Lemuroidea is a superfamily of primates. Members of this superfamily are called lemuroids, or lemurs. Lemuroidea is one of two superfamilies that form the suborder Strepsirrhini, itself one of two suborders in the order Primates. They are found exclusively on the island of Madagascar, primarily in forests but with some species also in savannas, shrublands, or wetlands. They range in size from the Margot Marsh's mouse lemur, at 8 cm (3 in) plus a 11 cm (4 in) tail, to the indri, at 90 cm (35 in) plus a 6 cm (2 in) tail. Lemuroids primarily eat fruit, leaves, and insects. Most lemuroids do not have population estimates, but the ones that do range from 40 mature individuals to 5,000. Most lemuroid species are at risk of extinction, with 45 species categorized as endangered, and a further 32 species categorized as critically endangered.

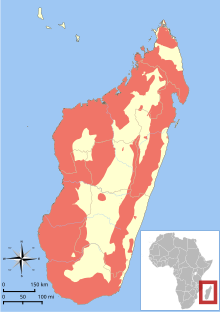
The 107 extant species of Lemuroidea are divided into five families. Cheirogaleidae contains 41 dwarf, mouse, and fork-marked lemur species in five genera. Daubentoniidae contains a single species, the aye-aye. Indriidae contains nineteen woolly lemur and sifaka species in three genera. Lemuridae contains 21 ruffed, ring-tailed, bamboo, and other lemur species in five genera. Lepilemuridae contains 25 sportive lemur species in a single genus.
Dozens of extinct prehistoric lemuroid species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.[1] At least 17 species and eight genera are believed to have become extinct in the 2,000 years since humans first arrived in Madagascar.[2][3] All known extinct species were large, ranging in weight from 10 to 200 kg (22 to 441 lb). The largest known subfossil lemur was Archaeoindris fontoynonti, a giant sloth lemur, which weighed more than a modern female gorilla. The extinction of the largest lemurs is often attributed to predation by humans and possibly habitat destruction.[2] Since all extinct lemurs were not only large (and thus ideal prey species), but also slow-moving (and thus more vulnerable to human predation), their presumably slow-reproducing and low-density populations were least likely to survive the introduction of humans.[2] Gradual changes in climate have also been blamed, and may have played a minor role; however since the largest lemurs also survived the climatic changes from previous ice ages and only disappeared following the arrival of humans, it is unlikely that climatic change was largely responsible.[2]
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (32 species) |
| EN | Endangered (45 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (24 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (1 species) |
| LC | Least concern (2 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (3 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (0 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the lemuroid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted.
Classification
The superfamily Lemuroidea consists of five extant families: Cheirogaleidae, Daubentoniidae, Indriidae, Lemuridae, and Lepilemuridae. Cheirogaleidae contains 41 species in five genera. Daubentoniidae contains a single species. Indriidae contains nineteen species in three genera. Lemuridae contains 21 species in five genera. Lepilemuridae contains 25 lemur species in a single genus. There are additionally three families which went extinct prior to modern record-keeping: Archaeolemuridae, Megaladapidae, and Palaeopropithecidae, as well as an extinct genus in Lemuridae.
Family Archaeolemuridae† (monkey lemurs)
- Genus Archaeolemur†: two extinct species
- Genus Hadropithecus†: one extinct species
Family Cheirogaleidae
- Genus Allocebus (hairy-eared dwarf lemur): one species
- Genus Cheirogaleus (dwarf lemurs): ten species
- Genus Microcebus (mouse lemurs): twenty-four species
- Genus Mirza (giant mouse lemurs): two species
- Genus Phaner (fork-marked lemurs): four species
Family Daubentoniidae
- Genus Daubentonia (aye-aye): one species
Family Indriidae
- Genus Avahi (woolly lemurs): nine species
- Genus Indri (indri): one species
- Genus Propithecus (sifakas): nine species
Family Lemuridae
