Western Armenia (Western Armenian: Արեւմտեան Հայաստան, Arevmdian Hayasdan) is a term to refer to the western parts of the Armenian highlands located within Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that comprise the historical homeland of the Armenians.[2] Western Armenia, also referred to as Byzantine Armenia, emerged following the division of Greater Armenia between the Byzantine Empire (Western Armenia) and Sassanid Persia (Eastern Armenia) in AD 387. Since the Armenian genocide, the Armenian diaspora as well as Armenians indigenous to modern Turkey have sought political representation in Western Armenia[3][4] or reunification with the Republic of Armenia.


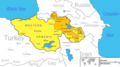
Orange: areas overwhelmingly populated by Armenians (Republic of Armenia: 98%;[1] Nagorno-Karabakh: 99%; Javakheti: 95%)
Yellow: Historically Armenian areas with presently no or insignificant Armenian population (Western Armenia and Nakhichevan)
The area was conquered by the Ottomans in the 16th century during the Ottoman–Safavid War (1532–1555) against their Iranian Safavid arch-rivals. Being passed on from the former to the latter, Ottoman rule over the region became only decisive after the Ottoman–Safavid War of 1623–1639.[5] The area then became known also as Turkish Armenia[6] or Ottoman Armenia.[7] During the 19th century, the Russian Empire conquered all of Eastern Armenia from Iran,[8] and also some parts of Turkish Armenia, such as Kars. The region's Armenian population was affected during the widespread massacres of Armenians in the 1890s.
The Armenians living in their ancestral lands were exterminated or deported by Ottoman forces during the 1915 Armenian genocide and over the following years. The systematic destruction of Armenian cultural heritage, which had endured over 4000 years,[9][10] is considered an example of cultural genocide.[11][12]
Since 2000, an organizing committee of the congress of heirs of Western Armenians who survived the Armenian genocide is active in diasporan communities.[13] On August 10, 2020, the three traditional Armenian parties—the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (ARF, Dashnaks), Social Democrat Hunchakian Party (Hunchaks) and the Armenian Democratic Liberal Party (Ramgavars)—issued a joint statement on the centenary of the Sèvres Treaty, stating that the treaty is the only international document defining the border between Armenia and Turkey. "The Treaty of Sevres is a valid international treaty, although it has not been ratified by all signatories, but it has not been legally replaced by any other international instrument. At least from the point of view of the rights of the Armenian Cause, the Republic of Armenia and the Armenian nation, it remains a promissory note based on international law."[14]
Etymology

In the Armenian language, there are several names for the region. Today, the most common is Arevmtyan Hayastan (Արևմտյան Հայաստան) in Eastern Armenian (mostly spoken in Armenia, Russia, Georgia, Iran) and Arevmdean Hayasdan (Արեւմտեան Հայաստան) in Western Armenian (spoken in the Diaspora: US, France, Lebanon, Syria, Argentina, etc.). Archaic names (used before the 1920s) include Tačkahayastan (Տաճկահայաստան) in Eastern and Daǰkahayasdan in Western Armenian. Also used in the same period were T'urk'ahayastan (Թուրքահայաստան) or T'rk'ahayastan (Թրքահայաստան), both meaning Turkish Armenia.[18]
In the Turkish language, the literal translation of Western Armenia is Batı Ermenistan. The region has been officially described as Eastern Anatolia (Doğu Anadolu) since the seven geographical regions of Turkey were defined at the 1941 First Geography Congress. Throughout much of recorded history the eastern boundary of Anatolia was not considered to extend as far as the Araxes, the river which marks the present day boundary between the states of Armenia and Iran.[19] Kurds refer to the southern parts of region as Bakurê Kurdistanê (Northern Kurdistan).[citation needed]
History
Ottoman conquest
After the Ottoman-Persian War (1623–1639), Western Armenia became decisively part of the Ottoman Empire.[5] After the Russo-Turkish War, 1828–1829, the term "Western Armenia" referred to the Armenian-populated historical regions of the Ottoman Empire that remained under Ottoman rule after the eastern part of Armenia was ceded to the Russian Empire by the Qajar Persians, following the Russo-Persian War (1804–1813) and Russo-Persian War (1826–1828).[20]
Western (Ottoman) Armenia consisted of six vilayets (vilâyat-ı sitte): the vilayets of Erzurum, Van, Bitlis, Diyarbekir, Kharput, and Sivas.[21]
The fate of Western Armenia – commonly referred to as "The Armenian Question" – is considered a key issue in the modern history of the Armenian people.[22]
World War I and later years

