Natufian culture (/nəˈtuːfiən/[1]) is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Neolithic prehistoric[2] Levant in Western Asia, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago.[3] The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduction of agriculture. Natufian communities may be the ancestors of the builders of the first Neolithic settlements of the region, which may have been the earliest in the world. Some evidence suggests deliberate cultivation of cereals, specifically rye, by the Natufian culture at Tell Abu Hureyra, the site of earliest evidence of agriculture in the world.[2] The world's oldest known evidence of the production of bread-like foodstuff has been found at Shubayqa 1, a 14,400-year-old site in Jordan's northeastern desert, 4,000 years before the emergence of agriculture in Southwest Asia.[4] In addition, the oldest known evidence of possible beer-brewing, dating to approximately 13,000 BP, was found in Raqefet Cave on Mount Carmel, although the beer-related residues may simply be a result of a spontaneous fermentation.[5][6]
A map of the Levant with Natufian regions across present-day Israel, Palestine, Jordan, and a long arm extending into Lebanon and Syria | |
| Geographical range | Levant, Western Asia |
|---|---|
| Period | Epipaleolithic |
| Dates | 15,000–11,500 BP |
| Type site | Shuqba cave, in Wadi Natuf |
| Major sites | Shuqba cave, Ain Mallaha, Ein Gev, Tell Abu Hureyra |
| Preceded by | Kebaran, Mushabian |
| Followed by | Neolithic: Khiamian, Shepherd Neolithic |
Generally, though, Natufians exploited wild cereals and hunted animals, including gazelles.[7] Archaeogenetic analysis has revealed derivation of later (Neolithic to Bronze Age) Levantines primarily from Natufians, besides substantial admixture from Chalcholithic Anatolians.[8]
Dorothy Garrod coined the term Natufian based on her excavations at the Shuqba cave (Wadi an-Natuf) near the town of Shuqba.
Discovery

The Natufian culture was discovered by British archaeologist Dorothy Garrod during her excavations of Shuqba cave in the Judaean Hills, on the West Bank of the Jordan River.[9][10] Prior to the 1930s, the majority of archaeological work taking place in British Palestine was biblical archaeology focused on historic periods, and little was known about the region's prehistory.
In 1928, Garrod was invited by the British School of Archaeology in Jerusalem (BSAJ) to excavate Shuqba cave, where prehistoric stone tools had been discovered by Père Mallon four years earlier. She discovered a layer sandwiched between the Upper Palaeolithic and Bronze Age deposits characterised by the presence of microliths. She identified this with the Mesolithic, a transitional period between the Palaeolithic and the Neolithic which was well-represented in Europe but had not yet been found in the Near East. A year later, when she discovered similar material at el-Wad Terrace, Garrod suggested the name "the Natufian culture", after Wadi an-Natuf that ran close to Shuqba.
Over the next two decades Garrod found Natufian material at several of her pioneering excavations in the Mount Carmel region, including el-Wad, Kebara and Tabun, as did the French archaeologist René Neuville, firmly establishing the Natufian culture in the regional prehistoric chronology. As early as 1931, both Garrod and Neuville drew attention to the presence of stone sickles in Natufian assemblages and the possibility that this represented a very early agriculture.[10]
Dating

Radiocarbon dating places the Natufian culture at an epoch from the terminal Pleistocene to the very beginning of the Holocene, a time period between 12,500 and 9,500 BC.[12]
The period is commonly split into two subperiods: Early Natufian (12,000–10,800 BC) and Late Natufian (10,800–9,500 BC). The Late Natufian most likely occurred in tandem with the Younger Dryas (10,800 to 9,500 BC). The Levant hosts more than a hundred kinds of cereals, fruits, nuts, and other edible parts of plants, and the flora of the Levant during the Natufian period was not the dry, barren, and thorny landscape of today, but rather woodland.[9]
Precursors and associated cultures
The Natufian developed in the same region as the earlier Kebaran culture. It is generally seen as a successor, which evolved out of elements within that preceding culture. There were also other industries in the region, such as the Mushabian culture of the Negev and the Sinai Peninsula, which are sometimes distinguished from the Kebaran culture or believed to have been involved in the evolution of the Natufian culture.
More generally there has been discussion of the similarities of these cultures with those found in coastal North Africa. Graeme Barker notes there are: "similarities in the respective archaeological records of the Natufian culture of the Levant and of contemporary foragers in coastal North Africa across the late Pleistocene and early Holocene boundary".[13] According to Isabelle De Groote and Louise Humphrey, Natufians practiced the Iberomaurusian and Capsian custom of sometimes extracting their maxillary central incisors (upper front teeth).[14]

