India is the most populous country in the world with one-sixth of the world's population. According to estimates from the United Nations (UN), India has overtaken China as the country with the largest population in the world, with a population of 1,425,775,850 at the end of April 2023.[6][7][8][9]
| Demographics of India | |
|---|---|
 India population pyramid in 2020 | |
| Population | |
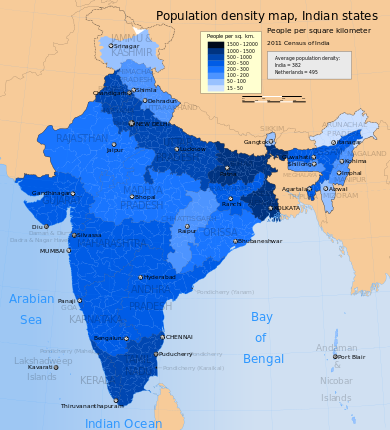
| Density | 473.42 people per.km2 (2021 est.)[2] |
| Growth rate | 0.68% (2022 est.)[2] |
| Birth rate | 16.1 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)[2] |
| Death rate | 6.6 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)[2] |
| Life expectancy | |
| • male | 70.5 years (2023 est.) |
| • female | 73.6 years (2023 est.) |
| Fertility rate | |
| Infant mortality rate | 29.94 deaths/1,000 live births (2018)[4] |
| Age structure | |
| 0–14 years | 25.68% (male 183,695,000/female 166,295,000) (2021 est.) |
| 15–64 years | 67.49% (male 472,653,000/female 447,337,000) (2021 est.) |
| 65 and over | 6.83% (male 44,275,000/female 48,751,000) (2021 est.) |
| Sex ratio | |
| Total | 1.06 male(s)/female (2023)[5] |
| At birth | 1.1 male(s)/female (2023)[5] |
| Under 15 | 1.11 male(s)/female (2023)[5] |
| 15–64 years | 1.07 male(s)/female (2023 est.) |
| 65 and over | 0.85 male(s)/female (2023)[5] |
| Nationality | |
| Major ethnic | See Ethnic groups of India |
| Language | |
| Official | See Languages of India |
| Spoken | |
Between 1975 and 2010, the population doubled to 1.2 billion, reaching the billion mark in 2000. According to the UN's World Population dashboard, India's population now stands at slightly over 1.428 billion, edging past China's population of 1.425 billion people, as reported by the news agency Bloomberg.[9] Its population is set to reach 1.7 billion by 2050.[10][11] In 2017 its population growth rate was 0.98%, ranking 112th in the world; in contrast, from 1972 to 1983, India's population grew by an annual rate of 2.3%.[12]
In 2022, the median age of an Indian was 28.7 years,[13] compared to 38.4 for China and 48.6 for Japan; and, by 2030; India's dependency ratio will be just over 0.4.[14] However, the number of children in India peaked more than a decade ago and is now falling. The number of children under the age of five peaked in 2007, and since then the number has been falling. The number of Indians under 15 years old peaked slightly later (in 2011) and is now also declining.[15]
India has many ethnic groups,[16] and every major religion is represented, as are four major families of languages (Indo-European, Dravidian, Austroasiatic and Sino-Tibetan languages) as well as two language isolates: the Nihali language,[17] spoken in parts of Maharashtra, and the Burushaski language, spoken in parts of Jammu and Kashmir. 1,000,000 people in India are Anglo-Indians and 700,000 United States citizens are living in India.[18] They represent over 0.1% of the total population of India. Overall, only the continent of Africa exceeds the linguistic, genetic and cultural diversity of the nation of India.[19]
The sex ratio was 944 females for 1000 males in 2016, and 940 per 1000 in 2011.[20] This ratio has been showing an upwards trend for the last two decades after a continuous decline in the 20th century.[21]
History

Prehistory to early 19th century
The following table lists estimates for the population of India (including what are now Pakistan and Bangladesh) from prehistory up until 1820. It includes estimates and growth rates according to five economic historians, along with interpolated estimates and overall aggregate averages derived from their estimates.[22][23]
