Fluvalinate[1] is a synthetic pyrethroid chemical compound contained as an active agent in the products Apistan,[2] Klartan, and Minadox, that is an acaricide (specifically, a miticide), commonly used to control Varroa mites in honey bee colonies,[citation needed] infestations that constitute a significant disease of such insects.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.233.047 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H22ClF3N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 502.92 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Fluvalinate is a stable, nonvolatile,[3] viscous, heavy oil (technical) soluble in organic solvents.[4] Although the compound may be found in drones, a study has found honey samples virtually absent of fluvalinate, on account of its affinity to beeswax.[5][better source needed]
Stereoisomerism
Fluvalinate is synthesized from racemic valine [(RS)-valine], the synthesis is not diastereoselective. Thus, fluvalinate is a mixture of four stereoisomers, each about 25%.[6]
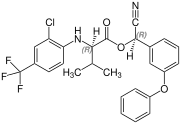 (R,R)-configuration |  (S,S)-configuration |
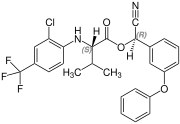 (S,R)-configuration | 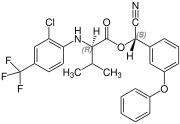 (R,S)-configuration |
Tau-fluvalinate (τ-fluvalinate) is the trivial name for (2R)-fluvalinate. The C atom in the valinate structure is in (R)-absolute configuration, while the second chiral atom is a mixture of (R)- and (S)-configurations:[4]
 (R,R)-configuration |  (R,S)-configuration |
See also
References
Further reading
- Bessin R (2016). "Varroa Mites Infesting Honey Bee Colonies [Insect & Pest Info, Home & Health Pests, ENTFACT-608, April 2016 revision]". North Lexington, KY: University of Kentucky, Department of Entomology. Retrieved 28 August 2016.
Apistan is a product available that will kill the mites and cause the mites to drop from the bees. … Apistan strips, which contain the miticide fluvalinate, are available from most large beekeeping suppliers and can be used both for detection and treatment of varroa infestations.
External links
- EPA: Tau-fluvalinate; Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Low Risk Pesticide; Notice of Availability
- Tau-fluvalinate in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
- Fluvalinate in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)