South Africa is divided into nine provinces.[1] On the eve of the 1994 general election, South Africa's former homelands, known as Bantustans, were reintegrated into the country, and the four provinces were increased to nine by dividing Cape Province and the Transvaal into three and four, respectively. The twelfth, thirteenth and sixteenth amendments to the Constitution of South Africa changed the borders of seven of the provinces.
| Provinces of South Africa | |
|---|---|
| Category | Regional state |
| Location | South Africa |
| Created |
|
| Number | 9 Provinces |
| Populations | 1,355,946 (Northern Cape) – 15,099,422 (Gauteng) |
| Areas | 18,178 km2 (7,019 sq mi) (Gauteng) – 372,889 km2 (143,973 sq mi) (Northern Cape) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions | |
History

The Union of South Africa was established in 1910 by combining four British colonies: the Cape Colony, the Natal Colony, the Transvaal Colony and the Orange River Colony (the latter two were, before the Second Boer War, independent republics known as the South African Republic and the Orange Free State). These colonies became the four original provinces of the Union: Cape Province, Transvaal Province, Natal Province and Orange Free State Province.
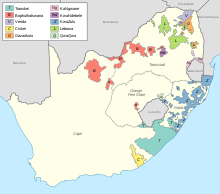
Segregation of the black population started as early as 1913, with ownership of land by the black majority being restricted to certain areas totalling about 13% of the country. From the late 1950s, these areas were gradually consolidated into "homelands", also called "bantustans". Four of these homelands were established as quasi-independent nation states of the black population during the apartheid era. In 1976, the homeland of Transkei was the first to accept independence from South Africa, and although this independence was never acknowledged by any other country, three other homelands – Bophuthatswana (1977), Venda (1979) and Ciskei (1981) – followed suit.
On 27 April 1994, the date of the first non-racial elections and of the adoption of the Interim Constitution, all of these provinces and homelands were dissolved, and nine new provinces were established. The boundaries of these provinces were established in 1993 by a Commission on the Demarcation/Delimitation of Regions created by CODESA, and were broadly based on planning regions demarcated by the Development Bank of Southern Africa in the 1980s,[2][3] and amalgamated from existing magisterial districts, with some concessions to political parties that wished to consolidate their power bases, by transferring districts between the proposed provinces.[4][5] The definitions of the new provinces in terms of magisterial districts were found in Schedule 1 of the Interim Constitution.
On 11 July 2003, the 11th amendment to the fifth constitution renamed the Northern Province to Limpopo. On 1 March 2006, the 12th and 13th amendments altered the boundaries of 7 provinces. On 3 April 2009 the 16th amendment altered the boundaries of the North West and Gauteng provinces.
Government

South Africa's provinces are governed, in different ways, on a national, provincial and local level.[6]
Nationally, there is the National Council of Provinces, one of the houses of Parliament. Then there is the provincial government and, below that, the administration of district and metropolitan municipalities.
National Council of Provinces
South Africa has two houses of parliament: the National Assembly, and the National Council of Provinces.[6] The second exists to ensure that the interests of each province are protected in the laws passed by the National Assembly.
Each one of South Africa's nine provinces sends 10 representatives to the National Council of Provinces. Six of these are permanent members of the council, and four are special delegates.
Provincial government
Each province is governed by a unicameral legislature. The size of the legislature is proportional to population, ranging from 30 members in the Northern Cape to 80 in KwaZulu-Natal. The legislatures are elected every five years by a system of party-list proportional representation; by convention, they are all elected on the same day, at the same time as the National Assembly election.[7]
The provincial legislature elects, from amongst its members, a Premier, who is the head of the executive. The Premier chooses an Executive Council consisting of between five and ten members of the legislature, which is the cabinet of the provincial government.[7] The Members of the Executive Council (MECs) are the provincial equivalent of ministers.
The powers of the provincial government are limited to specific topics listed in the national constitution. On some of these topics – for example, agriculture, education, health and public housing – the province's powers are shared with the national government, which can establish uniform standards and frameworks for the provincial governments to follow; on other topics the provincial government has exclusive power.[8]
The provinces do not have their own court systems, as the administration of justice is the responsibility of the national government.
