ECHELON, originally a secret government code name, is a surveillance program (signals intelligence/SIGINT collection and analysis network) operated by the five signatory states to the UKUSA Security Agreement:[1] Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States, also known as the Five Eyes.[2][3][4]



Created in the late 1960s to monitor the military and diplomatic communications of the Soviet Union and its Eastern Bloc allies during the Cold War, the ECHELON project became formally established in 1971.[5][6] By the end of the 20th century, it had greatly expanded.[7]
Organization
The UKUSA intelligence community was assessed by the European Parliament (EP) in 2000 to include the signals intelligence agencies of each of the member states:
- the Government Communications Headquarters of the United Kingdom,
- the National Security Agency of the United States,
- the Communications Security Establishment of Canada,
- the Australian Signals Directorate of Australia, and
- the Government Communications Security Bureau of New Zealand.
| Operated by the United States | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Location | Operator(s) | Codename |
 Brazil Brazil | Brasília, Federal District | SCS | |
 Germany Germany | Bad Aibling, Bavaria | GARLICK[10] | |
 India India | New Delhi | SCS | |
 Japan Japan | Misawa, Tōhoku region | LADYLOVE[13] | |
 Thailand Thailand | Bangkok (?) | LEMONWOOD[14] | |
 United Kingdom United Kingdom | Menwith Hill, Harrogate | MOONPENNY[14] | |
 United States United States | Sugar Grove, West Virginia | TIMBERLINE[17] | |
| Yakima, Washington | JACKKNIFE[14] | ||
| Sábana Seca, Puerto Rico | CORALINE[14] | ||
| Operated Jointly with the United States (2nd party) | |||
| Country | Location | Contributor(s) | Codename |
 Australia Australia | Geraldton, WA | STELLAR[12] | |
| Darwin, NT | SHOAL BAY[12] | ||
 New Zealand New Zealand | Waihopai, Blenheim | IRONSAND[12] | |
 United Kingdom United Kingdom | Bude, Cornwall | CARBOY[17] | |
 Cyprus Cyprus | Ayios Nikolaos Station | SOUNDER[21] | |
 Kenya Kenya | Nairobi | SCAPEL[14] | |
 Oman Oman | Seeb, Muscat | SNICK[14] | |
Reporting and disclosures
Public disclosures (1972–2000)
Former NSA analyst Perry Fellwock, under the pseudonym Winslow Peck, first blew the whistle on ECHELON to Ramparts in 1972,[22] when he revealed the existence of a global network of listening posts and told of his experiences working there. He also revealed the existence of nuclear weapons in Israel in 1972, the widespread involvement of CIA and NSA personnel in drugs and human smuggling, and CIA operatives leading Nationalist Chinese (Taiwan) commandos in burning villages inside PRC borders.[23]
In 1982, investigative journalist and author James Bamford wrote The Puzzle Palace, an in-depth history of the NSA and its practices, which notably leaked the existence of the eavesdropping operation Project SHAMROCK. Project SHAMROCK ran from 1945 to 1975, after which it evolved into ECHELON.[24][25]
In 1988, Margaret Newsham, a Lockheed employee under NSA contract, disclosed the ECHELON surveillance system to members of Congress. Newsham told a member of the US Congress that the telephone calls of Strom Thurmond, a Republican US senator, were being collected by the NSA. Congressional investigators determined that "targeting of US political figures would not occur by accident, but was designed into the system from the start."[26]
Also in 1988, an article titled "Somebody's Listening", written by investigative journalist Duncan Campbell in the New Statesman, described the signals intelligence gathering activities of a program code-named "ECHELON".[26] Bamford described the system as the software controlling the collection and distribution of civilian telecommunications traffic conveyed using communication satellites, with the collection being undertaken by ground stations located in the footprint of the downlink leg.[27]
A detailed description of ECHELON was provided by the New Zealand journalist Nicky Hager in his 1996 book Secret Power: New Zealand's Role in the International Spy Network.[28] Two years later, Hager's book was cited by the European Parliament in a report titled "An Appraisal of the Technology of Political Control" (PE 168.184).[29]