| Year | Maddison (2001)[24] | Clark (1967)[25][26][27] | Biraben (1979)[26][28][29] | Durand (1974)[30][26] | McEvedy (1978)[31][26] | Aggregate average | Period | Average % growth / century | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | % growth / century | Population | % growth / century | Population | % growth / century | Population | % growth / century | Population | % growth / century | Population | % growth / century | |||
| 10,000 BC | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 100,000 | — | 100,000 | — | Stone Age | 3.9 |
| 4000 BC | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,000,000 | 3.9 | 1,000,000 | 3.9 | ||
| 2000 BC | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 6,000,000 | 9.4 | 6,000,000 | 9.4 | Bronze Age | 9.4 |
| 500 BC | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 25,000,000 | 10 | 25,000,000 | 10 | Iron Age | 10.2 |
| 400 BC | — | — | — | — | 30,000,000 | — | — | — | 26,600,000 | 6.3 | 28,300,000 | 13.2 | ||
| 200 BC | — | — | — | — | 55,000,000 | 35.4 | — | — | 30,000,000 | 6.3 | 42,500,000 | 22.5 | Maurya era | 22.5 |
| 1 AD | 75,000,000 | — | 70,000,000 | — | 46,000,000 | –9.3 | 75,000,000 | — | 34,000,000 | 6.5 | 60,000,000 | 18.8 | Classical era | 5.3 |
| 200 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 72,500,000 | 1.7 | 45,000,000 | –1.1 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 39,000,000 | 7.1 | 61,300,000 | 1.1 | ||
| 400 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 75,000,000 | 1.7 | 32,000,000 | –18.6 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 45,000,000 | 7.4 | 60,400,000 | –0.7 | ||
| 500 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 33,000,000 | 3.1 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 48,000,000 | 6.5 | 61,200,000 | 1.3 | ||
| 600 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 37,000,000 | 12.1 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 51,000,000 | 6.5 | 62,600,000 | 2.3 | Early medieval era | 1.9 |
| 700 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 50,000,000 | 35.1 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 56,500,000 | 10.3 | 66,300,000 | 5.9 | ||
| 800 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 43,000,000 | –16.3 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 62,000,000 | 10.3 | 66,000,000 | –0.5 | ||
| 900 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 72,500,000 | –3.5 | 38,000,000 | –13.2 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 69,500,000 | 11.4 | 66,000,000 | 0 | ||
| 1000 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 70,000,000 | –3.5 | 40,000,000 | 5.3 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 77,000,000 | 11.4 | 67,400,000 | 2.1 | ||
| 1100 | 81,000,000 | 8 | 72,500,000 | 3.5 | 51,000,000 | 27.5 | 81,300,000 | 8.4 | 80,000,000 | 3.9 | 73,200,000 | 8.6 | Late medieval era | 8.1 |
| 1200 | 87,500,000 | 8 | 75,000,000 | 3.5 | 65,100,000 | 27.5 | 88,200,000 | 8.4 | 83,000,000 | 3.8 | 79,800,000 | 9 | ||
| 1300 | 94,500,000 | 8 | 75,000,000 | 0 | 83,000,000 | 27.5 | 95,700,000 | 8.4 | 88,000,000 | 6 | 87,200,000 | 9.3 | ||
| 1400 | 102,000,000 | 8 | 77,000,000 | 3.3 | 88,800,000 | 7 | 103,700,000 | 8.4 | 94,000,000 | 6.8 | 92,900,000 | 7 | ||
| 1500 | 110,000,000 | 8 | 79,000,000 | 3.3 | 95,000,000 | 7 | 112,500,000 | 8.4 | 100,000,000 | 6.4 | 99,300,000 | 7 | ||
| 1600 | 135,000,000 | 22.8 | 100,000,000 | 26.6 | 145,000,000 | 52.6 | 135,800,000 | 20.7 | 130,000,000 | 30 | 129,200,000 | 30.1 | Mughal era | 31.9 |
| 1650 | 150,000,000 | 22.2 | 150,000,000 | 125 | 160,000,000 | 20.7 | 149,100,000 | 20.7 | 145,000,000 | 24.4 | 150,800,000 | 36.2 | ||