- Genus Eulemur (true lemurs): twelve species
- Genus Hapalemur (bamboo lemurs): five species
- Genus Lemur (ring-tailed lemur): one species
- Genus Pachylemur†: two extinct species
- Genus Prolemur (greater bamboo lemur): one species
- Genus Varecia (ruffed lemurs): two species
Family Lepilemuridae
- Genus Lepilemur (sportive lemurs): twenty-five species
Family Megaladapidae† (koala lemurs)
- Genus: Megaladapis†
Family Palaeopropithecidae† (sloth lemurs)
- Genus: Archaeoindris†: one extinct species
- Genus: Babakotia†: one extinct species
- Genus: Mesopropithecus†: three extinct species
- Genus: Palaeopropithecus†: three extinct species
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| There are two competing lemur phylogenies, one by Horvath et al. (top)[4] and one by Orlando et al. (bottom).[5] |
Lemuroids
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by the reference work Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis, as supported by both the IUCN and the American Society of Mammalogists.[6]
Family Cheirogaleidae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hairy-eared dwarf lemur | A. trichotis (Günther, 1875) | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: 12–15 cm (5–6 in) long, plus about 17 cm (7 in) tail[7] Habitat: Forest[8] Diet: Nectar, fruit, gum, leaves, honey, and insects[8] | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankarana dwarf lemur | C. shethi Frasier et al., 2016 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 16–18 cm (6–7 in) long, plus about 18 cm (7 in) tail[9] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[10] Diet: Fruit[10] | EN
|
| Fat-tailed dwarf lemur | C. medius Geoffroy, 1812 | Southern, western, and northern Madagascar | Size: 20–23 cm (8–9 in) long, plus 20–27 cm (8–11 in) tail[11] Habitat: Forest[12] Diet: Fruit, as well as flowers, seeds, nectar, insects, and small vertebrates[11] | VU
|
| Furry-eared dwarf lemur | C. crossleyi Grandidier, 1870 | Scattered eastern Madagascar | Size: 22–26 cm (9–10 in) long, plus 21–27 cm (8–11 in) tail[13] Habitat: Forest[14] Diet: Nectar, fruit, leaves, and insects[13] | VU
|
| Greater dwarf lemur | C. major Geoffroy, 1812 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: 16–27 cm (6–11 in) long, plus 19–31 cm (7–12 in) tail[15] Habitat: Forest[16] Diet: Fruit, flowers, and nectar, as well as insects small vertebrates, and honey[15] | VU
|
| Groves' dwarf lemur | C. grovesi McLain et al., 2017 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: 16–24 cm (6–9 in) long, plus 27–31 cm (11–12 in) tail[17] Habitat: Forest[18] Diet: | DD
|
| Lavasoa dwarf lemur | C. lavasoensis Thiele, Razafimahatratra, & Hapke, 2013 | Southern Madagascar | Size: 50–55 cm (20–22 in) long, including tail[19] Habitat: Forest[20] Diet: | EN
|
| Lesser iron-gray dwarf lemur | C. minusculus Groves, 2000 | Central Madagascar | Size: Unknown[21] Habitat: Forest[22] Diet: Unknown[21] | DD
|
| Montagne d'Ambre dwarf lemur | C. andysabini Lei et al., 2015 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 16–18 cm (6–7 in) long, plus 26–27 cm (10–11 in) tail[23] Habitat: Forest[24] Diet: | EN
|
| Sibree's dwarf lemur | C. sibreei Forsyth Major, 1896 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: Unknown[25] Habitat: Forest[26] Diet: Unknown[25] | CR
|
| Thomas' dwarf lemur | C. thomasi (Forsyth Major, 1894) | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: Unknown Habitat: Forest[27] Diet: Fruit and flowers[27] | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anosy mouse lemur | M. tanosi Rasoloarison, Weisrock, Yoder, Rakotondravony, & Kappeler, 2013 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: 10–16 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 11–15 cm (4–6 in) tail[28] Habitat: Forest[29] Diet: Fruit and insects[29] | EN
|
| Arnhold's mouse lemur | M. arnholdi Louis et al., 2008 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 9–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 10–14 cm (4–6 in) tail[30] Habitat: Forest[31] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | VU
|
