Eppley Airfield (IATA: OMA, ICAO: KOMA, FAA LID: OMA), also known as Omaha Airport, is an airport in the midwestern United States, located three miles (5 km) northeast of downtown Omaha, Nebraska. On the west bank of the Missouri River in Douglas County, it is the largest airport in Nebraska, with more arrivals and departures than all other airports in the state combined. It is classified as a medium hub airport by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). It is owned and operated by the Omaha Airport Authority (OAA).
Eppley Airfield | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 The OMA logo, styled after the Dance of the Cranes statue situated on the airport grounds | |||||||||||||||||||
 Eppley Airfield in December 2006 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Omaha Airport Authority | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Eastern Nebraska and Western Iowa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | 4501 Abbott DriveOmaha, Nebraska, U.S. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 984 ft / 300 m | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 41°18′00″N 95°53′42″W / 41.30°N 95.895°W | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | flyoma.com | ||||||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||||||
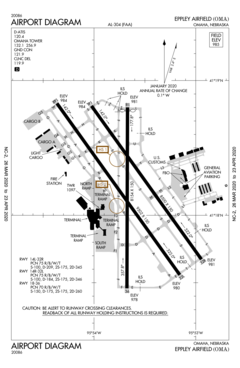 FAA airport diagram | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2023) | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
History
Eppley Airfield began as an extension of Levi Carter Park near East Omaha in 1925. That year, the City of Omaha acquired 200 acres (0.8 km2) of cleared land on the east side of Carter Lake. Almost immediately, planes started landing and taking off there.[4] A lawsuit was launched against the City in 1927 when a group wanted to build a hangar there. The lawsuit failed, and the land was called both the Omaha Municipal Airport and the American Legion Airport.[5]
The April 1957 Official Airline Guide shows 42 scheduled airline departures per day, with 23 by United Airlines and 19 by Braniff International Airways. The airport is named for Eugene C. Eppley, founder of the Eppley Hotel chain, from whose estate $1 million was used to ready the then-Omaha Municipal Airport for jet aircraft in 1959–60.[6] This was matched by the federal government and improvements were made to handle jets at the airport, which was renamed Eppley Airfield in his honor in 1960.[7] The first jets to land in Omaha were United Boeing 720s in August 1960.
The terminal building, opened in 1961, was designed by James C. Buckley, Inc.[8] Concourse B opened in 1970,[9] and was remodeled when Concourse A opened in 1986.[10]
Omaha Airport Authority
Created in 1959, the Omaha Airport Authority is governed by a five member appointed board and is responsible for sole jurisdiction and operation of Eppley Airfield.[11]
Hubs and operations
Midwest Airlines, then known as Midwest Express Airlines, operated a hub at Eppley Airfield from 1995 to 2002 with flights to Milwaukee, Newark, Kansas City, Los Angeles, Orlando, San Diego, and Washington–Reagan; the airport remained a focus city with nonstop flights to Milwaukee and Washington–Reagan until the airline merged with Frontier Airlines in 2009.[12]
During 2017, Southwest Airlines, Delta Air Lines, and United Airlines were the largest carriers and served 33.7, 21.6, and 18.7 percent of passengers, respectively.[2]
The airport has an on-site U.S. Customs and Border Protection facility that handles international, charter, and private flights. Eppley's first commercial, international flight began May 1, 2018, when Air Canada Express launched a daily flight to Toronto Pearson International Airport; this service ended on October 4, 2019.
Expansion
In January 2016, Eppley Airfield completed expansion of its on-site United States Customs and Border Protection facility (CBP) to provide greater customs and inspection services for international passengers. Eppley Airfield is classified as a "Customs Landing Rights Airport" for international flights by U.S. Customs and Border Protection. Scheduled, commercial international service began on May 1, 2018, when Air Canada Express launched a daily flight to Toronto–Pearson. That service ended on October 4, 2019. The airport also handles international cargo, charter, and private flights.
Extensive upgrades are planned for Eppley Airfield in the near future to modernize the terminal, add gates and facilities, and improve the passenger experience. In January 2024, the Omaha Airport Authority announced plans for a $950 million expansion of the terminal, details of which included some upgrades which had been previously announced and on which construction is ongoing or soon to begin. A new passenger drop-off lane, a protective canopy over the passenger pick-up and drop-off area, and improved ADA-compliant accessibility modifications to this area are scheduled to be completed by spring 2025.
Passenger security screening will be consolidated before the entrance to the new terminal so that passengers will not have to exit and go through security again to move between concourses as currently occurs. Councourses A and B will be joined by a long central corridor, expanding the new unified concourse from 375,000 to 646,000 square feet. The gates will be rearranged and two new gates added, for a total of twenty-two gates and the possibility of future expansion. Space for boarding areas at each gate as well as the baggage claim area will be increased, and new retail options and concessions will be added. Two gates will be devoted to international flights in a new Customs and Border Protection international arrivals hall.[13]
Location
The airport is northeast of downtown in east Omaha. Although the airport is in Nebraska on the west side of the Missouri River, it is surrounded on the east, west, and south by Iowa: the Missouri River formed an oxbow west of the land that became Eppley Airfield. The river cut off the oxbow during an 1877 flood, leaving behind Carter Lake on a portion of its former course; the Supreme Court ruled in 1893 that though the land cut off by the river's changed route now lay west of the Missouri, it remained part of Iowa. This land eventually became the city of Carter Lake, Iowa.[14]
Facilities
Eppley Airfield covers 2,650 acres (4.1 sq mi; 10.7 km2) at an elevation of 984 feet (300 m) above sea level. The airfield has three runways: 14R-32L, 14L-32R, and 18-36. On average, seven airlines provide approximately 88 departures per day to 33 nonstop destinations. The airport is also serviced by seven freight companies.[11][15]
Terminals
The South Terminal, including Concourse A, includes gates A1 through A10, baggage claims 1 through 3, and serves Alaska Airlines, Allegiant Air (ticket counter), American Airlines, Delta Air Lines, and Frontier Airlines. Gate assignments: Alaska Airlines (A9), American (A6-A8, A10), Delta (A2-A5), and Frontier (A1).