| 1700 | 165,000,000 | 22.2 | 200,000,000 | 77.8 | 175,000,000 | 20.7 | 163,900,000 | 20.7 | 160,000,000 | 21.8 | 172,800,000 | 31.3 | ||
| 1750 | 182,100,000 | 21.8 | 200,000,000 | 0 | 182,700,000 | 9 | 180,000,000 | 20.7 | 170,000,000 | 12.9 | 183,000,000 | 12.1 | Colonial era | 12.2 |
| 1800 | 200,900,000 | 21.8 | 190,000,000 | –10.8 | 190,700,000 | 9 | — | — | 185,000,000 | 18.4 | 190,400,000 | 8 | ||
| 1820 | 209,000,000 | 21.8 | 190,000,000 | 0 | 194,000,000 | 9 | — | — | 200,000,000 | 47.7 | 198,300,000 | 22 | ||
The population grew from the South Asian Stone Age in 10,000 BC to the Maurya Empire in 200 BC at a steadily increasing growth rate,[32] before population growth slowed down in the classical era up to 500 AD, and then became largely stagnant during the early medieval era era up to 1000 AD.[24][26] The population growth rate then increased in the late medieval era (during the Delhi Sultanate) from 1000 to 1500.[24][26]
Under the Mughal Empire, India experienced a high economic and demographic upsurge,[32] due to Mughal agrarian reforms that intensified agricultural production.[33] 15% of the population lived in urban centres, higher than the percentage of the population in 19th-century British India[34] and contemporary Europe[34] up until the 19th century.[35] These estimates by Abraham Eraly[34] and Paolo Malanima[35] have been criticised by Tim Dyson, who considers them exaggerations and estimates urbanisation of the Mughal Empire to be less than 9% of the population.[36]
Under the reign of Akbar (reigned 1556–1605) in 1600, the Mughal Empire's urban population was up to 17 million people, larger than the urban population in Europe.[37] By 1700, Mughal India had an urban population of 23 million people, larger than British India's urban population of 22.3 million in 1871.[38] Nizamuddin Ahmad (1551–1621) reported that, under Akbar's reign, Mughal India had 120 large cities and 3,200 townships.[34] A number of cities in India had a population between a quarter-million and half-million people,[34] with larger cities including Agra (in Agra Subah) with up to 800,000 people[39] and Dhaka (in Bengal Subah) with over 1 million people.[40] Mughal India also had a large number of villages, with 455,698 villages by the time of Aurangzeb (reigned 1658–1707).[37]
Late 19th century to early 20th century
The total fertility rate is the number of children born per woman. It is based on fairly good data for the entire years. Sources: Our World in Data and Gapminder Foundation.[41]
| Years | 1880 | 1881 | 1882 | 1883 | 1884 | 1885 | 1886 | 1887 | 1888 | 1889 | 1890 | 1902[41] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Fertility Rate in India | 5.95 | 5.92 | 5.89 | 5.86 | 5.82 | 5.79 | 4.38 | 5.76 | 5.76 | 5.75 | 5.75 | 5.75 |
| Years | 1921 | 1922 | 1923 | 1924 | 1925 | 1926 | 1927 | 1928 | 1929 | 1930[41] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Fertility Rate in India | 5.761 | 5.77 | 5.78 | 5.79 | 5.8 | 5.81 | 5.82 | 5.83 | 5.85 | 5.86 |
Life expectancy from 1881 to 1950
| Years | 1881 | 1891 | 1901 | 1905 | 1911 | 1915 | 1921 | 1925 | 1931 | 1935 | 1941 | 1950[42] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy in India | 25.4 | 24.3 | 23.5 | 24.0 | 23.2 | 24.0 | 24.9 | 27.6 | 29.3 | 31.0 | 32.6 | 35.4 |
The population of India under the British Raj (including what are now Pakistan and Bangladesh) according to censuses:
| Census year | Population | Growth (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1871[43] | 238,830,958 | – |
| 1881[44] | 253,896,330 | 6.3 |
| 1891[43] | 287,223,431 | 13.1 |
| 1901[43] | 293,550,310 | 2.2 |
| 1911[45] | 315,156,396 | 7.4 |
| 1921[45] | 318,942,480 | 1.2 |