List
| Province | Name in the most spoken native language[9] | Capital | Largest city | Area[10]: 9 | Population (2022)[11] | Density (2022) | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Cape | iMpuma-Koloni (Xhosa) | Bhisho (Bisho) | Gqeberha (Port Elizabeth) | 168,966 km2 (65,238 sq mi) | 7,230,204 | 42.8/km2 (111/sq mi) |  |
| Free State | Freistata (Sotho) | Bloemfontein | Bloemfontein | 129,825 km2 (50,126 sq mi) | 2,964,412 | 22.8/km2 (59/sq mi) |  |
| Gauteng | eGoli (Zulu) | Johannesburg | Johannesburg | 18,178 km2 (7,019 sq mi) | 15,099,422 | 830.6/km2 (2,151/sq mi) |  |
| KwaZulu-Natal | iKwaZulu-Natali (Zulu) | Pietermaritzburg[n 1] | Durban | 94,361 km2 (36,433 sq mi) | 12,423,907 | 131.7/km2 (341/sq mi) |  |
| Limpopo | Limpopo (Pedi) | Polokwane (Pietersburg) | Polokwane | 125,754 km2 (48,554 sq mi) | 6,572,720 | 52.3/km2 (135/sq mi) |  |
| Mpumalanga | iMpumalanga (Swazi) | Mbombela (Nelspruit) | Mbombela | 76,495 km2 (29,535 sq mi) | 5,143,324 | 67.2/km2 (174/sq mi) |  |
| North West | Bokone Bophirima (Tswana) | Mahikeng (Mafikeng) | Rustenburg | 104,882 km2 (40,495 sq mi) | 3,804,548 | 36.3/km2 (94/sq mi) |  |
| Northern Cape | Noord-Kaap (Afrikaans) | Kimberley | Kimberley | 372,889 km2 (143,973 sq mi) | 1,355,946 | 3.6/km2 (9.3/sq mi) |  |
| Western Cape[n 2] | Wes-Kaap (Afrikaans) | Cape Town | Cape Town | 129,462 km2 (49,986 sq mi) | 7,433,019 | 57.4/km2 (149/sq mi) |  |
| Republic of South Africa | iRiphabhuliki yaseNingizimu Afrika (Zulu) | Pretoria, Bloemfontein Cape Town[n 3][12] | Johannesburg | 1,220,813 km2 (471,359 sq mi) | 62,027,503 | 50.8/km2 (132/sq mi) |  |
Footnotes:
Provincial acronyms
| Province | HASC | ISO | FIPS | CSS | Conventional |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Cape | ZA.EC | EC | SF05 | 02 | EC |
| Free State | ZA.FS | FS | SF03 | 04 | FS |
| Gauteng | ZA.GT | GP | SF06 | 07 | GP |
| KwaZulu-Natal | ZA.NL | KZN | SF02 | 05 | KZN |
| Limpopo | ZA.NP | LP | SF09 | 09 | LP |
| Mpumalanga | ZA.MP | MP | SF07 | 08 | MP |
| Northern Cape | ZA.NC | NC | SF08 | 03 | NC |
| North-West | ZA.NW | NW | SF10 | 06 | NW |
| Western Cape | ZA.WC | WC | SF11 | 01 | WC |
| Notes HASC: Hierarchical administrative subdivision codes | |||||
Former administrative divisions
| Province | Capital | Peak population | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cape of Good Hope (1910–1994) | Cape Town | 6,125,335 |  |
| Natal (1910–1994) | Pietermaritzburg | 2,430,753 |  |
| Orange Free State (1910–1994) | Bloemfontein | 2,193,062 |  |
| Transvaal (1910–1994) | Pretoria | 9,491,265 | 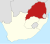 |
| Homelands | Capital | Peak population | Location |
| Bophuthatswana (1977–1994) † | Mmabatho | 1,478,950 | 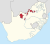 |
| Ciskei (1972–1994) † | Bisho | 677,920 | 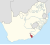 |
| Gazankulu (1971–1994) | Giyani | 954,771 | 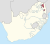 |
| KaNgwane (1981–1994) | Louieville Schoemansdal (de facto) | 779,240 |  |
| KwaNdebele (1981–1994) | KwaMhlanga | 404,246 |  |
| KwaZulu (1981–1994) | Nongoma (until 1980) Ulundi (1980–1994) | 5,524,774 | 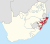 |
| Lebowa (1972–1994) | Lebowakgomo | 2,740,587 | 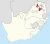 |
| QwaQwa (1974–1994) | Phuthaditjhaba | 342,886 | 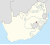 |
| Transkei (1976–1994) † | Umtata | 2,323,650 |  |
| Venda (1979–1994) † | Thohoyandou | 558,797 | 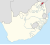 |
| Mandates | Capital | Peak population | |
| South West Africa | Windhoek | 1,415,000 |
Footnotes:
- † States for which the homeland was quasi-independent.
See also
- Elections in South Africa
- List of municipalities in South Africa
- List of renamed places in South Africa
- List of South African provinces by Human Development Index
- Members of the Executive Council (MEC)
- Municipalities of South Africa
- Premier (South Africa)
- Prince Edward Islands
- Proposals for South Africa to annex Lesotho
- Provincial governments of South Africa
- Provincial legislature (South Africa)
- Telephone numbers in South Africa
- Vehicle registration plates of South Africa
- Walvis Bay
- ISO 3166-2:ZA
