| Instrument | Uses |
|---|---|
| Bandage | material used to support a medical dressing or injured body part |
| Bedpan | for patients who are unconscious or too weak to sit up or walk to the toilet to defecate |
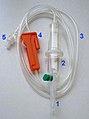
| Cannula | to create a permanent pathway to a vein (or artery) for the purpose of repeated injections or infusion of intravenous fluids |
| Catheter | to drain and collect urine directly from the bladder (primary use) also to act as a makeshift oxygen tube etc. |
| Crocodile forceps | to remove foreign bodies from ear or nasal cavities. |
| Electrocardiograph machine | to record the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time[1] |
| Enema equipment | to inject fluid into the lower bowel for several purposes, most frequently for relieving constipation |
| Endoscope | to look inside the gastrointestinal tract, used mainly in surgery or by surgical consultants |
| External cardioverter / Defibrillator | to correct arrhythmias of the heart[2] |
| Gas cylinder | as a supply of oxygen, nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide, etc. |
| Gauze sponge | to absorb blood and other fluids as well as clean wounds |
| Glucose monitor | to measure concentration of glucose in blood |
| Haemodialysis machine | to remove toxic materials from the blood that are generally removed by the kidneys; used in case of kidney failure[3] |
| Hypodermic needle / Syringe | for injections and aspiration of blood or fluid from the body |
| Infection control equipment | as in gloves, gowns, bonnets, shoe covers, face shields, goggles, and surgical masks for preventing nosocomial or healthcare-associated infection |
| Instrument sterilizer | to sterilize instruments in absence of an autoclave |
| Kidney dish | as a tray for instruments, gauze, tissue, etc. |
| Measuring tape | for length, height, head circumference and girth measurements |
| Medical halogen penlight | to see into the eye, natural orifices, etc. and to test for pupillary light reflex, etc. |
| Medical ultrasound | to create an image of internal body structures |
| Nasogastric tube | for nasogastric suction or the introduction of food or drugs into the body |
| Nebulizer | to produce aerosols of drugs to be administered by respiratory route |
| Ophthalmoscope | to look at the retina |
| Otoscope | to look into the external ear cavity |
| Oxygen mask and tubes | to deliver gases to the mouth/nostrils to assist in oxygen intake or to administer aerosolized or gaseous drugs |
| Pipette or dropper | to measure out doses of liquid, specially in children |
| Proctoscope | to look inside the anal canal and lower part of the rectum |
| Radiography | to view internal body structures |
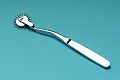
| Reflex hammer | to test motor reflexes of the body |
| Sphygmomanometer | to measure the patient's blood pressure |
| Stethoscope | to hear sounds from movements within the body like heart beats, intestinal movement, breath sounds, etc. |
| Suction device | to suck up blood or secretions |
| Surgical scissors | used for dissecting or cutting |
| Thermometer | to record body temperature |
| Tongue depressor | for use in oral examination |
| Transfusion kit | to transfuse blood and blood products |
| Tuning fork | to test for deafness and to categorize it |
| Ventilator | to assist or carry out the mechanical act of inspiration and expiration so the non-respiring patient can do so; a common component of "life support" |
| Wartenberg wheel | for neurological use |
| Watch / Stopwatch | for recording rates like heart rate, respiratory rate, etc.; for certain hearing tests. |
| Weighing scale | to measure weight |
Image gallery
- Bandage
- Bedpan
- Blood infusion set
- Cannula, intraveneous (separated)
- Catheter, Foley
- Defibrillator
- Dialyser, hemodialysis
- Enema bag and enema bucket
- Enema bulb
- Enema set
- Endoscope
- Face shield
- Gas cylinder, oxygen
- Gauze sponges
- Instrument sterilizer
- Kidney dish
- Medical halogen penlight
- Nasogastric tube, Levin
- Nebulizer
- Ophthalmoscope
- Reflex hammer
- Reflex hammer, queen square
- Sphygmomanometer, electronic
- Stethoscope
- Syringe and needle
- Thermometers, mercury
- Tongue depressors
- Tuning fork
- Ventilator, high-frequency
- Weighing scale
- Wartenberg wheel
Notes
References
- Khandpur, RS (2020). Compendium of Biomedical Instrumentation. United Kingdom: Wiley. ISBN 9781119288121. Retrieved 19 February 2024.
🔥 Top keywords: Main PageSpecial:SearchIndian Premier LeagueWikipedia:Featured picturesPornhubUEFA Champions League2024 Indian Premier LeagueFallout (American TV series)Jontay PorterXXXTentacionAmar Singh ChamkilaFallout (series)Cloud seedingReal Madrid CFCleopatraRama NavamiRichard GaddDeaths in 2024Civil War (film)Shōgun (2024 miniseries)2024 Indian general electionJennifer PanO. J. SimpsonElla PurnellBaby ReindeerCaitlin ClarkLaverne CoxXXX (film series)Facebook2023–24 UEFA Champions LeagueYouTubeCandidates Tournament 2024InstagramList of European Cup and UEFA Champions League finalsJude BellinghamMichael Porter Jr.Andriy LuninCarlo AncelottiBade Miyan Chote Miyan (2024 film)