| 1931[45] | 352,837,778 | 10.6 |
| 1941[45] | 388,997,955 | 10.2 |
Studies of India's population since 1881 have focused on such topics as total population, birth and death rates, geographic distribution, literacy, the rural and urban divide, cities of a million, and the three cities with populations over eight million: Delhi, Greater Mumbai (Bombay), and Kolkata (Calcutta).[46]
Mortality rates fell in the period 1920–45, primarily due to biological immunisation. Suggestions that it was the benefits of colonialism are refuted by academic thinking: "There can be no serious, informed belief… that… late colonial era mortality diminished and population grew rapidly because of improvements in income, living standards, nutrition, environmental standards, sanitation or health policies, nor was there a cultural transformation…".[47]
Salient features

(per 1000 people, national average)[48][49][50]

(per 1000 births, under age 1, national average)
India occupies 2.41% of the world's land area but supports over 18% of the world's population. At the 2001 census 72.2% of the population[51] lived in about 638,000 villages[52] and the remaining 27.8%[51] lived in more than 5,100 towns and over 380 urban agglomerations.[53]
India's population exceeded that of the entire continent of Africa by 200 million people in 2010.[54] However, because Africa's population growth is extremely high compared to the rest of the world,[55][56] it is expected to surpass both China and India by the early 2030s.[57]
Comparative demographics
| Category | Global ranking | References |
|---|---|---|
| Area | 7th | [58] |
| Population | 1st | [58] |
| Population growth rate | 102nd of 212 | in 2010[59] |
| Population density | 24th of 212 | in 2010[59] |
| Male to Female ratio, at birth | 12th of 214 | in 2009[60] |
List of states and union territories by demographics
| Census year | Population | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1951 | 361,088,003 | – |
| 1961 | 439,235,000 | 21.6 |
| 1971 | 548,160,000 | 24.8 |
| 1981 | 683,329,000 | 24.7 |
| 1991 | 846,387,888 | 23.9 |
| 2001 | 1,028,737,436 | 21.5 |
| 2011 | 1,210,193,422 | 17.7 |
| Rank | State/UT | Population[62] | Percent (%) | Male | Female | Difference between male and female | Sex ratio | Rural[63] | Urban[63] | Area[64] (km2) | Density (per km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Uttar Pradesh | 199,812,341 | 16.50 | 104,480,510 | 95,331,831 | 9,148,679 | 930 | 155,111,022 | 44,470,455 | 240,928 | 828 |
| 2 | Maharashtra | 112,374,333 | 9.28 | 58,243,056 | 54,131,277 | 4,111,779 | 929 | 61,545,441 | 50,827,531 | 307,713 | 365 |
| 3 | Bihar | 104,099,452 | 8.60 | 54,278,157 | 49,821,295 | 4,456,862 | 918 | 92,075,028 | 11,729,609 | 94,163 | 1,102 |
| 4 | West Bengal | 91,276,115 | 7.54 | 46,809,027 | 44,467,088 | 2,341,939 | 950 | 62,213,676 | 29,134,060 | 88,752 | 1,030 |
| 5 | Madhya Pradesh | 72,626,809 | 6.00 | 37,612,306 | 35,014,503 | 2,597,803 | 931 | 52,537,899 | 20,059,666 | 308,245 | 236 |
| 6 | Tamil Nadu | 72,147,030 | 5.96 | 36,137,975 | 36,009,055 | 128,920 | 996 | 37,189,229 | 34,949,729 | 130,058 | 555 |
| 7 | Rajasthan | 68,548,437 | 5.66 | 35,550,997 | 32,997,440 | 2,553,557 | 928 | 51,540,236 | 17,080,776 | 342,239 | 201 |
| 8 | Karnataka | 61,095,297 | 5.05 | 30,966,657 | 30,128,640 | 838,017 | 973 | 37,552,529 | 23,578,175 | 191,791 | 319 |
| 9 | Gujarat | 60,439,692 | 4.99 | 31,491,260 | 28,948,432 | 2,542,828 | 919 | 34,670,817 | 25,712,811 | 196,024 | 308 |
| 10 | Andhra Pradesh | 49,386,799 | 4.08 | 24,738,068 | 24,648,731 | 89,337 | 996 | 34,776,389 | 14,610,410 | 160,205 | 308 |