| Bemanasy mouse lemur | M. manitatra Hotaling et al., 2016 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: 12–13 cm (5 in) long, plus about 15 cm (6 in) tail Habitat: Forest[33] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | CR
|
| Bongolava mouse lemur | M. bongolavensis Olivieri et al., 2007 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 11–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 14–17 cm (6–7 in) tail[34] Habitat: Forest[35] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | EN
|
| Brown mouse lemur | M. rufus Geoffroy, 1834 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: About 13 cm (5 in) long, plus about 12 cm (5 in) tail[36] Habitat: Forest[37] Diet: Fruit, as well as insects, leaves, flowers, gum, nectar, and pollen[36] | VU
|
| Claire's mouse lemur | M. mamiratra Andriantompohavana et al., 2006 | Northern Madagascar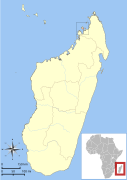 | Size: 11–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 14–17 cm (6–7 in) tail[38] Habitat: Forest[39] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | EN
|
| Danfoss's mouse lemur | M. danfossi Olivieri et al., 2007 | Northern Madagascar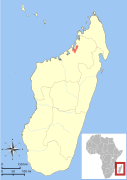 | Size: 10–12 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 15–17 cm (6–7 in) tail[40] Habitat: Forest[41] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | VU
|
| Ganzhorn's mouse lemur | M. ganzhorni Hotaling et al., 2016 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: Habitat: Forest[42] Diet: Fruit and insects[42] | EN
|
| Gerp's mouse lemur | M. gerpi Radespiel et al., 2012 | Eastern Madagascar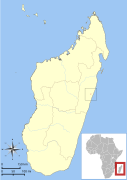 | Size: 9–10 cm (4 in) long, plus about 15 cm (6 in) tail[43] Habitat: Forest[44] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | CR
|
| Golden-brown mouse lemur | M. ravelobensis Zimmermann, Cepok, Rakotoarison, Zietemann, & Radespiel, 1998 | Northern Madagascar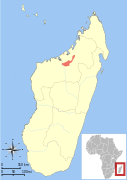 | Size: 12–14 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 14–18 cm (6–7 in) tail[45] Habitat: Forest[46] Diet: Gum, insect excretions, nectar, fruit, leaves, and animal matter[46] | VU
|
| Goodman's mouse lemur | M. lehilahytsara Roos & Kappeler, 2005 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: 9–10 cm (4 in) long, plus 11–12 cm (4–5 in) tail[47] Habitat: Forest[48] Diet: Fruit and insects[48] | NT
|
| Gray mouse lemur | M. murinus (J. F. Miller, 1777) | Western and southern Madagascar | Size: 12–14 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 13–15 cm (5–6 in) tail[49] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[50] Diet: Insects, as well as small reptiles, plants, leaves, fruit, and flowers[49] | LC
|
| Jolly's mouse lemur | M. jollyae Louis et al., 2006 | Eastern Madagascar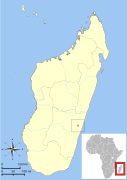 | Size: 9–10 cm (4 in) long, plus 12–13 cm (5 in) tail[51] Habitat: Forest[52] Diet: Fruit[52] | EN
|
| MacArthur's mouse lemur | M. macarthurii Radespiel et al., 2008 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 11–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 13–15 cm (5–6 in) tail[53] Habitat: Forest[54] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | EN
|
| Madame Berthe's mouse lemur | M. berthae Rasoloarison, Goodman, & Ganzhorn, 2000 | Western Madagascar | Size: 9–11 cm (4 in) long, plus 12–14 cm (5–6 in) tail[55] Habitat: Forest[56] Diet: Honeydew, as well as gum, flowers, fruit, arthropods, and small vertebrates[55] | CR
|
| Margot Marsh's mouse lemur | M. margotmarshae Andriantompohavana et al., 2006 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 8–13 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 11–16 cm (4–6 in) tail[30] Habitat: Forest[57] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | EN
|
| Marohita mouse lemur | M. marohita Rasoloarison, Weisrock, Yoder, Rakotondravony, & Kappeler, 2013 | Eastern Madagascar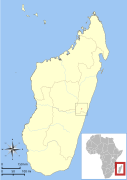 | Size: 13–15 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 13–15 cm (5–6 in) tail[28] Habitat: Forest[58] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | CR
|
