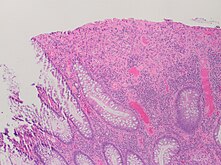
Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine (colon).[1] Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. It broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases.
| Colitis | |
|---|---|
 | |
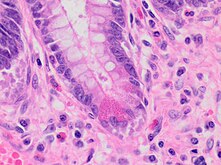
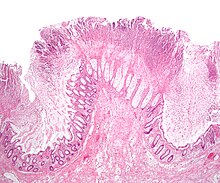
| A micrograph demonstrating cryptitis, a microscopic correlate of colitis. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
In a medical context, the label colitis (without qualification) is used if:
- The cause of the inflammation in the colon is undetermined; for example, colitis may be applied to Crohn's disease at a time when the diagnosis is unknown, or
- The context is clear; for example, an individual with ulcerative colitis is talking about their disease with a physician who knows the diagnosis.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of colitis are quite variable and dependent on the cause of the given colitis and factors that modify its course and severity.[2]
Common symptoms of colitis may include: mild to severe abdominal pains and tenderness (depending on the stage of the disease), persistent hemorrhagic diarrhea with pus either present or absent in the stools, fecal incontinence, flatulence, fatigue, loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss.[3]
More severe symptoms may include: shortness of breath, a fast or irregular heartbeat and fever.[3]
Other less common or rare non-specific symptoms that may accompany colitis include: arthritis, mouth ulcers, painful, red and swollen skin and irritated, bloodshot eyes.[3]
Signs seen on colonoscopy include: colonic mucosal erythema (redness of the colon's inner surface), ulcerations and hemorrhage.[4]
Diagnosis
Symptoms suggestive of colitis are worked-up by obtaining the medical history, a physical examination and laboratory tests (CBC, electrolytes, stool culture and sensitivity, stool ova and parasites et cetera). Additional tests may include medical imaging (e.g. abdominal computed tomography, abdominal X-rays) and an examination with a camera inserted into the rectum (sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy).[5]
An important investigation in the assessment of colitis is biopsy for histopathology. A very small piece of tissue (usually about 2mm) is removed from the bowel mucosa during endoscopy and examined under the microscope by a histopathologist. A biopsy report generally does not state the diagnosis, but should state any presence of chronic colitis, give an indication of disease activity, as well as state the presence of any epithelial damage (erosions and ulcerations).[6]
Histopathology findings generally associated with chronic colitis include:[6]
- Crypt degeneration
- Crypt branching and other architectural distortions
- Paneth cell (pictured) or gastric metaplasia (only applies in the left colon and rectum)
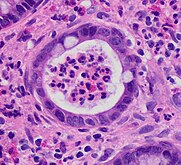
Other findings include basal plasmacytosis and mucin depletion.[6]Histopathology findings generally associated with active colitis include:[6]
- Neutrophilic cryptitis (neutrophils within crypt epithelium)
- Crypt abscesses (luminal neutrophilic aggregates)
- Gland destruction
- Ulceration (seen here as absence of epithelium, and granulation tissue with many fibroblasts)
Types
There are many types of colitis. They are usually classified by the cause.
Types of colitis include:
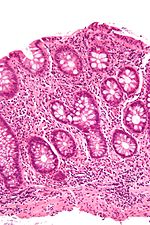

Autoimmune
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) – a group of chronic colitides.
- Ulcerative colitis (UC) – a chronic colitis that affects the large intestine.[7]
- Crohn's disease (CD) – another type of IBD that often leads to colitis.
Unknown
- Microscopic colitis – a colitis diagnosed by microscopic examination of colonic tissue; macroscopically ("to the eye") it appears normal.
Treatment-caused
- Diversion colitis
- Chemical colitis
- Chemotherapy-induced colitis
- Radiation colitis
- Checkpoint inhibitor induced colitis
Vascular disease
Infectious
- Infectious colitis
A subtype of infectious colitis is Clostridioides difficile colitis,[8] which is informally abbreviated as "C-diff colitis". It classically forms pseudomembranes and is often referred to as pseudomembranous colitis, which is its (nonspecific) histomorphologic description.
Enterohemorrhagic colitis may be caused by Shiga toxin in Shigella dysenteriae or Shigatoxigenic group of Escherichia coli (STEC), which includes serotype O157:H7 and other enterohemorrhagic E. coli.[9]
Parasitic infections, like those caused by Entamoeba histolytica, can also cause colitis.
Unclassifiable colitides
Indeterminate colitis is the classification for colitis that has features of both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.[10] Indeterminate colitis' behaviour is usually closer to ulcerative colitis than Crohn's disease.[11]
Atypical colitis is a phrase that is occasionally used by physicians for a colitis that does not conform to criteria for accepted types of colitis. It is not an accepted diagnosis per se and, as such, a colitis that cannot be definitively classified.[citation needed]
Treatment
Treatment for this condition can include medications such as steroids and dietary changes. In some instances, hospitalization and surgery may be required. [12]
Moreover, several studies recently have found significant relationship between colitis and dairy allergy (including: cow milk, cow milk UHT and casein),[13][14][15][16] suggesting some patients may benefit from an elimination diet.
Microbiome modification
The use of oral probiotic supplements to modify the composition and behavior of the microbiome has been considered as a possible therapy for both induction and maintenance of remission in people with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. A Cochrane review in 2020 did not find clear evidence of improved remission likelihood, nor lower adverse events, in people with Crohn's disease, following probiotic treatment.[17]
For ulcerative colitis, there is low-certainty evidence that probiotic supplements may increase the probability of clinical remission.[18] People receiving probiotics were 73% more likely to experience disease remission and over 2x as likely to report improvement in symptoms compared to those receiving a placebo, with no clear difference in minor or serious adverse effects.[18]Although there was no clear evidence of greater remission when probiotic supplements were compared with 5‐aminosalicylic acid treatment as a monotherapy, the likelihood of remission was 22% higher if probiotics were used in combination with 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy.[18] Whereas in people who are already in remission, it is unclear whether probiotics help to prevent future relapse, either as a monotherapy or combination therapy.[19]
Research
In the lab, the CRISPR-Cas systems effectively killed C. difficile bacteria. Researchers tested this approach in mice infected with C. difficile. Two days after the CRISPR treatment, the mice showed reduced C. difficile levels. Next steps include retooling the phage to prevent C. difficile from returning after the initial effective killing.[20]
In 2022, Yang et al. published a report on a successful treatment, using mesenchymal stem cells, of experimental colitis in mice.[21]
Additional research was conducted by Huang et al. that analyzed specific genes and biological markers that are associated with the risk of colon cancer development in patients with colitis. The results showed a correlation between certain biomarkers and the development of disease.[22]
Colitis is common in parts of the world where helminthic colonisation is rare, and uncommon in those areas where most people carry worms. Infections with helminths may alter the autoimmune response that causes the disease. Early trials of Trichuris suis ova (TSO) showed promising results when used in people with IBD[23][24][25][26] but later trials failed at Phase 2, and most were eventually discontinued.[27] However, the phase 2 trials had used a different formulation of TSO from the one that had been used in the earlier studies that had shown positive outcomes.[28]
References
External links