| 11 | Odisha | 41,974,218 | 3.47 | 21,212,136 | 20,762,082 | 450,054 | 979 | 34,951,234 | 6,996,124 | 155,707 | 269 |
| 12 | Telangana | 35,193,978 | 2.91 | 17,704,078 | 17,489,900 | 214,178 | 988 | 21,585,313 | 13,608,665 | 114,840 | 307 |
| 13 | Kerala | 33,406,061 | 2.76 | 16,027,412 | 17,378,649 | −1,351,237 | 1084 | 17,445,506 | 15,932,171 | 38,863 | 859 |
| 14 | Jharkhand | 32,988,134 | 2.72 | 16,930,315 | 16,057,819 | 872,496 | 948 | 25,036,946 | 7,929,292 | 79,714 | 414 |
| 15 | Assam | 31,205,576 | 2.58 | 15,939,443 | 15,266,133 | 673,310 | 958 | 26,780,526 | 4,388,756 | 78,438 | 397 |
| 16 | Punjab | 27,743,338 | 2.29 | 14,639,465 | 13,103,873 | 1,535,592 | 895 | 17,316,800 | 10,387,436 | 50,362 | 550 |
| 17 | Chhattisgarh | 25,545,198 | 2.11 | 12,832,895 | 12,712,303 | 120,592 | 991 | 19,603,658 | 5,936,538 | 135,191 | 189 |
| 18 | Haryana | 25,351,462 | 2.09 | 13,494,734 | 11,856,728 | 1,638,006 | 879 | 16,531,493 | 8,821,588 | 44,212 | 573 |
| 19 | Delhi (UT) | 16,787,941 | 1.39 | 8,887,326 | 7,800,615 | 1,086,711 | 868 | 944,727 | 12,905,780 | 1,484 | 11,297 |
| 20 | Jammu and Kashmir | 12,541,302 | 1.04 | 6,640,662 | 5,900,640 | 740,022 | 889 | 9,134,820 | 3,414,106 | 222,236 | 56 |
| 21 | Uttarakhand | 10,086,292 | 0.83 | 5,137,773 | 4,948,519 | 189,254 | 963 | 7,025,583 | 3,091,169 | 53,483 | 189 |
| 22 | Himachal Pradesh | 6,864,602 | 0.57 | 3,481,873 | 3,382,729 | 99,144 | 972 | 6,167,805 | 688,704 | 55,673 | 123 |
| 23 | Tripura | 3,673,917 | 0.30 | 1,874,376 | 1,799,541 | 74,835 | 960 | 2,710,051 | 960,981 | 10,486 | 350 |
| 24 | Meghalaya | 2,966,889 | 0.25 | 1,491,832 | 1,475,057 | 16,775 | 989 | 2,368,971 | 595,036 | 22,429 | 132 |
| 25 | Manipur | 2,855,794 | 0.24 | 1,438,687 | 1,417,107 | 21,580 | 985 | 1,899,624 | 822,132 | 22,327 | 128 |
| 26 | Nagaland | 1,978,502 | 0.16 | 1,024,649 | 953,853 | 70,796 | 931 | 1,406,861 | 573,741 | 16,579 | 119 |
| 27 | Goa | 1,458,545 | 0.12 | 739,140 | 719,405 | 19,735 | 973 | 551,414 | 906,309 | 3,702 | 394 |
| 28 | Arunachal Pradesh | 1,383,727 | 0.11 | 713,912 | 669,815 | 44,097 | 938 | 1,069,165 | 313,446 | 83,743 | 17 |
| 29 | Puducherry (UT) | 1,247,953 | 0.10 | 612,511 | 635,442 | −22,931 | 1037 | 394,341 | 850,123 | 479 | 2,598 |
| 30 | Mizoram | 1,097,206 | 0.09 | 555,339 | 541,867 | 13,472 | 976 | 529,037 | 561,997 | 21,081 | 52 |
| 31 | Chandigarh (UT) | 1,055,450 | 0.09 | 580,663 | 474,787 | 105,876 | 818 | 29,004 | 1,025,682 | 114 | 9,252 |
| 32 | Sikkim | 610,577 | 0.05 | 323,070 | 287,507 | 35,563 | 890 | 455,962 | 151,726 | 7,096 | 86 |
| 33 | Andaman and Nicobar Islands (UT) | 380,581 | 0.03 | 202,871 | 177,710 | 25,161 | 876 | 244,411 | 135,533 | 8,249 | 46 |
| 34 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli (UT) | 343,709 | 0.03 | 193,760 | 149,949 | 43,811 | 774 | 183,024 | 159,829 | 491 | 698 |
| 35 | Daman and Diu (UT) | 243,247 | 0.02 | 150,301 | 92,946 | 57,355 | 618 | 60,331 | 182,580 | 112 | 2,169 |
| 36 | Lakshadweep (UT) | 64,473 | 0.01 | 33,123 | 31,350 | 1,773 | 946 | 14,121 | 50,308 | 32 | 2,013 |
| – | Total (India) | 1,210,854,977 | 100 | 623,724,248 | 586,469,174 | 35,585,741 | 943 | 833,087,662 | 377,105,760 | 3,287,240 | 382 |
Religious demographics
The table below summarises India's demographics (excluding the Mao-Maram, Paomata and Purul subdivisions of Senapati district of Manipur state due to cancellation of census results) according to religion at the 2011 census in per cent. The data are "unadjusted" (without excluding Assam and Jammu and Kashmir); the 1981 census was not conducted in Assam and the 1991 census was not conducted in Jammu and Kashmir. Missing citing/reference for "Changes in religious demagraphics over time" table below.