Ofer Bar-Yosef has argued that there are signs of influences coming from North Africa to the Levant, citing the microburin technique and "microlithic forms such as arched backed bladelets and La Mouillah points."[15] But recent research has shown that the presence of arched backed bladelets, La Mouillah points, and the use of the microburin technique was already apparent in the Nebekian industry of the Eastern Levant.[16] And Maher et al. state that, "Many technological nuances that have often been always highlighted as significant during the Natufian were already present during the Early and Middle EP [Epipalaeolithic] and do not, in most cases, represent a radical departure in knowledge, tradition, or behavior."[17]
Authors such as Christopher Ehret have built upon the little evidence available to develop scenarios of intensive usage of plants having built up first in North Africa, as a precursor to the development of true farming in the Fertile Crescent, but such suggestions are considered highly speculative until more North African archaeological evidence can be gathered.[18][19] In fact, Weiss et al. have shown that the earliest known intensive usage of plants was in the Levant 23,000 years ago at the Ohalo II site.[20][21][22]
Anthropologist C. Loring Brace (1993) cross-analysed the craniometric traits of Natufian specimens with those of various ancient and modern groups from the Near East, Africa and Europe. The Late Pleistocene Epipalaeolithic Natufian sample was described as problematic due to its small size (consisting of only three males and one female), as well as the lack of a comparative sample from the Natufians' putative descendants in the Neolithic Near East. Brace observed that the Natufian fossils lay between those of the Niger–Congo-speaking series included and the other samples (Near East, Europe), which he suggested may point to a Sub-Saharan influence in their constitution.[23] Subsequent ancient DNA analysis of Natufian skeletal remains by Lazaridis et al. (2016) found that the specimens instead were a mix of 50% Basal Eurasian ancestral component (see Archaeogenetics) and 50% West-Eurasian Unknown Hunter Gatherer (UHG) population related to European Western Hunter-Gatherers.[24]
According to Bar-Yosef and Belfer-Cohen, "It seems that certain preadaptive traits, developed already by the Kebaran and Geometric Kebaran populations within the Mediterranean park forest, played an important role in the emergence of the new socioeconomic system known as the Natufian culture."[25]
Settlements

Settlements occur mostly in Israel and Palestine. This could be deemed the core zone of the Natufian culture, but Israel is a place that has been excavated more frequently than other places hence the greater number of sites.[26] During the years more sites have been found outside the core zone of Israel and Palestine stretching into what now is Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, the Sinai Peninsula and the Negev desert.[26] The settlements in the Natufian culture were larger and more permanent than in preceding ones. Some Natufian sites had stone built architecture; Ain Mallaha is an example of round stone structures.[27] Cave sites are also seen frequently during the Natufian culture. El Wad is a Natufian cave site with occupation in the front part of the cave also called the terrace.[28] Some Natufian sites were located in forest/steppe areas and others near inland mountains. The Natufian settlements appear to be the first to exhibit evidence of food storage; not all Natufian sites have storage facilities, but they have been identified at certain sites.[29] Natufians are also suggested to have visted Cyprus, requiring travel over significant distances of water.[30]

