GNOME Shell is the graphical shell of the GNOME desktop environment starting with version 3,[5] which was released on April 6, 2011. It provides basic functions like launching applications and switching between windows, and is also a widget engine. GNOME Shell replaced GNOME Panel[6] and some ancillary components of GNOME 2.
 GNOME Shell 46 (released in March 2024) | |
| Developer(s) | The GNOME Project |
|---|---|
| Initial release | April 6, 2011 |
| Stable release | 46.1[1] |
| Repository | gitlab |
| Written in | C and JavaScript[2][3] |
| Operating system | BSD, Linux, Unix |
| Available in | 75 languages[4] |
List of languages Afrikaans, Arabic, Aragonese, Assamese, Asturian, Basque, Belarusian, Bengali, Bosnian, Brazilian Portuguese, British English, Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Esperanto, Estonian, Finnish, French, Friulian, Galician, German, Greek, Gujarati, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Icelandic, Indonesian, Interlingua, Irish, Italian, Japanese, Kannada, Kazakh, Khmer, Kirghiz, Korean, Kurdish, Latvian, Lithuanian, Macedonian, Malay, Malayalam, Marathi, Nepali, Norwegian Bokmål, Norwegian Nynorsk, Occitan, Oriya, Persian, Polish, Portuguese, Punjabi, Romanian, Russian, Scottish Gaelic, Serbian, Serbian Latin, Sinhala, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Swedish, Tajik, Tamil, Telugu, Thai, Turkish, Uighur, Ukrainian, Uzbek (Cyrillic), Vietnamese | |
| Type | |
| License | GPL-2.0-or-later |
| Website | wiki |
GNOME Shell is written in C and JavaScript as a plugin for Mutter.
In contrast to the KDE Plasma Workspaces, a software framework intended to facilitate the creation of multiple graphical shells for different devices, the GNOME Shell is intended to be used on desktop computers with large screens operated via keyboard and mouse, as well as portable computers with smaller screens operated via their keyboard, touchpad or touchscreen.
History
The first concepts for GNOME Shell were created during GNOME's User Experience Hackfest 2008 in Boston.[7][8][9]
After criticism of the traditional GNOME desktop and accusations of stagnation and lacking vision,[10] the resulting discussion led to the announcement of GNOME 3.0 in April 2009.[11] Since then Red Hat has been the main driver of GNOME Shell's development.[12]
Pre-release versions of GNOME Shell were first made available in August 2009[13] and became regular, non-default part of GNOME in version 2.28 in September 2009.[14] It was finally shipped as GNOME's default user interface on April 6, 2011.[15][16]
Design
As graphical shell (graphical front-end/graphical shell/UX/UI) of the GNOME desktop environment, its design is guided by the GNOME UX Design Team.[17]
Design components
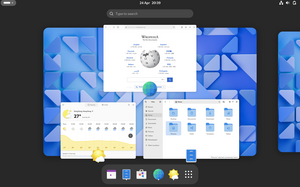
GNOME Shell Overview mode
| ||||||||||||||||
The GNOME Shell comprises the following graphical and functional elements:[18]
- Top bar
- System status area
- Activities Overview
- Dash
- Window picker
- Application picker
- Search
- Notifications and messaging tray
- Application switcher
- Indicators tray (deprecated, waiting on new specification[19])
Software architecture
| GNOME Wiki | |
|---|---|
 Projects/GnomeShell/Technology Projects/GnomeShell/Technology |
GNOME Shell is tightly integrated with Mutter, a compositing window manager and Wayland compositor. It is based upon Clutter to provide visual effects and hardware acceleration.[20] According to GNOME Shell maintainer[21] Owen Taylor, it is set up as a Mutter plugin largely written in JavaScript[22] and uses GUI widgets provided by GTK+ version 3.
Features
Changes to the user interface (UI) include, but are not limited to:
- Clutter and Mutter support multi-touch gestures.[23]
- Support for HiDPI monitors.[24]
- A new Activities overview, which houses:
- A dock (called "Dash") for quickly switching between and launching applications
- A window picker, similar to macOS's Mission Control, also incorporating a workspace switcher/manager
- An application picker
- Search
- "Snapping" windows to screen borders to make them fill up a half of the screen or the whole screen
- A single window button by default, Close, instead of three (configurable). Minimization has been removed due to the lack of a panel to minimize to, in favor of workspace window management. Maximization can be accomplished using the afore-mentioned window snapping, or by double-clicking the window title bar.
- A fallback mode is offered in versions 3.0–3.6 for those without hardware acceleration which offers the GNOME Panel desktop. This mode can also be toggled through the System Settings menu.[25] GNOME 3.8 removed the fallback mode and replaced it with GNOME Shell extensions that offer a more traditional look and feel.[26]
Extensibility
The functionality of GNOME Shell can be changed with extensions, which can be written in JavaScript. Users can find and install extensions using the GNOME extensions website. Some of these extensions are hosted in GNOME's git repository, though they are not official.[27]
Gallery
- GNOME Shell Overlay Mode Windows
- GNOME Shell Overlay Mode Applications in version 3.32
Adoption
- Arch Linux dropped support of GNOME 2 in favor of GNOME 3 in its repositories in April 2011.[28]
- Fedora Linux uses GNOME Shell by default since release 15, May 2011.[29]
- Sabayon Linux uses the latest version of GNOME Shell.
- openSUSE's GNOME edition has used GNOME Shell since version 12.1 in November 2011.[30]
- Mageia 2 and later include GNOME Shell, since May 2012.[31]
- Debian 8 and later features GNOME Shell in the default desktop, since April 2015.[32][33]
- Solaris 11.4 replaced GNOME 2 with GNOME Shell in August 2018.[34][35]
- Ubuntu uses GNOME Shell by default since 17.10, October 2017, after Canonical ceased development of Unity.[36] It has been available for installation in the repositories since version 11.10.[37] An alternative flavor, Ubuntu GNOME, was released alongside Ubuntu 12.10,[38] and gained official flavor status by Ubuntu 13.04.[39]
Reception
GNOME Shell has received mixed reviews: it has been criticized for a variety of reasons, mostly related to design decisions and reduced user control over the environment. For example, users in the free software community have raised concerns that the planned tight integration with Mutter will mean that users of GNOME Shell will not be able to switch to an alternative window manager without breaking their desktop. In particular, users might not be able to use Compiz with GNOME Shell while retaining access to the same types of features that older versions of GNOME allowed.[40]
Reviews have generally become more positive over time, with upcoming releases addressing many of the annoyances reported by users.[41][42]
See also
References
External links