| Jonah's mouse lemur | M. jonahi Schüssler et al., 2020 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: 12–14 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 12–14 cm (5–6 in) tail[53] Habitat: Forest[59] Diet: Fruit and insects[59] | EN
|
| Northern rufous mouse lemur | M. tavaratra (Rasoloarison, Goodman, & Ganzhorn, 2000) | Northern Madagascar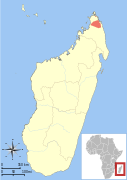 | Size: 11–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 14–17 cm (6–7 in) tail[60] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[61] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | VU
|
| Nosy Boraha mouse lemur | M. boraha Hotaling et al., 2016 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: Habitat: Unknown[62] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | DD
|
| Pygmy mouse lemur | M. myoxinus Peters, 1852 | Western Madagascar | Size: 12–13 cm (5 in) long, plus 24–26 cm (9–10 in) tail[63] Habitat: Forest[64] Diet: Fruit, as well as flowers, gums, and insects[63] | VU
|
| Reddish-gray mouse lemur | M. griseorufus Kollman, 1910 | Southern Madagascar | Size: 11–14 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 13–16 cm (5–6 in) tail[47] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[65] Diet: Fruit and gum, as well as flowers and arthropods[65] | LC
|
| Sambirano mouse lemur | M. sambiranensis Rasoloarison et al., 2000 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 11–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 13–15 cm (5–6 in) tail[66] Habitat: Forest[67] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | EN
|
| Simmons' mouse lemur | M. simmonsi Louis et al., 2006 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: 9–10 cm (4 in) long, plus 14–15 cm (6 in) tail[68] Habitat: Forest[69] Diet: Insect secretions, arthropods, small vertebrates, fruit, and flowers[32] | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coquerel's giant mouse lemur | M. coquereli Grandidier, 1867 | Western Madagascar | Size: 23–27 cm (9–11 in) long, plus 31–32 cm (12–13 in) tail[70] Habitat: Forest[71] Diet: Fruit, flowers, and invertebrates, as well as small vertebrates[70] | EN
|
| Northern giant mouse lemur | M. zaza Kappeler & Roos, 2005 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 23–25 cm (9–10 in) long, plus 26–29 cm (10–11 in) tail[72] Habitat: Forest[73] Diet: Fruit, insect secretions, and sap[73] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amber Mountain fork-marked lemur | P. electromontis Groves & Tattersall, 1991 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 22–29 cm (9–11 in) long, plus 28–37 cm (11–15 in) tail[74] Habitat: Forest[75] Diet: | EN
|
| Masoala fork-marked lemur | P. furcifer Blainville, 1839 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: 22–29 cm (9–11 in) long, plus 28–37 cm (11–15 in) tail[76] Habitat: Forest[77] Diet: Gum, as well as insects[76] | EN
|
| Pale fork-marked lemur | P. pallescens Groves & Tattersall, 1991 | Western Madagascar | Size: 23–29 cm (9–11 in) long, plus 29–37 cm (11–15 in) tail[78] Habitat: Forest[79] Diet: Sap and gum, as well as insects, insect secretions, fruit, flowers, and nectar[79] | EN
|
| Pariente's fork-marked lemur | P. parienti Groves & Tattersall, 1991 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 22–29 cm (9–11 in) long, plus 28–37 cm (11–15 in) tail[74] Habitat: Forest[80] Diet: Gum[80] | EN
|
Family Daubentoniidae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aye-aye | D. madagascariensis Gmelin, 1788 | Western and eastern Madagascar | Size: 36–44 cm (14–17 in) long, plus tail[81] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[82] Diet: Fruit, nuts, and sap[81] | EN
|
Family Indriidae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bemaraha woolly lemur | A. cleesei Thalmann & Geissmann, 2005 | Western Madagascar | Size: 26–37 cm (10–15 in) long, plus 29–35 cm (11–14 in) tail[83] Habitat: Forest[84] Diet: Buds and leaves[85] | CR
|
| Betsileo woolly lemur | A. betsileo Andriantompohavana et al., 2007 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: 25–34 cm (10–13 in) long, plus 28–35 cm (11–14 in) tail[83] Habitat: Forest[86] Diet: | EN
|