In March 1999, for the first time in history, the Australian government admitted that news reports about the top secret UKUSA Agreement were true.[30] Martin Brady, the director of Australia's Defence Signals Directorate (DSD, now known as Australian Signals Directorate, or ASD) told the Australian broadcasting channel Nine Network that the DSD "does co-operate with counterpart signals intelligence organisations overseas under the UKUSA relationship."[31]
In 2000, James Woolsey, the former Director of the US Central Intelligence Agency, confirmed that US intelligence uses interception systems and keyword searches to monitor European businesses.[32]
Lawmakers in the United States feared that the ECHELON system could be used to monitor US citizens.[33] According to The New York Times, the ECHELON system has been "shrouded in such secrecy that its very existence has been difficult to prove."[33] Critics said the ECHELON system emerged from the Cold War as a "Big Brother without a cause".[34]
European Parliament investigation (2000–2001)

The program's capabilities and political implications were investigated by a committee of the European Parliament during 2000 and 2001 with a report published in 2001.[7] In July 2000, the Temporary Committee on the ECHELON Interception System was established by the European parliament to investigate the surveillance network.[36] It was chaired by the Portuguese politician Carlos Coelho, who was in charge of supervising investigations throughout 2000 and 2001.
In May 2001, as the committee finalised its report on the ECHELON system, a delegation travelled to Washington, D.C. to attend meetings with US officials from the following agencies and departments:
- US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)[37]
- US Department of Commerce (DOC)[37]
- US National Security Agency (NSA)[37]
All meetings were cancelled by the US government and the committee was forced to end its trip prematurely.[37] According to a BBC correspondent in May 2001, "The US Government still refuses to admit that Echelon even exists."[5]
In July 2001, the Committee released its final report.[38] The EP report concluded that it seemed likely that ECHELON is a method of sorting captured signal traffic, rather than a comprehensive analysis tool.[7] On 5 September 2001, the European parliament voted to accept the report.[39]
The European Parliament stated in its report that the term ECHELON is used in a number of contexts, but that the evidence presented indicates that it was the name for a signals intelligence collection system.[7] The report concludes that, on the basis of information presented, ECHELON was capable of interception and content inspection of telephone calls, fax, e-mail and other data traffic globally through the interception of communication bearers including satellite transmission, public switched telephone networks (which once carried most Internet traffic), and microwave links.[7]
Confirmation of ECHELON (2015)
Two internal NSA newsletters from January 2011 and July 2012, published as part of Edward Snowden's leaks by the website The Intercept on 3 August 2015, for the first time confirmed that NSA used the code word ECHELON and provided some details about the scope of the program: ECHELON was part of an umbrella program with the code name FROSTING, which was established by the NSA in 1966 to collect and process data from communications satellites. FROSTING had two sub-programs:[40]
- TRANSIENT: for intercepting Soviet satellite transmissions
- ECHELON: for intercepting Intelsat satellite transmissions
The European Parliament's Temporary Committee on the ECHELON Interception System stated, "It seems likely, in view of the evidence and the consistent pattern of statements from a very wide range of individuals and organisations, including American sources, that its name is in fact ECHELON, although this is a relatively minor detail".[7] The US intelligence community uses many code names (see, for example, CIA cryptonym).