|
|
- Characteristics of religious groups[66]
| Religious group | Population (2011) % | Growth (2001–2011)[67][68] | Sex ratio (2011) (total)[69] | Sex ratio (2011) (rural) | Sex ratio (2011) (urban) | Sex ratio (2011) (child)[70] | Literacy (2011) (%)[71] | Work participation (2011) (%)[69][72] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hinduism | 79.80% | 16.8% | 939 | 946 | 921 | 913 | 73.3% | 41.0% |
| Islam | 14.23% | 24.6% | 951 | 957 | 941 | 943 | 68.5% | 32.6% |
| Christianity | 2.30% | 15.5% | 1023 | 1008 | 1046 | 958 | 84.5% | 41.9% |
| Sikhism | 1.72% | 8.4% | 903 | 905 | 898 | 828 | 75.4% | 36.3% |
| Buddhism | 0.70% | 6.1% | 965 | 960 | 973 | 933 | 81.3% | 43.1% |
| Jainism | 0.37% | 5.4% | 954 | 935 | 959 | 889 | 94.9% | 35.5% |
| Others/Religion Not Specified | 0.90% | n/a | 959 | 947 | 975 | 974 | n/a | n/a |

Neonatal and infant demographics

The table below represents the infant mortality rate trends in India, based on sex, over the last 15 years. In the urban areas of India, average male infant mortality rates are slightly higher than average female infant mortality rates.[75]
| Year | Male | Female | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1998[76] | 69.8 | 73.5 | 71.6 |
| 2005[75] | 56.3 | 58 | 57[77] |
| 2009[78] | 49 | 52 | – |
| 2014[79] | 43.7 | 37.90 | 40.7[77] |
| 2018[80] | 29.95 | 29.88 | 29.94[80] |
India's 2011 census shows a serious decline in the number of girls under the age of seven – activists posit that eight million female fetuses may have been aborted between 2001 and 2011.[81]
Population within the age group of 0–6
| State or UT code | State or UT | Total | Male | Female | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jammu and Kashmir | 2,008,670 | 1,080,662 | 927,982 | 152,680 |
| 2 | Himachal Pradesh | 763,864 | 400,681 | 363,183 | 37,498 |
| 3 | Punjab | 2,941,570 | 1,593,262 | 1,348,308 | 244,954 |
| 4 | Chandigarh | 117,953 | 63,187 | 54,766 | 8,421 |
| 5 | Uttarakhand | 1,328,844 | 704,769 | 624,075 | 80,694 |
| 6 | Haryana | 3,297,724 | 1,802,047 | 1,495,677 | 306,370 |
| 7 | Delhi | 1,970,510 | 1,055,735 | 914,775 | 140,960 |
| 8 | Rajasthan | 10,504,916 | 5,580,212 | 4,924,004 | 656,208 |
| 9 | Uttar Pradesh | 29,728,235 | 15,653,175 | 14,075,060 | 1,578,115 |
| 10 | Bihar | 18,582,229 | 9,615,280 | 8,966,949 | 648,331 |
| 11 | Sikkim | 61,077 | 31,418 | 29,659 | 1,759 |
| 12 | Arunachal Pradesh | 202,759 | 103,430 | 99,330 | 4,100 |
| 13 | Nagaland | 285,981 | 147,111 | 138,870 | 8,241 |
| 14 | Manipur | 353,237 | 182,684 | 170,553 | 12,131 |
| 15 | Mizoram | 165,536 | 83,965 | 81,571 | 2,394 |
| 16 | Tripura | 444,055 | 227,354 | 216,701 | 10,653 |
| 17 | Meghalaya | 555,822 | 282,189 | 273,633 | 8,556 |
| 18 | Assam | 4,511,307 | 2,305,088 | 2,206,219 | 98,869 |
| 19 | West Bengal | 10,112,599 | 5,187,264 | 4,925,335 | 261,929 |
| 20 | Jharkhand | 5,237,582 | 2,695,921 | 2,541,661 | 154,260 |
| 21 | Odisha | 5,035,650 | 2,603,208 | 2,432,442 | 170,766 |
| 22 | Chhattisgarh | 3,584,028 | 1,824,987 | 1,759,041 | 65,946 |
| 23 | Madhya Pradesh | 10,548,295 | 5,516,957 | 5,031,338 | 485,619 |