Armenian genocide
In 1894–1896 and 1915 the Ottoman Empire perpetrated systematic massacres and forced deportations of Armenians[23] resulting in the Armenian genocide.The massive deportation and killings of Armenians began in the spring 1915. On 24 April 1915, Armenian intellectuals and community leaders were deported from Constantinople. Depending on the sources cited, about 1,500,000 Armenians were killed during this act.
Caucasus campaign
During the Caucasus campaign of World War I, the Russian Empire occupied most of the Armenian-populated regions of the Ottoman Empire. A temporary provincial government was established in occupied areas between 1915 and 1918.
The chaos caused by the Russian Revolution of 1917 put a stop to all Russian military operations and Russian forces began to conduct withdrawals. The first and second congresses of Western Armenians took place in Yerevan in 1917 and 1919.[24]
Sazonov–Paléologue Agreement
The Sazonov–Paléologue Agreement of 26 April 1916 between Russian Foreign minister Sergey Sazonov and French ambassador to Russia Maurice Paléologue proposed to give Western Armenia to Russia in return for Russian assent to the Sykes–Picot agreement.[25][26]
Current situation

Currently, Armenia does not have any territorial claims against Turkey, although one political party, the Armenian Revolutionary Federation, the largest Armenian party in the diaspora, claims the area given to the Republic of Armenia (1918–1920) by US President Woodrow Wilson's arbitral award as part of the Treaty of Sèvres in 1920, also known as Wilsonian Armenia.
Since 2000, an organizing committee of the congress of heirs of Western Armenians who survived the Armenian genocide is active in diasporan communities.[13]
A 2014 survey in Armenia asked what kind of demands should Armenia make to Turkey. Some 80% agreed that Armenia should make territorial claims (30% said only territorial claims, while another 50% said territorial, moral, financial, and proprietary). Only 5.5% said no demands should be made.[27] According to a 2012 survey, 36% of Armenians asked agree or somewhat agree that Turkish recognition of the Armenian Genocide will result in territorial compensation, while 45% believe it will not.[28] The online publication Barometer.am wrote: "It appears that our pragmatic population believes that all possible demands should be forwarded to Turkey [...] but a relative majority consider the practical realization of territorial claims to Turkey is unrealistic."[27]
Territories claimed

| Area | Part of | Area (km2) | Population | Armenians | % Armenian | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Armenia |  Turkey Turkey | 132,967 | 6,461,400 | 70.000[29] | 0.09 | 2009 estimate[30] |
Gallery
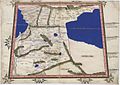
- Western Armenia the first half of the 18th century. Herman Moll's map,1736.
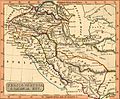
- Armenia Turkomania on 1810 map.
- Persis, Parthia, Armenia. Rest Fenner, published in 1835.
- The Six Armenian vilayets (provinces) of the Ottoman Empire were defined as Western Armenia.
- Autonomous Armenian province within the Ottoman Empire, proposed by the Russian Empire, the Armenian National Assembly and the Armenian Catholicosate in 1913.
- Armenian reform package in Ottoman Empire, finally signed by representatives of the Ottoman Empire and the Russian Empire on February 8, 1914, and providing for the creation of 2 provinces under the control of inspectors general appointed by the Great Powers.
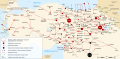
- Armenian genocide: map of massacre locations and deportation and extermination centers.
- The area of Russian occupation of Western Armenia in summer 1916 (Russian map).
- The area of Russian occupation of that region in summer 1916.
- Administrative-territorial division of Western Armenia, occupied by Russian troops in 1915-1917 .
- USSR (Armenian SSR and Georgian SSR) territorial claims against Turkey 1945–1953.
- The modern concept of United Armenia as used by Woodrow Wilson and the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (Dashnaktsutyun).
- Early 1600s spread of Armenians, a few decades after Ottoman conquest, within modern Turkey, per the State Committee of the Real Estate Cadastre of Armenia[31]
See also
Notes
References
Further reading
- Arman J. Kirakosian, "English Policy towards Western Armenia and Public Opinion in Great Britain (1890–1900)", Yerevan, 1981, 26 p. (in Armenian and Russian).
- Armen Ayvazyan, "Western Armenia vs Eastern Anatolia", Europe & Orient – n°4, 2007