| Eastern woolly lemur | A. laniger Gmelin, 1788 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: 30–45 cm (12–18 in) long plus tail[87] Habitat: Forest[88] Diet: Leaves, as well as flowers and fruit[87] | VU
|
| Moore's woolly lemur | A. mooreorum Lei et al., 2008 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: 28–34 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 29–38 cm (11–15 in) tail[89] Habitat: Forest[90] Diet: Leaves[90] | EN
|
| Peyrieras's woolly lemur | A. peyrierasi Zaramody et al., 2006 | Southern Madagascar | Size: 26–32 cm (10–13 in) long, plus 28–35 cm (11–14 in) tail[91] Habitat: Forest[92] Diet: Leaves, as well as flowers and fruit[92] | VU
|
| Ramanantsoavana's woolly lemur | A. ramanantsoavani Zaramody et al., 2006 | Southern Madagascar | Size: 27–34 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 26–39 cm (10–15 in) tail[83] Habitat: Forest[93] Diet: | VU
|
| Sambirano woolly lemur | A. unicolor Thalmann & Geissmann, 2000 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 25–29 cm (10–11 in) long, plus 31–36 cm (12–14 in) tail[94] Habitat: Forest[95] Diet: | CR
|
| Southern woolly lemur | A. meridionalis Zaramody et al., 2006 | Southern Madagascar | Size: 29–33 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 29–38 cm (11–15 in) tail[83] Habitat: Forest[96] Diet: Leaves[96] | EN
|
| Western woolly lemur | A. occidentalis Liburnau, 1898 | Northern Madagascar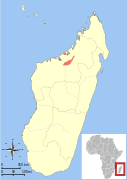 | Size: 25–29 cm (10–11 in) long, plus 31–37 cm (12–15 in) tail[97] Habitat: Forest[98] Diet: Leaves[97] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indri | I. indri (Gmelin, 1788) Two subspecies
| Northeastern Madagascar | Size: 60–90 cm (24–35 in) long, plus 5–6 cm (2 in) tail[99] Habitat: Forest[100] Diet: Fruit, leaves, and flowers[99] | CR
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coquerel's sifaka | P. coquereli Grandidier, 1867 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 42–50 cm (17–20 in) long, plus 50–60 cm (20–24 in) tail[101] Habitat: Forest[102] Diet: Leaves, seeds, flowers, fruit, and bark[103] | CR
|
| Crowned sifaka | P. coronatus H. Milne-Edwards, 1871 | Western Madagascar | Size: About 45 cm (18 in) long, plus 56 cm (22 in) tail[104] Habitat: Forest[105] Diet: Flowers and leaves, as well as fruit[105] | CR
|
| Diademed sifaka | P. diadema Bennett, 1832 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: 45–55 cm (18–22 in) long, plus 43–56 cm (17–22 in)[106] Habitat: Forest[107] Diet: Leaves, flowers, fruit, and shoots[106] | CR
|
| Golden-crowned sifaka | P. tattersalli Simons, 1988 | Northern lemur | Size: About 48 cm (19 in) long, plus about 39 cm (15 in) tail[108] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[109] Diet: Seeds, fruit, leaves, and flowers, as well as bark[108] | CR
|
| Milne-Edwards's sifaka | P. edwardsi Grandidier, 1871 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: 42–52 cm (17–20 in) long, plus 41–48 cm (16–19 in) tail[110] Habitat: Forest[111] Diet: Fruit, as well as leaves, seeds, and flowers[110] | EN
|
| Perrier's sifaka | P. perrieri Lavauden, 1931 | Northern Madagascar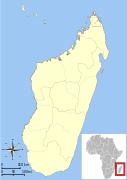 | Size: About 49 cm (19 in) long, plus tail[112] Habitat: Forest[113] Diet: Leaves, flowers, and fruit[112] | CR
|
| Silky sifaka | P. candidus Grandidier, 1871 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 48–54 cm (19–21 in) long, plus 45–51 cm (18–20 in) tail[114] Habitat: Forest[115] Diet: Leaves, seeds, fruit, and flowers, as well as bark and soil[114] | CR
|
| Verreaux's sifaka | P. verreauxi Grandidier, 1867 | Southwestern Madagascar | Size: 45–55 cm (18–22 in) long, plus 43–56 cm (17–22 in) tail[116] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[117] Diet: Leaves, bark, and flowers, as well as fruit[116] | CR
|
| Von der Decken's sifaka | P. deckenii Grandidier, 1867 | Western Madagascar | Size: About 45 cm (18 in) long, plus 45 cm (18 in) tail[118] Habitat: Forest[119] Diet: Leaves[119] | CR
|
Family Lemuridae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black lemur | E. macaco (Linnaeus, 1766) | Northern Madagascar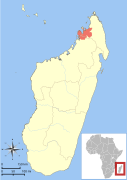 | Size: 30–50 cm (12–20 in) long, plus 40–60 cm (16–24 in) tail[120] Habitat: Forest[121] Diet: Fruit, as well as flowers, nectar, leaves, bark, soil, and ants[120] | EN