| 24 | Gujarat | 7,564,464 | 3,974,286 | 3,519,890 | 454,396 |
| 25 | Daman and Diu | 25,880 | 13,556 | 12,314 | 1,242 |
| 26 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli | 49,196 | 25,575 | 23,621 | 1,954 |
| 27 | Maharashtra | 12,848,375 | 6,822,262 | 6,026,113 | 796,149 |
| 28 | Andhra Pradesh | 8,642,686 | 4,448,330 | 4,194,356 | 253,974 |
| 29 | Karnataka | 6,855,801 | 3,527,844 | 3,327,957 | 199,887 |
| 30 | Goa | 139,495 | 72,669 | 66,826 | 5,843 |
| 31 | Lakshadweep | 7,088 | 3,715 | 3,373 | 342 |
| 32 | Kerala | 3,322,247 | 1,695,889 | 1,626,358 | 69,531 |
| 33 | Tamil Nadu | 6,894,821 | 3,542,351 | 3,352,470 | 189,881 |
| 34 | Puducherry | 127,610 | 64,932 | 62,678 | 2,254 |
| 35 | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 39,497 | 20,094 | 19,403 | 691 |
| – | Total (India) | 158,789,287 | 82,952,135 | 75,837,152 | 7,114,983 |
Population above the age of seven
| State or UT code | State or UT | Total | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jammu and Kashmir | – | – | – |
| 2 | Himachal Pradesh | – | – | – |
| 3 | Punjab | – | – | – |
| 4 | Chandigarh | – | – | – |
| 5 | Uttarakhand | – | – | – |
| 6 | Haryana | 22,055,357 | 11,703,083 | 10,352,274 |
| 7 | Delhi | 14,782,725 | 7,920,675 | 6,862,050 |
| 8 | Rajasthan | 58,116,096 | 30,039,874 | 28,076,222 |
| 9 | Uttar Pradesh | 169,853,242 | 88,943,240 | 80,910,002 |
| 10 | Bihar | 85,222,408 | 44,570,067 | 40,652,341 |
| 11 | Sikkim | 546,611 | 290,243 | 256,368 |
| 12 | Arunachal Pradesh | 1,179,852 | 616,802 | 563,050 |
| 13 | Nagaland | 1,694,621 | 878,596 | 816,025 |
| 14 | Manipur | 2,368,519 | 1,187,080 | 1,181,439 |
| 15 | Mizoram | 925,478 | 468,374 | 457,104 |
| 16 | Tripura | 3,226,977 | 1,644,513 | 1,582,464 |
| 17 | Meghalaya | 2,408,185 | 1,210,479 | 1,197,706 |
| 18 | Assam | 26,657,965 | 13,649,839 | 13,008,126 |
| 19 | West Bengal | 81,235,137 | 41,740,125 | 39,495,012 |
| 20 | Jharkhand | 27,728,656 | 14,235,767 | 13,492,889 |
| 21 | Odisha | 36,911,708 | 18,598,470 | 18,313,238 |
| 22 | Chhattisgarh | 21,956,168 | 11,002,928 | 10,953,240 |
| 23 | Madhya Pradesh | 62,049,270 | 32,095,963 | 29,953,307 |
| 24 | Gujarat | 52,889,452 | 27,507,996 | 25,381,456 |
| 25 | Daman and Diu | 217,031 | 136,544 | 80,487 |
| 26 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli | 293,657 | 167,603 | 126,054 |
| 27 | Maharashtra | 99,524,597 | 51,539,135 | 47,985,462 |
| 28 | Andhra Pradesh | 76,022,847 | 38,061,551 | 37,961,296 |
| 29 | Karnataka | 54,274,903 | 27,529,898 | 26,745,005 |
| 30 | Goa | 1,318,228 | 668,042 | 650,186 |
| 31 | Lakshadweep | 57,341 | 29,391 | 27,950 |
| 32 | Kerala | – | – | – |
| 33 | Tamil Nadu | 65,244,137 | 32,616,520 | 32,627,617 |
| 34 | Puducherry | 1,116,854 | 545,553 | 571,301 |
| 35 | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 340,447 | 182,236 | 158,211 |
| – | Total (India) | 1,051,404,135 | 540,772,113 | 510,632,022 |
Literacy rate

| State or UT code | State or UT | Overall (%) | Male (%) | Female (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jammu and Kashmir | 68.74 | 76.75 | 58.01 |