Former NSA employee Margaret Newsham said that she worked on the configuration and installation of software that makes up the ECHELON system while employed at Lockheed Martin, from 1974 to 1984 in Sunnyvale, California, in the United States, and in Menwith Hill, England, in the UK.[41] At that time, according to Newsham, the code name ECHELON was NSA's term for the computer network itself. Lockheed called it P415. The software programs were called SILKWORTH and SIRE. A satellite named VORTEX intercepted communications. An image available on the internet of a fragment apparently torn from a job description shows Echelon listed along with several other code names.[42][43]
Britain's The Guardian newspaper summarized the capabilities of the ECHELON system as follows:
A global network of electronic spy stations that can eavesdrop on telephones, faxes and computers. It can even track bank accounts. This information is stored in Echelon computers, which can keep millions of records on individuals.Officially, however, Echelon doesn't exist.[44]
Documents leaked by the former NSA contractor Edward Snowden revealed that the ECHELON system's collection of satellite data is also referred to as FORNSAT - an abbreviation for "Foreign Satellite Collection".[45][46]
Intercept stations
First revealed by the European Parliament report (p. 54 ff)[7] and confirmed later by the Edward Snowden disclosures the following ground stations presently have, or have had, a role in intercepting transmissions from Satellite and other means of communication:[7]
- RAF Little Sai Wan (Closed) (Hong Kong) Map
- Australian Defence Satellite Communications Station (Geraldton, Western Australia) Map
- RAF Menwith Hill (Yorkshire, England – Largest known ECHELON facility)[47] Map
- Misawa Security Operations Center (Oura, Misawa, Aomori, Tōhoku, Japan) Map
- GCHQ Bude (formerly CSO Morwenstow) (Cornwall, UK)[7] Map
- Pine Gap (Outside Alice Springs, Northern Territory, Australia) Map
- Sugar Grove (Closed) (West Virginia, US) Map
- Yakima Training Center (Closed)[48] (Washington State, US) Map
- Buckley Space Force Base (Aurora, Colorado)[49] Map
- GCSB Waihopai (Marlborough, New Zealand)[50][51] Map
- GCSB Tangimoana (Manawatu-Wanganui, New Zealand)[50] Map
- CFS Leitrim (Ottawa, Ontario, Canada)[52] Map
- Teufelsberg (Closed 1992), *Berlin, Germany[53] – Responsible for listening in to the Eastern Bloc.)[54] Map
- Ayios Nikolaos (British Sovereign Base area of Dhekelia, Cyprus – Cyprus)
- Gibraltar (UK)
- Diego Garcia (UK)
- Bad Aibling Station (Bad Aibling, Germany – US)
- Fort Eisenhower (Georgia, US)
- CFB Gander (Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada)[56][57]
- Guam (Pacific Ocean, US)
- Kunia Regional SIGINT Operations Center (Hawaii, US)
- Lackland Air Force Base, Medina Annex (San Antonio, Texas, US)
- RAF Edzell (Closed 1996) (Scotland)[7]
- RAF Boulmer (England)[7]
- SNICK International Processing Center (Seeb, Oman) Map
History and context

The ability to intercept communications depends on the medium used, be it radio, satellite, microwave, cellular or fiber-optic.[7] During World War II and through the 1950s, high-frequency ("short-wave") radio was widely used for military and diplomatic communication[58] and could be intercepted at great distances.[7] The rise of geostationary communications satellites in the 1960s presented new possibilities for intercepting international communications.[59] In 1964, plans for the establishment of the ECHELON network took off after dozens of countries agreed to establish the International Telecommunications Satellite Organization (Intelsat), which would own and operate a global constellation of communications satellites.[30]

In 1966, the first Intelsat satellite was launched into orbit. From 1970 to 1971, the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) of Britain began to operate a secret signal station at Morwenstow, near Bude in Cornwall, England. The station intercepted satellite communications over the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. Soon afterwards, the US National Security Agency (NSA) built a second signal station at Yakima, near Seattle, for the interception of satellite communications over the Pacific Ocean.[30] In 1981, GCHQ and the NSA started the construction of the first global wide area network (WAN). Soon after Australia, Canada, and New Zealand joined the ECHELON system.[30] The report to the European Parliament of 2001 states: "If UKUSA states operate listening stations in the relevant regions of the earth, in principle they can intercept all telephone, fax, and data traffic transmitted via such satellites."[7]
