The U.S. state of Washington has 39 counties. The Provisional Government of Oregon established Vancouver and Lewis Counties in 1845 in unorganized Oregon Country, extending from the Columbia River north to 54°40′ north latitude. After the region was organized within the Oregon Territory with the current northern border of 49° north, Vancouver County was renamed Clark, and six more counties were created out of Lewis County before the organization of Washington Territory in 1853; 28 were formed during Washington's territorial period, two of which only existed briefly. The final five were established in the 22 years after Washington was admitted to the Union as the 42nd state in 1889.[1][2]
| Counties of Washington | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | State of Washington |
| Number | 39 |
| Populations | 2,363 (Garfield) – 2,271,380 (King) |
| Areas | 175 square miles (450 km2) (San Juan) – 5,268 square miles (13,640 km2) (Okanogan) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions |
|
Article XI of the Washington State Constitution addresses the organization of counties. New counties must have a population of at least 2,000 and no county can be reduced to a population below 4,000 due to partitioning to create a new county.[3] To alter the area of a county, the state constitution requires a petition of the "majority of the voters" in that area. A number of county partition proposals in the 1990s interpreted this as a majority of people who voted, until a 1998 ruling by the Washington Supreme Court clarified that they would need a majority of registered voters.[4] No changes to counties have been made since the formation of Pend Oreille County in 1911, except when the small area of Cliffdell was moved from Kittitas to Yakima County in 1970.[5]
King County, home to the state's largest city, Seattle, holds almost 30 percent of Washington's population (2,271,380 residents of 7,812,880 in 2023), and has the highest population density, with more than 1,000 people per square mile (400/km2). Garfield County is both the least populated (2,363) and least densely populated (3.3/sq mi [1.3/km2]). Two counties, San Juan and Island, are composed only of islands. The average county is 1,830 square miles (4,700 km2), with 200,330 people.
Seventeen counties have Native American–derived names, including nine names of tribes whose land settlers would occupy. Another seventeen were named for political figures, only five of whom had lived in the region. The last five are named for geographic places.[6]
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) code, used by the United States government to uniquely identify counties, is provided with each entry. The FIPS code links in the table point to U.S. Census data pages for each county. Washington's FIPS state code is 53.
Governance

Counties provide a broad scope of services, including court operation, parks and recreation, libraries, arts, social services, elections, waste collection, roads and transportation, zoning and permitting, as well as taxation.[7][8] The extent of these vary, and some are administered by municipalities. Counties are not subdivided into minor civil divisions like townships; sub-county local government is only by incorporated cities and towns, as well as by 29 Indian reservations, while unincorporated areas are governed only by the county. There are 242 census county divisions for statistical purposes only.[9]