Material culture

Lithics
The Natufian had a microlithic industry centered on short blades and bladelets. The microburin technique was used. Geometric microliths include lunates, trapezes, and triangles. There are backed blades as well. A special type of retouch (Helwan retouch) is characteristic for the early Natufian. In the late Natufian, the Harif-point, a typical arrowhead made from a regular blade, became common in the Negev. Some scholars[who?] use it to define a separate culture, the Harifian.
Sickle blades also appear for the first time in the Natufian lithic industry. The characteristic sickle-gloss shows that they were used to cut the silica-rich stems of cereals, indirectly suggesting the existence of incipient agriculture. Shaft straighteners made of ground stone indicate the practice of archery. There are heavy ground-stone bowl mortars as well.
Art
The Ain Sakhri lovers, a carved stone object held at the British Museum, is the oldest known depiction of a couple having sex. It was found in the Ain Sakhri cave in the Judean desert.[31]
Burials

Natufian grave goods are typically made of shell, teeth (of red deer), bones, and stone. There are pendants, bracelets, necklaces, earrings, and belt-ornaments as well.

In 2008, the 12,400–12,000 cal BC grave of an apparently significant Natufian female was discovered in a ceremonial pit in the Hilazon Tachtit cave in northern Israel.[32] Media reports referred to this person as a "shaman".[33] The burial contained the remains of at least three aurochs and 86 tortoises, all of which are thought to have been brought to the site during a funeral feast. The body was surrounded by tortoise shells, the pelvis of a leopard, forearm of a boar, a wingtip of a golden eagle, and skull of a beech marten.[34][35]
Long-distance exchange
At Ain Mallaha (in Northern Israel), Anatolian obsidian and shellfish from the Nile valley have been found. The source of malachite beads is still unknown. Epipaleolithic Natufians carried parthenocarpic figs from Africa to the southeastern corner of the Fertile Crescent, c. 10,000 BC.[36]
Other finds
There was a rich bone industry, including harpoons and fish hooks. Stone and bone were worked into pendants and other ornaments. There are a few human figurines made of limestone (El-Wad, Ain Mallaha, Ain Sakhri), but the favorite subject of representative art seems to have been animals. Ostrich-shell containers have been found in the Negev.
In 2018, the world's oldest brewery was found, with the residue of 13,000-year-old beer, in a prehistoric cave near Haifa in Israel when researchers were looking for clues into what plant foods the Natufian people were eating. This is 8,000 years earlier than experts previously thought beer was invented.[37]
A study published in 2019 shows an advanced knowledge of lime plaster production at a Natufian cemetery in Nahal Ein Gev II site in the Upper Jordan Valley dated to 12 thousand (calibrated) years before present [k cal BP]. Production of plaster of this quality was previously thought to have been achieved some 2,000 years later.[38]
Subsistence