Most reports on ECHELON focus on satellite interception. Testimony before the European Parliament indicated that separate but similar UKUSA systems are in place to monitor communication through undersea cables, microwave transmissions, and other lines.[60] The report to the European Parliament points out that interception of private communications by foreign intelligence services is not necessarily limited to the US or British foreign intelligence services.[7] The role of satellites in point-to-point voice and data communications has largely been supplanted by fiber optics. In 2006, 99% of the world's long-distance voice and data traffic was carried over optical-fiber.[61] The proportion of international communications accounted for by satellite links is said to have decreased substantially to an amount between 0.4% and 5% in Central Europe.[7] Even in less-developed parts of the world, communications satellites are used largely for point-to-multipoint applications, such as video.[62] Thus, the majority of communications can no longer be intercepted by earth stations; they can only be collected by tapping cables and intercepting line-of-sight microwave signals, which is possible only to a limited extent.[7]
Concerns
British journalist Duncan Campbell and New Zealand journalist Nicky Hager said in the 1990s that the United States was exploiting ECHELON traffic for industrial espionage, rather than military and diplomatic purposes.[60] Examples alleged by the journalists include the gear-less wind turbine technology designed by the German firm Enercon[7][63] and the speech technology developed by the Belgian firm Lernout & Hauspie.[64]
In 2001, the Temporary Committee on the ECHELON Interception System recommended to the European Parliament that citizens of member states routinely use cryptography in their communications to protect their privacy, because economic espionage with ECHELON has been conducted by the US intelligence agencies.[7]
American author James Bamford provides an alternative view, highlighting that legislation prohibits the use of intercepted communications for commercial purposes, although he does not elaborate on how intercepted communications are used as part of an all-source intelligence process.[65]
In its report, the committee of the European Parliament stated categorically that the Echelon network was being used to intercept not only military communications, but also private and business ones. In its epigraph to the report, the parliamentary committee quoted Juvenal, "Sed quis custodiet ipsos custodes." ("But who will watch the watchers").[7] James Bamford, in The Guardian in May 2001, warned that if Echelon were to continue unchecked, it could become a "cyber secret police, without courts, juries, or the right to a defence".[66]
Alleged examples of espionage conducted by the members of the "Five Eyes" include:
- On behalf of the British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher, the Communications Security Establishment allegedly spied on two British cabinet ministers in 1983.[67]
- The US National Security Agency spied on and intercepted the phone calls of Diana, Princess of Wales right up until she died in a Paris car crash with Dodi Fayed in 1997. The NSA currently holds 1,056 pages of classified information about Princess Diana, which has been classified as top secret "because their disclosure could reasonably be expected to cause exceptionally grave damage to the national security ... the damage would be caused not by the information about Diana, but because the documents would disclose 'sources and methods' of US intelligence gathering".[68] An official said that "the references to Diana in intercepted conversations were 'incidental'," and she was never a 'target' of the NSA eavesdropping.[68]
- UK agents monitored the conversations of the 7th Secretary-General of the United Nations, Kofi Annan.[69][70]
- US agents gathered "detailed biometric information" on the 8th Secretary-General of the United Nations, Ban Ki-moon.[71][72]
- In the early 1990s, the US National Security Agency intercepted the communications between the European aerospace company Airbus and the Saudi Arabian national airline. In 1994, Airbus lost a $6 billion contract with Saudi Arabia after the NSA, acting as a whistleblower, reported that Airbus officials had been bribing Saudi officials to secure the contract.[73] As a result, the American aerospace company McDonnell Douglas (now part of Boeing) won the multibillion-dollar contract instead of Airbus.[74]
