Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1C subunit (also known as Cav1.2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACNA1C gene.[5] Cav1.2 is a subunit of L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel.[6]
Structure and function
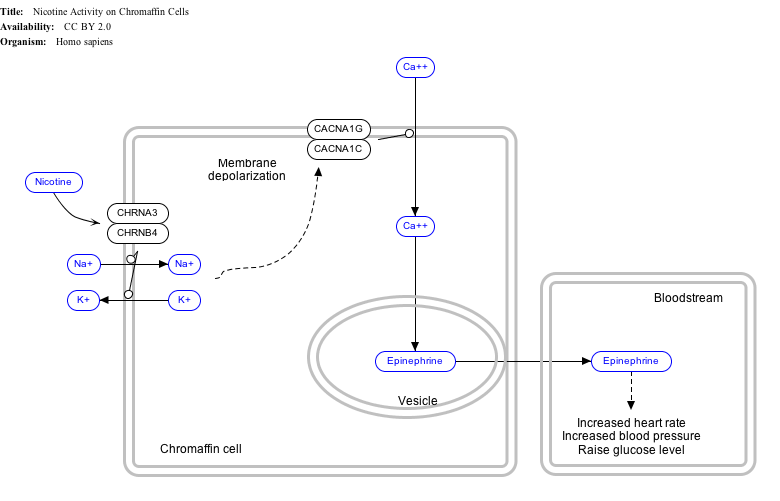
This gene encodes an alpha-1 subunit of a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions (Ca2+) into the cell upon membrane polarization (see membrane potential and calcium in biology).[7]
The alpha-1 subunit consists of 24 transmembrane segments and forms the pore through which ions pass into the cell. The calcium channel consists of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta and beta subunits in a 1:1:1 ratio. The S3-S4 linkers of Cav1.2 determine the gating phenotype and modulated gating kinetics of the channel.[8] Cav1.2 is widely expressed in the smooth muscle, pancreatic cells, fibroblasts, and neurons.[9][10] However, it is particularly important and well known for its expression in the heart where it mediates L-type currents, which causes calcium-induced calcium release from the ER Stores via ryanodine receptors. It depolarizes at -30mV and helps define the shape of the action potential in cardiac and smooth muscle.[8] The protein encoded by this gene binds to and is inhibited by dihydropyridine.[11] In the arteries of the brain, high levels of calcium in mitochondria elevates activity of nuclear factor kappa B NF-κB and transcription of CACNA1c and functional Cav1.2 expression increases.[12] Cav1.2 also regulates levels of osteoprotegerin.[13]
Regulation
The activity of CaV1.2 channels is tightly regulated by the Ca2+ signals they produce. An increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration implicated in Cav1.2 facilitation, a form of positive feedback called Ca2+-dependent facilitation, that amplifies Ca2+ influx. In addition, increasing influx intracellular Ca2+ concentration has implicated to exert the opposite effect Ca2+ dependent inactivation.[15] These activation and inactivation mechanisms both involve Ca2+ binding to calmodulin (CaM) in the IQ domain in the C-terminal tail of these channels.[16] Cav1.2 channels are arranged in cluster of eight, on average, in the cell membrane. When calcium ions bind to calmodulin, which in turn binds to a Cav1.2 channel, it allows the Cav1.2 channels within a cluster to interact with each other.[17] This results in channels working cooperatively when they open at the same time to allow more calcium ions to enter and then close together to allow the cell to relax.[17]

Clinical significance
Mutation in the CACNA1C gene, the single-nucleotide polymorphism located in the third intron of the Cav1.2 gene,[18] are associated with a variant of Long QT syndrome called Timothy's syndrome[19] and more broadly with other CACNA1C-related disorders,[19] and also with Brugada syndrome.[20] Large-scale genetic analyses have shown the possibility that CACNA1C is associated with bipolar disorder[21] and subsequently also with schizophrenia.[22][23][24] Also, a CACNA1C risk allele has been associated to a disruption in brain connectivity in patients with bipolar disorder, while not or only to a minor degree, in their unaffected relatives or healthy controls.[25].In a first study in Indian population, the Schizophrenia associated Genome-wide association study (GWAS) SNP was found not to be associated with the disease. Furthermore, the main effect of rs1006737 was found to be associated with spatial abilityefficiency scores. Subjects with genotypes carrying the risk allele of rs1006737 (G/A and A/A) were found to have higher spatial abilityefficiency scores as compared to those with the G/G genotype. While in healthy controls those with G/A and A/A genotypes were found to have higher spatial memoryprocessing speed scores than those with G/G genotypes, the former had lower scores than the latter in schizophrenia subjects. In the same study the genotypes with the risk allele of rs1006737 namely A/A was associated with a significantly lower Align rank transformed Abnormal and involuntary movement scale(AIMS) scores of Tardive dyskinesia(TD).[26]
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective Wikipedia articles. [§ 1]
See also
References
Further reading
External links
- GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on Brugada syndrome
- CACNA1C+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on Timothy Syndrome
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.