Synucleinopathies (also called α-Synucleinopathies) are neurodegenerative diseases characterised by the abnormal accumulation of aggregates of alpha-synuclein protein in neurons, nerve fibres or glial cells.[1] There are three main types of synucleinopathy: Parkinson's disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA).[1] Other rare disorders, such as various neuroaxonal dystrophies, also have α-synuclein pathologies.[2] Additionally, autopsy studies have shown that around 6% of sporadic Alzheimer's Disease exhibit α-synuclein positive Lewy pathology, and are sub-classed as Alzheimer's Disease with Amygdalar Restricted Lewy Bodies (AD/ALB).[3][4][5][6][7]
| Synucleinopathy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | α-Synucleinopathies |
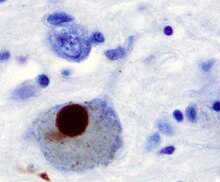 | |
| Positive α-Synuclein staining of a Lewy body in a patient with Parkinson's disease. | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Presentation
The synucleinopathies have shared features of parkinsonism, impaired cognition, sleep disorders, and visual hallucinations.[8]
Synucleinopathies can sometimes overlap with tauopathies, possibly because of interaction between the synuclein and tau proteins.[9]
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a parasomnia in which individuals with RBD lose the paralysis of muscles (atonia) that is normal during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, and act out their dreams or have other abnormal movements or vocalizations.[10] Abnormal sleep behaviors may appear decades before any other symptoms, often as an early sign of a synucleinopathy.[11] On autopsy, 94 to 98% of individuals with polysomnography-confirmed RBD are found to have a synucleinopathy—most commonly DLB or PD.[10][12][13] Other symptoms of the specific synucleinopathy usually manifest within 15 years of the diagnosis of RBD,[14] but may emerge up to 50 years after RBD diagnosis.[10]
Alpha-synuclein deposits can affect the cardiac muscle and blood vessels.[15] Almost all people with synucleinopathies have cardiovascular dysfunction, although most are asymptomatic.[15]
From chewing to defecation, alpha-synuclein deposits affect every level of gastrointestinal function. Symptoms include upper gastrointestinal tract dysfunction such as delayed gastric emptying or lower gastrointestinal dysfunction, such as constipation and prolonged stool transit time.[15]
Urinary retention, waking at night to urinate, increased urinary frequency and urgency, and over- or underactive bladder are common in people with synucleinopathies.[15] Sexual dysfunction usually appears early in synucleinopathies, and may include erectile dysfunction, and difficulties achieving orgasm or ejaculating.[15]
Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
Persons with PD are typically less caught up in their visual hallucinations than those with DLB.[16] There is a lower incidence of tremor at rest in DLB than in PD, and signs of parkinsonism in DLB are more symmetrical.[11] In MSA, autonomic dysfunction appears earlier and is more severe, and is accompanied by uncoordinated movements, while visual hallucinations and fluctuating cognition are less common than in DLB.[17] Urinary difficulties are one of the earliest symptoms with MSA, and are often severe.[15]
DNA damage
Alpha-synuclein modulates DNA repair processes, including the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by the non-homologous end joining pathway.[18] The DNA repair function of alpha-synuclein appears to be compromised in Lewy body inclusion bearing neurons, and this may trigger cell death. Study of synucleinopathy mouse models of Parkinson's disease indicates that alpha-synuclein pathogenesis is associated with increased DNA damage and activation of the DNA damage response.[19]