The default form of county government is the non-charter commission, with three to five elected commissioners serving as both the legislature and executive. Seven counties have adopted charters providing for home rule distinct from state law: King, Clallam, Whatcom, Snohomish, Pierce, San Juan, and Clark. Of these, King, Whatcom, Snohomish, and Pierce, four major counties on Puget Sound, elect a county executive. Councils in the other three charter counties appoint a manager to administer the government.[10] Voters may also elect a clerk, treasurer, sheriff, assessor, coroner, auditor (or recorder), and prosecuting attorney. Elections are nonpartisan in non-charter counties, but charter counties may choose to make some positions partisan, though all elections are by top-two primary.[10]
List of counties
| County | FIPS code | County seat[11] | Est.[11][12] | Formed from[12][13] | Etymology | Population (2023)[14] | Land area[11] | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adams County | 001 | Ritzville | 1883 | Whitman County | John Adams (1735–1826), 2nd U.S. President[15] | 20,820 | 1,925 sq mi (4,986 km2) |  |
| Asotin County | 003 | Asotin | 1883 | Garfield County | The Nez Percé name for Eel Creek[16] | 22,549 | 636 sq mi (1,647 km2) |  |
| Benton County | 005 | Prosser | 1905 | Yakima and Klickitat Counties | Thomas Hart Benton (1782–1858), a U.S. Senator from Missouri[17] | 215,219 | 1,700 sq mi (4,403 km2) |  |
| Chelan County | 007 | Wenatchee | 1899 | Okanogan and Kittitas Counties | A Native American word meaning "deep water", referring to Lake Chelan[18] | 79,997 | 2,920 sq mi (7,563 km2) |  |
| Clallam County | 009 | Port Angeles | 1854 | Jefferson County | A Klallam word meaning "brave people" or "the strong people"[19] | 77,616 | 1,738 sq mi (4,501 km2) |  |
| Clark County | 011 | Vancouver | 1845 | Original County | William Clark (1770–1838), the co-captain of the Lewis and Clark Expedition[19] | 521,150 | 629 sq mi (1,629 km2) |  |
| Columbia County | 013 | Dayton | 1875 | Walla Walla County | The Columbia River[19] | 4,053 | 869 sq mi (2,251 km2) | 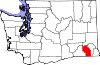 |
| Cowlitz County | 015 | Kelso | 1854 | Lewis County | Cowlitz, an Indian tribe[20] | 112,864 | 1,139 sq mi (2,950 km2) |  |
| Douglas County | 017 | Waterville | 1883 | Lincoln County | Stephen A. Douglas (1813–1861), U.S. Senator from Illinois[21] | 44,798 | 1,819 sq mi (4,711 km2) | 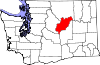 |
| Ferry County | 019 | Republic | 1899 | Stevens County | Elisha P. Ferry (1825–1895), 1st Governor of Washington[22] | 7,497 | 2,204 sq mi (5,708 km2) |  |
| Franklin County | 021 | Pasco | 1883 | Whitman County | Benjamin Franklin (1706–1790), writer, orator, inventor, and U.S. Founding Father[23] | 99,034 | 1,242 sq mi (3,217 km2) |  |
| Garfield County | 023 | Pomeroy | 1881 | Columbia County | James A. Garfield (1831–1881), 20th U.S. President[23] | 2,363 | 710 sq mi (1,839 km2) |  |
| Grant County | 025 | Ephrata | 1909 | Douglas County | Ulysses S. Grant (1822–1885), 18th U.S. President[24] | 102,678 | 2,680 sq mi (6,941 km2) |  |
| Grays Harbor County | 027 | Montesano | 1854 | Thurston County | Grays Harbor, a body of water named after explorer and merchant Robert Gray (1755–1806)[24] | 77,290 | 1,902 sq mi (4,926 km2) |  |
| Island County | 029 | Coupeville | 1852 | Thurston County | Consists solely of islands, including Whidbey and Camano islands[25] | 86,267 | 209 sq mi (541 km2) |  |
| Jefferson County | 031 | Port Townsend | 1852 | Thurston County | Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), 3rd U.S. President and principal author of the Declaration of Independence[25] | 33,714 | 1,804 sq mi (4,672 km2) |  |
| King County | 033 | Seattle | 1852 | Thurston County | William R. King (1786–1853), U.S. Vice President under Franklin Pierce; officially renamed in 2005 after civil rights leader Martin Luther King Jr. (no relation) (1929–1968)[26] | 2,271,380 | 2,115 sq mi (5,478 km2) |  |
