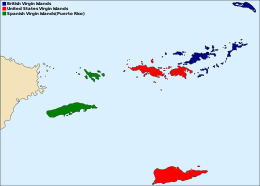
The Virgin Islands (Spanish: Islas Vírgenes) are an archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. They are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles,[1] While the British Virgin Islands are officially designated as “The Virgin Islands”, the name is most often used to refer to the entire international grouping of the British and United States Virgin Islands together with the Spanish Virgin Islands, which, contrary to their name are in fact officially part of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, itself an unincorporated territory of the United States. Geographically, the northern islands belong to the Puerto Rico Trench. St. Croix is a displaced part of that same geologic structure. Politically, the British Virgin Islands have been governed as the western island group of the Leeward Islands, which are the northern part of the Lesser Antilles, and form the border between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The archipelago is separated from the true Lesser Antilles by the Anegada Passage and from the main island of Puerto Rico by the Virgin Passage.
 | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Caribbean Sea, Atlantic Ocean |
| Coordinates | 18°12′N 64°48′W / 18.2°N 64.8°W |
| Archipelago | Leeward Islands |
| Insular area | United States Virgin Islands |
| Insular area | Puerto Rico |
| Overseas territory | British Virgin Islands |
The islands fall into three different political jurisdictions:
- Virgin Islands, informally referred to as British Virgin Islands, a British overseas territory,
- Virgin Islands of the United States, an unincorporated territory of the United States,
- Spanish Virgin Islands, the easternmost islands of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, itself also an unincorporated territory of the United States.
Etymology


Christopher Columbus named the islands after Saint Ursula and the 11,000 Virgins (Spanish: Santa Úrsula y las Once Mil Vírgenes), shortened to the Virgins (las Vírgenes). The official name of the British territory is the Virgin Islands, and the official name of the U.S. territory is the Virgin Islands of the United States. In practice, the two island groups are almost universally referred to as the British Virgin Islands and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
History
The Virgin Islands were originally inhabited by the Arawak and Carib, many of whom are thought to have perished during the colonial period due to enslavement, foreign disease, and war brought about by European colonists.[2]
European colonists later settled here and established sugar plantations, at least one tobacco plantation, and bought slaves from Africa. The descendants of the enslaved people remain the bulk of the population, sharing a common African-Caribbean heritage with the rest of the English-speaking Caribbean.
Like mainland Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands that belonged to Spain were ceded to the United States in 1898. The United States took possession of the islands after the signing of the armistice that put an end to military operations in the Spanish–American War.
A 1916 treaty between the United States and Denmark (not ratified by the United States until 1917) resulted in Denmark selling the Danish Virgin Islands to the United States for $25 million in gold.
Historical affiliations
The Virgin Islands have been under the sovereignty of several nations and groups throughout history. Below is a table which represents the affiliation of the various islands:
*Largely under control of pirates
**Coexisting claim
***Leased/shared territory
Demography
The total population of the Virgin Islands is 147,778: 104,901 in the U.S. Virgin Islands, 31,758 in the British, and 11,119 in the Spanish. Roughly three-quarters of islanders are black in the British and U.S. Virgin Islands, while the majority of inhabitants in Culebra and Vieques are Puerto Rican of European descent, with a significant Afro-Puerto Rican community. The main languages are English and Virgin Islands Creole in the U.S. and British Virgin Islands, and Spanish in the Puerto Rican territory. St. Thomas is the most populous island, with St. Croix close behind (51,634 and 50,601, respectively).
| Name | Sovereign State | Subdivisions | Area (km2) | Population (2005 est.) | Population density (per km2) | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| British Virgin Islands | United Kingdom | Districts | 153.0 | 31,758 | 207.6 | Road Town |
| Spanish Virgin Islands (Puerto Rico) | United States | Barrios | 165.1 | 11,119 | 67.3 | San Juan, PR |
| United States Virgin Islands | United States | Districts | 346.4 | 104,901 | 302.8 | Charlotte Amalie |
| Total | 664.5 | 147,778 | 222.4 |
Traffic control
Motor vehicles are driven on the left-hand side of the road in both the British and the U.S. Virgin Islands, although the steering wheels on most cars are located on the left side (as is the norm for drive-on-the-right localities). In the Spanish Virgin Islands, vehicles are driven on the right-hand side of the road.
See also
Citations
General sources
- Colin Thomas, J.; Allard, William Albert; Wolinsky, Cary (February 1981). "Paradise Comes of Age: The U.S. Virgin Islands". National Geographic. Vol. 159, no. 2. pp. 225–243.
External links

Virgin Islands.