|
| Blue-eyed black lemur | E. flavifrons Gray, 1867 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 39–45 cm (15–18 in) long, plus 51–65 cm (20–26 in) tail[122] Habitat: Forest[123] Diet: Fruit and leaves[123] | CR
|
| Collared brown lemur | E. collaris Geoffroy, 1817 | Southern Madagascar | Size: 39–40 cm (15–16 in) long, plus 50–55 cm (20–22 in) tail[124] Habitat: Forest[125] Diet: Fruit, as well as flowers, young leaves, and insects[125] | EN
|
| Common brown lemur | E. fulvus Geoffroy, 1796 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: 41–51 cm (16–20 in) long, plus 41–51 cm (16–20 in) tail[126] Habitat: Forest[127] Diet: Leaves, as well as flowers, fruit, and bark[128] | VU
|
| Crowned lemur | E. coronatus (Gray, 1842) | Northern Madagascar | Size: About 34 cm (13 in) long, plus about 45 cm (18 in) tail[129] Habitat: Forest[130] Diet: Fruit, as well as leaves[129] | EN
|
| Gray-headed lemur | E. cinereiceps Grandidier & A. Milne-Edwards, 1890 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: 39–41 cm (15–16 in) long, plus 50–55 cm (20–22 in) tail[131] Habitat: Forest[132] Diet: Fruit, as well as flowers, leaves, nectar, fungi, and insects[131] | CR
|
| Mongoose lemur | E. mongoz (Linnaeus, 1766) | Northern Madagascar | Size: About 35 cm (14 in) long, plus about 48 cm (19 in) tail[133] Habitat: Forest[134] Diet: Flowers, pollen, fruit, and leaves[133] | CR
|
| Red lemur | E. rufus (Audebert, 1799) | Northwestern lemur | Size: About 38 cm (15 in) long, plus 49–51 cm (19–20 in)[135] Habitat: Forest[136] Diet: Fruit, as well as leaves, flowers, insects, and arthropods[135] | VU
|
| Red-bellied lemur | E. rubriventer Geoffroy, 1850 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: 36–42 cm (14–17 in) long, plus 46–54 cm (18–21 in) tail[137] Habitat: Forest[138] Diet: Flowers, fruits and leaves, as well as invertebrates[137] | VU
|
| Red-fronted lemur | E. rufifrons Bennett, 1833 | Southwestern and southeastern Madagascar | Size: About 30 cm (12 in) long, plus about 50 cm (20 in) tail[139] Habitat: Forest[140] Diet: Fruit, leaves, buds, and flowers, as well as invertebrates[139] | VU
|
| Sanford's brown lemur | E. sanfordi Archbold, 1932 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 38–40 cm (15–16 in) long, plus 50–55 cm (20–22 in) tail[141] Habitat: Forest[142] Diet: Fruit, as well as leaves, flowers, and invertebrates[142] | EN
|
| White-headed lemur | E. albifrons Geoffroy, 1796 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: About 40 cm (16 in) long, plus about 50 cm (20 in) tail[143] Habitat: Forest[144] Diet: Fruit and flowers[144] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern lesser bamboo lemur | H. griseus Link, 1795 | Western and eastern Madagascar | Size: 28–30 cm (11–12 in) long, plus 35–37 cm (14–15 in) tail[145] Habitat: Forest[146] Diet: Bamboo, as well as grass, fruit, and leaves[147] | VU
|
| Golden bamboo lemur | H. aureus Meier, Albignac, Peyriéras, Rumpler, & Wright,, 1987 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: About 34 cm (13 in) long, plus about 41 cm (16 in) tail[148] Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands[149] Diet: Bamboo, as well as grass, leaves, fruit, fungi, and soil[148] | CR
|
| Lac Alaotra bamboo lemur | H. alaotrensis Rumpler, 1975 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: About 40 cm (16 in) long, plus tail[150] Habitat: Inland wetlands[151] Diet: Marsh plants[151] | CR
|
| Southern lesser bamboo lemur | H. meridionalis Warter, Randrianasolo, Dutrillaux, & Rumpler, 1987 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: 24–30 cm (9–12 in) long, plus 32–40 cm (13–16 in) tail[152] Habitat: Forest[153] Diet: Grass, pith, stems, and leaves, as well as fruit[153] | VU
|