| Kitsap County | 035 | Port Orchard | 1857 | King and Jefferson Counties | Chief Kitsap (d. 1860), leader of the Suquamish tribe[27] | 277,658 | 395 sq mi (1,023 km2) |  |
| Kittitas County | 037 | Ellensburg | 1883 | Yakima County | Yakama word of uncertain meaning, with popular translations ranging from "white chalk" to "land of the plenty"[27] | 45,508 | 2,297 sq mi (5,949 km2) |  |
| Klickitat County | 039 | Goldendale | 1859 | Walla Walla County | Klickitat tribe, also meaning "robber" and "beyond"[27] | 23,589 | 1,872 sq mi (4,848 km2) | 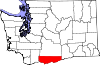 |
| Lewis County | 041 | Chehalis | 1845 | Clark County | Meriwether Lewis (1774–1809), the co-captain of the Lewis and Clark Expedition[28] | 86,154 | 2,403 sq mi (6,224 km2) |  |
| Lincoln County | 043 | Davenport | 1883 | Whitman County | Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), 16th U.S. President[28] | 11,738 | 2,311 sq mi (5,985 km2) |  |
| Mason County | 045 | Shelton | 1854 | King County | Charles H. Mason (1830–1859), 1st Secretary of Washington Territory[29] | 68,389 | 959 sq mi (2,484 km2) |  |
| Okanogan County | 047 | Okanogan | 1888 | Stevens County | A Salish word meaning "rendezvous"[30] | 43,712 | 5,268 sq mi (13,644 km2) | 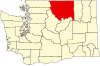 |
| Pacific County | 049 | South Bend | 1851 | Lewis County | The Pacific Ocean[31] | 24,200 | 933 sq mi (2,416 km2) | 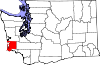 |
| Pend Oreille County | 051 | Newport | 1911 | Stevens County | The Pend d'Oreille tribe, named by French traders for their "ear bobs"[32] | 14,361 | 1,400 sq mi (3,626 km2) |  |
| Pierce County | 053 | Tacoma | 1852 | Thurston County | Franklin Pierce (1804–1869), 14th U.S. President[32] | 928,696 | 1,670 sq mi (4,325 km2) |  |
| San Juan County | 055 | Friday Harbor | 1873 | Whatcom County | San Juan Islands, itself derived from Juan Vicente de Güemes[33] | 18,566 | 174 sq mi (451 km2) |  |
| Skagit County | 057 | Mount Vernon | 1883 | Whatcom County | The Skagit tribe[34] | 131,417 | 1,731 sq mi (4,483 km2) |  |
| Skamania County | 059 | Stevenson | 1854 | Clark County | A Chinookan word meaning "swift water"[34] | 12,640 | 1,656 sq mi (4,289 km2) |  |
| Snohomish County | 061 | Everett | 1861 | Island and King Counties | The Snohomish tribe, word origin disputed[35] | 844,761 | 2,087 sq mi (5,405 km2) | 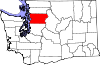 |
| Spokane County | 063 | Spokane | 1879 | Stevens County | The Spokane tribe | 551,455 | 1,764 sq mi (4,569 km2) |  |
| Stevens County | 065 | Colville | 1863 | Walla Walla County | Isaac Stevens (1818–1862), 1st Governor of the Washington Territory[36] | 48,837 | 2,478 sq mi (6,418 km2) |  |
| Thurston County | 067 | Olympia | 1852 | Lewis County | Samuel Thurston (1815–1851), the Oregon Territory's first delegate to U.S. Congress[37] | 299,003 | 722 sq mi (1,870 km2) |  |
| Wahkiakum County | 069 | Cathlamet | 1854 | Cowlitz County | Wakaiakam, chief of the Kathlamet tribe[38] | 4,765 | 264 sq mi (684 km2) |  |
| Walla Walla County | 071 | Walla Walla | 1854 | Skamania County | The Walla Walla tribe, also a Nez Percé name for running water[38] | 61,568 | 1,270 sq mi (3,289 km2) |  |
| Whatcom County | 073 | Bellingham | 1854 | Island County | Whatcom, chief of the Nooksack tribe and named for a Nooksack word meaning "noisy water"[39] | 231,919 | 2,107 sq mi (5,457 km2) |  |
| Whitman County | 075 | Colfax | 1871 | Stevens County | Marcus Whitman (1802–1847), a Methodist missionary[40] | 48,012 | 2,159 sq mi (5,592 km2) | 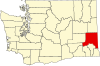 |
| Yakima County | 077 | Yakima | 1865 | Ferguson County (defunct) | The Yakama tribe, meaning "runaway [waters]" or "big belly"[41] | 256,643 | 4,296 sq mi (11,127 km2) |  |
Former county names
Four counties changed their name between 1849 and 1925.
