with NASA, which argued that the solicitation contained no preference on the use of the facility as either multi-use or single-use. "The [solicitation] document merely [asked] bidders to explain their reasons for selecting one approach instead of the other and how they would manage the facility".[116] NASA selected the SpaceX proposal in late 2013 and signed a 20-year lease contract for Launch Pad 39A to SpaceX in April 2014.[118]
The company placed their first bid via the NASA Sustaining Lunar Development (SLD) competition to fund and develop a lunar lander capable of transporting astronauts to and from the lunar surface. The Blue Origin led team called the "National Team" included, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and Draper. On April 30, 2020, the company and its partners won a $579 million contract to start developing and testing an integrated Human Landing System (HLS) for the Artemis program to return humans to the Moon.[119][120] However, the Blue Origin led team lost their first bid to work for NASA's Artemis program and on April 16, 2021, NASA officially selected the Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) to develop, test and build their version of the Human Landing System (HLS) for Artemis missions 2 (II), 3 (III) and 4 (IV).
In early 2021, the company received over $275 million from NASA for lunar lander projects and sub-orbital research flights.[121]
The company then announced on December 6, 2022, that it had submitted a second bid via the NASA Sustaining Lunar Development (SLD) competition to fund and develop a second lunar lander capable for transporting astronauts to and from the lunar surface. The announcement fell within NASA's deadline for Sustaining Lunar Development (SLD) proposals. As with their first bid, the company is leading another team called the "National Team" which includes Draper, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Astrobotic, Honeybee Robotics and Blue Origin.[122]
On May 19, 2023 NASA contracted the company to develop, test and deploy its Blue Moon landing system for the agency's Artemis V mission, which explores the Moon and prepares future manned missions to Mars. The project includes an unmanned test mission followed by a manned Moon landing in 2029. The contract value is $3.4 billion.[35][36]
Internal and additional U.S Government funding
By July 2014, Jeff Bezos had invested over $500 million into the company.[123] and the vast majority of further funding into 2016 was to support technology development and operations where a majority of funding came from Jeff Bezos' private investment fund. In April 2017, an annual amount was published showing that Jeff Bezos was selling approximately $1 billion in Amazon stock per year to invest in the company.[124] Jeff Bezos has been criticized for spending excessive amounts of his fortune on spaceflight.[125]
The company received $181 million from the United States Air Force for launch vehicle development in 2019. The company was also eligible to benefit from further grants totaling $500M as part of the U.S. Space Force Launch Services Agreement competition.[126] On November 18, 2022, the U.S. Space Systems Command announced that an agreement with the company that "paves the way" for the company's New Glenn rocket to compete for national security launch contracts once it completes its required flight certifications for Top Secret military payloads.
In an interview with the Bob Smith by the financial Times in 2023, Smith said that the company had "hundreds of millions in revenue as well as billions of dollars in orders".[127]
Early test vehicles
Charon

The companies first flight test vehicle, called Charon after Pluto's moon,[128] was powered by four vertically mounted Rolls-Royce Viper Mk. 301 jet engines rather than rockets. The low-altitude vehicle was developed to test autonomous guidance and control technologies, and the processes that the company would use to develop its later rockets. Charon made its only test flight at Moses Lake, Washington on March 5, 2005. It flew to an altitude of 96 m (316 ft) before returning for a controlled landing near the liftoff point.[129][130] As of 2016, Charon is on display at the Museum of Flight in Seattle, Washington.[131]
Goddard
The next test vehicle, named Goddard (also known as PM1), first flew on November 13, 2006. The flight was successful. A test flight for December 2 never launched.[132][133] According to Federal Aviation Administration records, two further flights were performed by Goddard.[134] Blue Engine 1, or BE-1, was the first rocket engine developed by the company and was used in the company's Goddard development vehicle.
PM2
Another early suborbital test vehicle, PM2, had two flight tests in 2011 in west Texas. The vehicle designation may be short for "Propulsion Module".[135] The first flight was a short hop (low altitude, VTVL takeoff and landing mission) flown on May 6, 2011. The second flight, August 24, 2011, failed when ground personnel lost contact and control of the vehicle. The company released its analysis of the failure nine days later. As the vehicle reached a speed of Mach 1.2 and 14 km (46,000 ft) altitude, a "flight instability drove an angle of attack that triggered [the] range safety system to terminate thrust on the vehicle".[136] Blue Engine 2, or BE-2, was a pump-fed bipropellant engine burning kerosene and peroxide which produced 140 kN (31,000 lbf) of thrust.[137][138] Five BE-2 engines powered the companies PM-2 development vehicle on two test flights in 2011.[139]
See also
- Billionaire space race, Blue Origin vs. SpaceX vs. Virgin Galactic
References
External links