The Natufian people lived by hunting and gathering. The preservation of plant remains is poor because of the soil conditions, but at some sites such as Tell Abu Hureyra substantial amounts of plant remains discovered through flotation have been excavated.[39] However wild cereals like legumes, almonds, acorns and pistachios have been collected throughout most of the Levant. Animal bones show that mountain and goitered gazelles (Gazella gazella and Gazella subgutturosa) were the main prey.
Additionally, deer, aurochs and wild boar were hunted in the steppe, as well as onagers and caprids (ibex). Waterfowl and freshwater fish formed part of the diet in the Jordan river valley. Animal bones from Salibiya I (12,300 – 10,800 cal BP) have been interpreted as evidence for communal hunts with nets, however, the radiocarbon dates are far too old compared to the cultural remains of this settlement, indicating contamination of the samples.[40]
Development of agriculture
A pita-like bread has been found from 12,500 BC attributed to Natufians. This bread is made of wild cereal seeds and papyrus cousin tubers, ground into flour.[41]
According to one theory,[33] it was a sudden change in climate, the Younger Dryas event (c. 10,800 to 9500 BC), which inspired the development of agriculture. The Younger Dryas was a 1,000-year-long interruption in the higher temperatures prevailing since the Last Glacial Maximum, which produced a sudden drought in the Levant. This would have endangered the wild cereals, which could no longer compete with dryland scrub, but upon which the population had become dependent to sustain a relatively large sedentary population. By artificially clearing scrub and planting seeds obtained from elsewhere, they began to practice agriculture. However, this theory of the origin of agriculture is controversial in the scientific community.[42]
- Grinding tool from Gilgal, Natufian culture, 12,500–9500 BC
- Basalt sharpening stones, Eynan and Nahal Oren, Natufian Culture, 12,500–9500 BC
- Bovine-rib dagger, HaYonim Cave, Natufian Culture, 12,500–9500 BC
- Stone mortars from Eynan, Natufian period, 12,500–9500 BC
- Stone mortar from Eynan, Natufian period, 12,500–9500 BC
- Limestone and basalt mortars, Eynan, Early Natufian, c. 12,000 BC
Domesticated dog
At the Natufian site of Ain Mallaha in Israel, dated to 12,000 BC, the remains of an elderly human and a four-to-five-month-old puppy were found buried together.[43] At another Natufian site at the cave of Hayonim, humans were found buried with two canids.[43]
Archaeogenetics
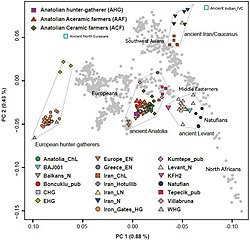
The population associated with the Natufian culture formed genetically by the merger of a West Eurasian-like population, sharing deep ancestry with Western Hunter-Gatherers of Europe, and Basal Eurasians of local Arabian origin. The Natufian population also displays ancestral ties to Paleolithic Taforalt samples, the makers of the Epipaleolithic Iberomaurusian culture of the Maghreb, the Pre-Pottery Neolithic culture of the Levant, the Early Neolithic Ifri N'Amr Ou Moussa culture of the Maghreb, the Late Neolithic Kelif el Boroud culture of the Maghreb, with samples associated with these early cultures all sharing a common genomic component dubbed the "Natufian component", which diverged from other West Eurasian lineages ~26,000 years ago, and is most closely linked to the Arabian lineage. Possible bidirectional geneflow events between these groups has also been suggested, with particular evidence for affinity between the Natufians and Iberomaurusians. Contact between Natufians, other Neolithic Levantines, Caucasus hunter-gatherers (CHG), Anatolian and Iranian farmers is believed to have decreased genetic variability among later populations in the Middle East. Migrations from the Near-East also occurred towards Africa, and the West Eurasian-like ancestry among populations in the Horn of Africa is best represented by the Levant Neolithic, and may be associated with the spread of Afroasiatic languages.[45][46][47][48]
Ferreira et al. in 2021 found that ancient Natufians cluster with modern Saudi Arabians and Yemenis.[49] Sirak et al. 2024 found that medieval Socotra (the Soqotri people), like modern Saudis, Yemenis and Bedouin, have a majority component that is "maximized in Late Pleistocene (Epipaleolithic) Natufian hunter–gatherers from the Levant".[50]