- Chehalis County, originally named for the Chehalis people, was renamed Grays Harbor County in 1915.[42][43]
- Sawamish County, originally named for the Sahewamish Native American tribe, was renamed Mason County in 1864.[44]
- Slaughter County, originally named for Lieutenant William A. Slaughter who was killed during the Indian Wars, was renamed Kitsap County shortly after its formation in 1857.[45] The initial proposals for this county called it Madison County or Kitsap County.[46]
- Vancouver County, originally named for George Vancouver, was renamed Clarke County in 1849[47][48] and corrected to Clark in 1925.[49]
Former counties
During Washington's territorial period, Washington split off from an Oregon county, three counties were disestablished, and three split into separate territories.
- Clackamas County, Oregon was established in 1844 and included the land south and east of the Columbia River until Washington Territory was formed in 1853, when the area was no longer organized as a county.[50]
- Spokane County was established in Washington Territory in 1858 until it merged into Stevens County in 1864; it was reestablished in 1879.[51]
- Missoula County was established in Washington Territory in 1860 until it split off with the Idaho Territory in 1863.[51]
- Shoshone County, Idaho County, and Nez Perce County were established in Washington Territory in 1861, and Boise County in 1863, until they split off into the Idaho Territory in March 1863, leaving the current borders of Washington.[51]
- Ferguson County, named for Washington legislator James L. Ferguson, was established on January 23, 1863, from Walla Walla County and dissolved on January 18, 1865. Yakima County was established in its place.[52][53]
- Quillehuyte County was split from Jefferson and Clallam counties in 1868 and returned to those counties a year later before it could be organized.[54]
Proposed counties
Several counties were proposed prior to or during the existence of Washington Territory and nine counties were proposed within the first 16 years of Washington's statehood, but none were established.
- The representatives at the Cowlitz Convention of 1851 discussed a proposal to form Columbia Territory, which included a number of new counties in what later became Washington. The next session of the Oregon Territorial Legislature created only one of these counties: Thurston County (which was originally proposed as Simmons County).[55][56]
- Buchanan County was proposed in 1856 as a division of Clark County.[57]
- Proposed counties during Washington's early statehood included Big Bend (1891), Palouse (1891 and 1903), Sherman (1891), Washington (1891), Wenatchee (1893), McKinley (1903), Steptoe (1903), and Coulee (1905).[6]
- Since the 1990s, there have been several proposals for county secession in Washington, largely from rural areas in the major counties of Western Washington. Cedar, Freedom, and Skykomish counties submitted petitions to secede from King and Snohomish counties in 1995 and 1996, with some support in the state legislature to put them to a public referendum.[4][58][59]
See also
References
Works
- Holman, Frederick V. (March 1910). "History of the Counties of Oregon". Oregon Historical Quarterly. XI (1). Portland, Oregon: Ivy Press.
- Meany, Edmond S. (January 1922). "The Cowlitz Convention: Inception of Washington Territory". The Washington Historical Quarterly. XIII (1). Seattle, Washington: University of Washington.
- Phillips, James W. (1971). Washington State Place Names. University of Washington Press. ISBN 0-295-95158-3. OCLC 1052713900 – via The Internet Archive.
- Smith, Charles W. (October 1913) [1909]. "The Naming of Counties in the State of Washington". Seattle: University of Washington. OCLC 8676092.
External links
- Washington State Association of Counties
- Washington County Profiles – Municipal Research and Services Center of Washington
- County officials – Washington Association of County Officials
- National Association of Counties – Find A County