| Western lesser bamboo lemur | H. occidentalis Rumpler, 1975 | 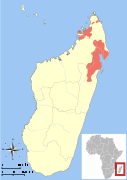 | Size: 27–28 cm (11–11 in) long, plus 36–39 cm (14–15 in) tail[154] Habitat: Forest[155] Diet: Fruit, bamboo, flowers, fungi, and soil[155] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ring-tailed lemur | L. catta Linnaeus, 1758 | Southwestern Madagascar | Size: 39–46 cm (15–18 in) long, plus 56–63 cm (22–25 in) tail[156] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, rocky areas, and caves[157] Diet: Omnivorous, including fruit, leaves, stems, flowers, sap, spiders, spider webs, chameleons, insects, small birds, and termite mounds[156] | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greater bamboo lemur | P. simus Gray, 1871 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: 40–45 cm (16–18 in) long, plus 43–48 cm (17–19 in) tail[158] Habitat: Forest[159] Diet: Bamboo shoots and pith, as well as flowers, leaves, soil, and fruit[158] | CR
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black-and-white ruffed lemur | V. variegata Kerr, 1792 Three subspecies
| Eastern Madagascar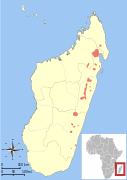 | Size: About 45 cm (18 in) long, plus 60–61 cm (24–24 in) tail[145] Habitat: Forest[160] Diet: Fruit, as well as leaves, flowers, and nectar[161] | CR
|
| Red ruffed lemur | V. rubra (Geoffroy, 1812) | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: About 50 cm (20 in) long, plus about 60 cm (24 in) tail[162] Habitat: Forest[163] Diet: Fruit, nectar, and pollen, as well as leaves and seeds[162] | CR
|
Family Lepilemuridae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEECL's sportive lemur | L. aeeclis Andriaholinirina et al., 2017 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 28–33 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 24–26 cm (9–10 in) tail[164] Habitat: Forest[165] Diet: Leaves[165] | EN
|
| Ahmanson's sportive lemur | L. ahmansoni Louis et al., 2006 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 24–30 cm (9–12 in) long, plus 23–25 cm (9–10 in) tail[166] Habitat: Forest[167] Diet: Leaves[167] | CR
|
| Ankarana sportive lemur | L. ankaranensis Rumpler, 1975 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: About 28 cm (11 in) long, plus about 25 cm (10 in) tail[168] Habitat: Forest[169] Diet: Leaves and fruit, as well as latex[169] | EN
|
| Betsileo sportive lemur | L. betsileo Louis et al., 2006 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: About 28 cm (11 in) long, plus about 33 cm (13 in) tail[170] Habitat: Forest[171] Diet: Leaves and flowers[170] | EN
|
| Daraina sportive lemur | L. milanoii Louis et al., 2006 | Northeastern Madagascar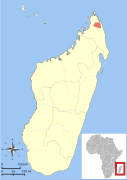 | Size: 25–29 cm (10–11 in) long, plus 24–27 cm (9–11 in) tail[172] Habitat: Forest[173] Diet: Leaves[173] | EN
|
| Fleurete's sportive lemur | L. fleuretae Louis et al., 2006 | Southern Madagascar | Size: 28–37 cm (11–15 in) long, plus about 30 cm (12 in) tail[174] Habitat: Forest[175] Diet: Leaves, fruit, and flowers[175] | EN
|
| Gray-backed sportive lemur | L. dorsalis Gray, 1870 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 23–26 cm (9–10 in) long, plus 26–28 cm (10–11 in) tail[176] Habitat: Forest[177] Diet: Leaves, as well as flowers, fruit, and bark[176] | EN
|
| Grewcock's sportive lemur | L. grewcocki Louis et al., 2006 | Northern Madagascar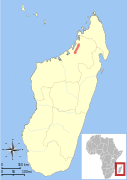 | Size: 29–33 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 26–30 cm (10–12 in) tail[178] Habitat: Forest[179] Diet: | CR
|
| Hawks' sportive lemur | L. tymerlachsoni Louis et al., 2006 | Northern Madagascar | Size: 28–41 cm (11–16 in) long, plus 22–27 cm (9–11 in) tail[180] Habitat: Forest[181] Diet: Leaves, as well as fruit and bark[181] | CR
|
| Holland's sportive lemur | L. hollandorum Ramaromilanto et al., 2009 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: Habitat: Forest[182] Diet: Leaves[182] | CR
|
| Hubbard's sportive lemur | L. hubbardi Louis et al., 2006 | Southwestern Madagascar | Size: 28–34 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 23–25 cm (9–10 in) tail[183] Habitat: Forest[184] Diet: Leaves[184] | EN
|
| James' sportive lemur | L. jamesi Louis et al., 2006 | Southeastern Madagascar | Size: 32–35 cm (13–14 in) long, plus 28–32 cm (11–13 in) tail[185] Habitat: Forest[186] Diet: | CR
|