Language
Alexander Militarev, Vitaly Shevoroshkin and others have linked the Natufian culture to the proto-Afroasiatic language,[51][52] which they in turn believe has a Levantine origin. Some scholars, for example Christopher Ehret, Roger Blench and others, contend that the Afroasiatic Urheimat is to be found in North Africa or Northeast Africa, probably in the area of Egypt, the Sahara, Horn of Africa or Sudan.[53][54][55][56][57] Within this group, Ehret, who like Militarev believes Afroasiatic may already have been in existence in the Natufian period, would associate Natufians only with the Near Eastern Proto-Semitic branch of Afroasiatic.
Sites
The Natufian culture has been documented at dozens of sites. Around 90 have been excavated, including:[58]
- Aammiq 2
- Tell Abu Hureyra
- Abu Salem
- Abu Usba
- Ain Choaab
- Ain Mallaha (Eynan)
- Ain Rahub
- Ain Sakhri
- Ala Safat
- Antelias Cave
- Azraq 18 (Ain Saratan)
- Baaz
- Bawwab al Ghazal
- Beidha
- Dederiyeh
- Dibsi Faraj
- El Khiam
- El Kowm I
- El Wad
- Erq el Ahmar
- Fazael IV & VI
- Gilgal II
- Givat Hayil I
- Har Harif K7
- Hatoula
- Hayonim Cave and Hayonim Terrace
- Hilazon Tachtit
- Hof Shahaf
- Huzuq Musa
- Iraq ed Dubb
- Iraq el Barud
- Iraq ez Zigan
- J202
- J203
- J406a
- J614
- Jayroud 1–3 & 9
- Jebel Saaidé II
- Jeftelik
- Jericho
- Kaus Kozah
- Kebara
- Kefar Vitkin 3
- Khallat Anaza (BDS 1407)
- Khirbat Janba
- Kosak Shamali
- Maaleh Ramon East
- Maaleh Ramon West
- Moghr el Ahwal
- Mureybet
- Mushabi IV & XIX
- Nachcharini Cave
- Nahal Ein Gev II
- Nahal Hadera I and Nahal Hadera IV (Hefsibah)
- Nahal Oren
- Nahal Sekher 23
- Nahal Sekher VI
- Nahr el Homr 2
- Qarassa 3
- Ramat Harif (G8)
- Raqefet Cave
- Rosh Horesha
- Rosh Zin
- Sabra 1
- Saflulim
- Salibiya 1
- Salibiya 9
- Sands of Beirut
- Shluhat Harif
- Shubayqa 1
- Shubayqa 6
- Shukhbah Cave
- Shunera VI
- Shunera VII
- Tabaqa (WHS 895)[59]
- Taibé
- TBAS 102
- TBAS 212
- Tor at Tariq (WHS 1065)
- Tugra I
- Upper Besor 6
- Wadi Hammeh 27
- Wadi Jilat 22
- Wadi Judayid (J2)
- Wadi Mataha
- Yabrud 3
- Yutil al Hasa (WHS 784)
See also
References
Further reading
- Balter, Michael (2005), The Goddess and the Bull, New York: Free Press, ISBN 978-0-7432-4360-5
- Bar-Yosef, Ofer (1998), "The Natufian Culture in the Levant, Threshold to the Origins of Agriculture" (PDF), Evolutionary Anthropology, 6 (5): 159–177, doi:10.1002/(SICI)1520-6505(1998)6:5<159::AID-EVAN4>3.0.CO;2-7, S2CID 35814375
- Bar-Yosef, Ofer; Belfer-Cohen, Anna (1999). "Encoding information: unique Natufian objects from Hayonim Cave, Western Galilee, Israel". Antiquity. 73 (280): 402–409. doi:10.1017/s0003598x00088347. S2CID 160868877.
- Bar-Yosef, Ofer (1992), Valla, Francois R. (ed.), The Natufian Culture in the Levant, Ann Arbor: International Monographs in Prehistory, ISBN 978-1-879621-03-9
- Campana, Douglas V.; Crabtree, Pam J. (1990). "Communal Hunting in the Natufian of the Southern Levant: The Social and Economic Implications". Journal of Mediterranean Archaeology. 3 (2): 223–243. doi:10.1558/jmea.v3i2.223.
- Clutton-Brock, Juliet (1999), A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals (2nd ed.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-63247-8
- Dubreuil, Laure (2004), "Long-term trends in Natufian subsistence: a use-wear analysis of ground stone tools", Journal of Archaeological Science, 31 (11): 1613–1629, Bibcode:2004JArSc..31.1613D, doi:10.1016/j.jas.2004.04.003
- Munro, Natalie D. (August–October 2004). "Zooarchaeological measures of hunting pressure and occupation intensity in the Natufian: Implications for agricultural origins" (PDF). Current Anthropology. 45: S5–S33. doi:10.1086/422084. S2CID 42749024.
- Simmons, Alan H. (2007), The Neolithic Revolution in the Near East: Transforming the Human Landscape, University of Arizona Press, ISBN 978-0-8165-2966-7
External links
- Epi-Palaeolithic (European Mesolithic) Natufian Culture of Israel (The History of the Ancient Near East)
- Cultural Complexity (Hierarchical Societies [Socio-Economic-Political Inequalities]) in Mesopotamia: An Outline, archived from the original on 8 October 2016, retrieved 2 June 2002
- The genetic structure of the world's first farmers, Lazaridis et al, 2016