- The United States defense contractor Raytheon won a US$1.3 billion contract with the Government of Brazil to monitor the Amazon rainforest after the US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), acting as a whistleblower, reported that Raytheon's French competitor Thomson-Alcatel had been paying bribes to get the contract.[75]
- In order to boost the United States position in trade negotiations with the then Japanese Trade Minister Ryutaro Hashimoto, in 1995 the CIA eavesdropped on the conversations between Japanese bureaucrats and executives of car manufacturers Toyota and Nissan.[76]
Workings
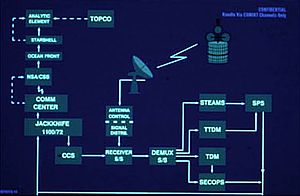
TOPCO = Terminal Operations Control
CCS = Computer Control Subsystem
STEAMS = System Test, Evaluation, Analysis, and Monitoring Subsystem
SPS = Signal Processing Subsystem
TTDM = Teletype Demodulator
The first United States satellite ground station for the ECHELON collection program was built in 1971 at a military firing and training center near Yakima, Washington. The facility, which was codenamed JACKKNIFE, was an investment of ca. 21.3 million dollars and had around 90 people. Satellite traffic was intercepted by a 30-meter single-dish antenna. The station became fully operational on 4 October 1974. It was connected with NSA headquarters at Fort Meade by a 75-baud secure Teletype orderwire channel.[40]
In 1999 the Australian Senate Joint Standing Committee on Treaties was told by Professor Desmond Ball that the Pine Gap facility was used as a ground station for a satellite-based interception network. The satellites were said to be large radio dishes between 20 and 100 meters in diameter in geostationary orbits. The original purpose of the network was to monitor the telemetry from 1970s Soviet weapons, air defence and other radars' capabilities, satellites' ground stations' transmissions and ground-based microwave communications.[78]
Examples of industrial espionage
In 1999, Enercon, a German company and leading manufacturer of wind energy equipment, developed a breakthrough generator for wind turbines. After applying for a US patent, it had learned that Kenetech, an American rival, had submitted an almost identical patent application shortly before. By the statement of a former NSA employee, it was later claimed that the NSA had secretly intercepted and monitored Enercon's data communications and conference calls and passed information regarding the new generator to Kenetech.[79] However, later German media reports contradicted this story, as it was revealed that the American patent in question was actually filed three years before the alleged wiretapping was said to have taken place.[80] As German intelligence services are forbidden from engaging in industrial or economic espionage, German companies have complained that this leaves them defenceless against industrial espionage from the United States or Russia. According to Wolfgang Hoffmann, a former manager at Bayer, German intelligence services know which companies are being targeted by US intelligence agencies, but refuse to inform the companies involved.[81]
See also
Bibliography
- Aldrich, Richard J.; GCHQ: The Uncensored Story of Britain's Most Secret Intelligence Agency, HarperCollins, July 2010. ISBN 978-0-00-727847-3
- Bamford, James; The Puzzle Palace, Penguin, ISBN 0-14-006748-5; 1983
- Bamford, James; The Shadow Factory: The Ultra-Secret NSA from 9/11 to the Eavesdropping on America, Doubleday, ISBN 0-385-52132-4; 2008
- Hager, Nicky; Secret Power: New Zealand's Role in the International Spy Network; Craig Potton Publishing, Nelson, NZ; ISBN 0-908802-35-8; 1996
- Keefe, Patrick Radden Chatter: Dispatches from the Secret World of Global Eavesdropping; Random House Publishing, New York, NY; ISBN 1-4000-6034-6; 2005
- Keefe, Patrick (2006). Chatter : uncovering the echelon surveillance network and the secret world of global eavesdropping. New York: Random House Trade Paperbacks. ISBN 978-0-8129-6827-9.
- Lawner, Kevin J.; Post-Sept. 11th International Surveillance Activity - A Failure of Intelligence: The Echelon Interception System & the Fundamental Right to Privacy in Europe, 14 Pace Int'l L. Rev. 435 (2002)
Notes and references
External links

- Campbell, Duncan (3 August 2015). "GCHQ and Me, My Life Unmasking British Eavesdroppers". The Intercept.
- "Paper 1: Echelon and its role in COMINT". Heise. 27 May 2001.