| Milne-Edwards' sportive lemur | L. edwardsi Forsyth Major, 1894 | Northern Madagascar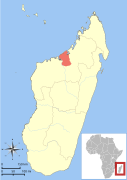 | Size: 27–29 cm (11–11 in) long, plus 27–29 cm (11–11 in) tail[187] Habitat: Forest[188] Diet: Leaves, as well as seeds, flowers, and fruit[187] | EN
|
| Northern sportive lemur | L. septentrionalis Rumpler & Albignac, 1975 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: About 28 cm (11 in) long, plus 25 cm (10 in) tail[189] Habitat: Forest[190] Diet: Leaves, as well as flowers and fruit[189] | CR
|
| Otto's sportive lemur | L. otto Craul, Zimmermann, Rasoloharijaona, Randrianambinina, & Radespiel, 2007 | Northern Madagascar | Size: Habitat: Forest[191] Diet: | EN
|
| Petter's sportive lemur | L. petteri Louis et al., 2006 | Southern Madagascar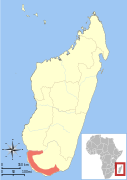 | Size: 27–29 cm (11–11 in) long, plus 22–25 cm (9–10 in) tail[183] Habitat: Forest[192] Diet: Leaves[192] | EN
|
| Randrianasolo's sportive lemur | L. randrianasoloi Andriaholinirina et al., 2017 | Western Madagascar | Size: About 29 cm (11 in) long, plus about 28 cm (11 in) tail[193] Habitat: Forest[194] Diet: Leaves, as well as pollen, seeds, fruit, flowers, and bark[193] | EN
|
| Red-tailed sportive lemur | L. ruficaudatus Grandidier, 1867 | Southwestern Madagascar | Size: About 28 cm (11 in) long, plus about 25 cm (10 in) tail[195] Habitat: Forest[196] Diet: Fruit and leaves[196] | CR
|
| Sahamalaza sportive lemur | L. sahamalaza Andriaholinirina et al., 2017 | Northern Madagascar | Size: About 26 cm (10 in) long, plus about 27 cm (11 in) tail[197] Habitat: Forest[198] Diet: Leaves, fruit, spiders, and insects[198] | CR
|
| Scott's sportive lemur | L. scottorum Lei et al., 2008 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: 31–35 cm (12–14 in) long, plus 25–30 cm (10–12 in) tail[89] Habitat: Forest[199] Diet: Leaves[199] | EN
|
| Seal's sportive lemur | L. seali Louis et al., 2006 | Northeastern Madagascar | Size: 32–38 cm (13–15 in) long, plus 24–38 cm (9–15 in) tail[89] Habitat: Forest[200] Diet: | VU
|
| Small-toothed sportive lemur | L. microdon Forsyth Major, 1894 |  | Size: 27–32 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 28–32 cm (11–13 in) tail[201] Habitat: Forest[202] Diet: Leaves[202] | EN
|
| Weasel sportive lemur | L. mustelinus Geoffroy, 1851 | Eastern Madagascar | Size: 24–30 cm (9–12 in) long, plus 22–29 cm (9–11 in) tail[203] Habitat: Forest[204] Diet: Leaves, as well as fruit, flowers, and bark[203] | VU
|
| White-footed sportive lemur | L. leucopus Forsyth Major, 1894 | Southern Madagascar | Size: 24–26 cm (9–10 in) long, plus 21–26 cm (8–10 in) tail[205] Habitat: Forest[206] Diet: Leaves and vines, as well as flowers and fruit[205] | EN
|
| Wright's sportive lemur | L. wrighti Louis et al., 2006 | Southern Madagascar | Size: 31–38 cm (12–15 in) long, plus 23–28 cm (9–11 in) tail[89] Habitat: Forest[207] Diet: Leaves[207] | EN
|
Extinct species
All known extinct lemurs from Madagascar are known from recent, subfossil remains.[208] Conditions for fossilization were not ideal on the island, so little is known about ancestral lemur populations. All known extinct lemurs are thought to have died out after the arrival of humans.
See also
References
Sources
- Burnie, David; Wilson, Don E., eds. (2017). Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide. DK. ISBN 978-1-4654-7086-7.
- Garbutt, Nick (2007). Mammals of Madagascar: A Complete Guide. A & C Black. ISBN 978-0-300-12550-4.
- Nowak, Ronald M. (1999). Walker's Primates of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-6251-9.
- Mittermeier, R. A.; Louis, E. E.; Richardson, M.; Schwitzer, C.; et al. (2010). Lemurs of Madagascar. Illustrated by S.D. Nash (3rd ed.). Conservation International. ISBN 978-1-934151-23-5.
- Godfrey, L. R.; Jungers, W. L.; Burney, D. A. (2010). "Chapter 21: Subfossil Lemurs of Madagascar". In Werdelin, L.; Sanders, W.J (eds.). Cenozoic Mammals of Africa. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-25721-4.
- Groves, Colin P. (2005). Wilson, Don E.; Reeder, DeeAnn M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World. Vol. 1 (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.





































