The North Terminal, including Concourse B, includes gates B11 through B20, baggage claims 4 through 6, and serves Allegiant Air (gate), Southwest Airlines, and United Airlines. Gate assignments: Allegiant Air (B19), Southwest (B16-B18), Sun Country (B15), and United (B11-B14). Gate B20 is unassigned.
Ground transportation
The airport is near four major highways: Interstate 80, Interstate 480, Interstate 680, and Interstate 29.
The airport has a consolidated rental car facility connected to the North Terminal.
Metro Transit Line 16[16] provides limited weekday-only rush-hour service southbound toward downtown and northbound toward the North Omaha Transit Center. Express Arrow intercity buses to Norfolk stop at the terminal.[17] Passenger access is located directly outside the terminal.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
| Passenger destinations map |
|---|
Cargo
Statistics
Top destinations
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  Denver, Colorado Denver, Colorado | 397,590 | Frontier, Southwest, United |
| 2 |  Atlanta, Georgia Atlanta, Georgia | 220,250 | Delta, Southwest |
| 3 |  Chicago–O'Hare, Illinois Chicago–O'Hare, Illinois | 212,350 | American, United |
| 4 |  Chicago–Midway, Illinois Chicago–Midway, Illinois | 177,290 | Southwest |
| 5 |  Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Arizona Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Arizona | 177,170 | American, Southwest |
| 6 |  Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas | 175,250 | American |
| 7 |  Las Vegas, Nevada Las Vegas, Nevada | 134,450 | Allegiant, Frontier, Southwest |
| 8 |  Charlotte, North Carolina Charlotte, North Carolina | 109,290 | American |
| 9 |  Minneapolis/St. Paul, Minnesota Minneapolis/St. Paul, Minnesota | 101,250 | Delta |
| 10 |  St. Louis, Missouri St. Louis, Missouri | 92,370 | Southwest |
| Carrier | Passengers (arriving and departing) |
|---|---|
| Southwest | 1,742,000(36.59%) |
| American | 728,000(15.30%) |
| United | 701,000(14.73%) |
| SkyWest | 513,000(10.79%) |
| Delta | 408,000(8.58%) |
| Other Airlines | 668,000(14.03%) |
Annual traffic
| 2000s | 2010s | 2020s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Passengers | Change | Year | Passengers | Change | Year | Passengers | Change |
| 2000 | 3,814,440 |  1.08% 1.08% | 2010 | 4,287,428 |  1.65% 1.65% | 2020 | 2,140,016 |  57.4% 57.4% |
| 2001 | 3,653,521 |  4.21% 4.21% | 2011 | 4,212,399 |  1.75% 1.75% | 2021 | 3,749,337 |  75.2% 75.2% |
| 2002 | 3,608,231 |  1.23% 1.23% | 2012 | 4,127,344 |  2.02% 2.02% | 2022 | 4,506,713 |  20.2% 20.2% |
| 2003 | 3,667,190 |  1.63% 1.63% | 2013 | 4,042,333 |  2.06% 2.06% | 2023 | 5,026,639 |  11.5% 11.5% |
| 2004 | 3,868,217 |  5.48% 5.48% | 2014 | 4,119,730 |  1.91% 1.91% | |||
| 2005 | 4,193,046 |  8.40% 8.40% | 2015 | 4,169,467 |  1.21% 1.21% | |||
| 2006 | 4,229,856 |  0.88% 0.88% | 2016 | 4,349,486 |  4.32% 4.32% | |||
| 2007 | 4,421,274 |  4.53% 4.53% | 2017 | 4,611,906 |  6.03% 6.03% | |||
| 2008 | 4,370,137 |  1.16% 1.16% | 2018 | 5,043,194 |  9.35% 9.35% | |||
| 2009 | 4,217,718 |  3.49% 3.49% | 2019 | 5,023,668 |  0.39% 0.39% | |||
Accidents and incidents
- On December 6, 1978, a Douglas DC-6 operated by the Mexican Air Force, a military flight bound for San Antonio International Airport, suffered an engine fire on takeoff and crashed into a flood-control levee at the airport boundary half a mile north of Eppley, killing all seven occupants on board. The aircraft had been undergoing maintenance for three days and was reportedly leaking oil from one of its engines as it attempted to take off.[43]
See also
Gallery
- Eppley on June 16, 2011 during the 2011 Missouri River floods
- Eppley Airfield and downtown Omaha
- Omaha Airport Police cruiser
References
External links
- Official website

- Eppley Airport Guide on Omaha.net
- Aviation Photos from airliners.net
- Aviation Photos from jetphotos.net
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective April 18, 2024
- FAA Terminal Procedures for OMA, effective April 18, 2024
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KOMA
- ASN accident history for OMA
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KOMA
- FAA current OMA delay information