| 2 | Himachal Pradesh | 83.78 | 90.83 | 76.60 |
| 3 | Punjab | 86.60 | 81.48 | 71.34 |
| 4 | Chandigarh | 86.43 | 90.54 | 81.38 |
| 5 | Uttarakhand | 79.63 | 88.33 | 70.70 |
| 6 | Haryana | 76.64 | 85.38 | 66.77 |
| 7 | Delhi | 86.34 | 91.03 | 80.93 |
| 8 | Rajasthan | 67.06 | 80.51 | 52.66 |
| 9 | Uttar Pradesh | 69.72 | 79.24 | 59.26 |
| 10 | Bihar | 63.82 | 73.39 | 53.33 |
| 11 | Sikkim | 82.20 | 87.29 | 76.43 |
| 12 | Arunachal Pradesh | 66.95 | 73.69 | 59.57 |
| 13 | Nagaland | 80.11 | 83.29 | 76.69 |
| 14 | Manipur | 79.85 | 86.49 | 73.17 |
| 15 | Mizoram | 91.58 | 93.72 | 89.40 |
| 16 | Tripura | 87.75 | 92.18 | 83.15 |
| 17 | Meghalaya | 75.48 | 77.17 | 73.78 |
| 18 | Assam | 73.18 | 78.81 | 67.27 |
| 19 | West Bengal | 77.08 | 82.67 | 71.16 |
| 20 | Jharkhand | 67.63 | 78.45 | 56.21 |
| 21 | Odisha | 72.90 | 82.40 | 64.36 |
| 22 | Chhattisgarh | 71.04 | 81.45 | 60.59 |
| 23 | Madhya Pradesh | 70.63 | 80.53 | 60.02 |
| 24 | Gujarat | 79.31 | 87.23 | 70.73 |
| 25 | Daman and Diu | 87.07 | 91.48 | 79.59 |
| 26 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli | 77.65 | 86.46 | 65.93 |
| 27 | Maharashtra | 83.20 | 89.82 | 75.48 |
| 28 | Andhra Pradesh[84] | 67.35 | 74.77 | 59.96 |
| 29 | Karnataka | 75.60 | 82.85 | 68.13 |
| 30 | Goa | 87.40 | 92.81 | 81.84 |
| 31 | Lakshadweep | 92.28 | 96.11 | 88.25 |
| 32 | Kerala | 93.91 | 96.02 | 91.98 |
| 33 | Tamil Nadu | 80.33 | 86.81 | 73.86 |
| 34 | Puducherry | 86.55 | 92.12 | 81.22 |
| 35 | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 86.27 | 90.11 | 81.84 |
| – | Overall (India) | 74.03 | 82.14 | 65.46 |
Linguistic demographics
According to the 2001 census, 41.03% of the Indians spoke Hindi natively, while the rest spoke Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Maithili, Kannada, Malayalam, Marathi, Odia, Punjabi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu and a variety of other languages. There are a total of 122 languages and 234 mother tongues spoken in India. Of these, 22 languages are specified in the Eighth Schedule of Indian Constitution, while 100 are non-specified.
The table below excludes Mao-Maram, Paomata and Purul subdivisions of Senapati District of Manipur state due to cancellation of census results.
| Rank | Language | Speakers | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hindi[note 1] | 422,048,642 | 41.030 |
| 2 | Bengali | 83,369,769 | 8.110 |
| 3 | Telugu | 74,002,856 | 7.190 |
| 4 | Marathi | 71,936,894 | 6.990 |
| 5 | Tamil | 60,793,814 | 5.910 |
| 6 | Urdu | 51,536,111 | 5.010 |
| 7 | Gujarati | 46,091,617 | 4.480 |
| 8 | Kannada | 37,924,011 | 3.690 |
| 9 | Malayalam | 33,066,392 | 3.210 |
| 10 | Odia | 33,017,446 | 3.210 |
| 11 | Punjabi | 29,102,477 | 2.830 |
| 12 | Assamese | 13,168,484 | 1.280 |
| 13 | Maithili | 12,179,122 | 1.180 |
| 14 | Bhili/Bhilodi | 9,582,957 | 0.930 |
| 15 | Santali | 6,469,600 | 0.630 |
| 16 | Kashmiri | 5,527,698 | 0.540 |
| 17 | Nepali | 2,871,749 | 0.280 |
| 18 | Gondi | 2,713,790 | 0.260 |
| 19 | Sindhi | 2,535,485 | 0.250 |
| 20 | Konkani | 2,489,015 | 0.240 |
| 21 | Dogri | 2,282,589 | 0.220 |
| 22 | Khandeshi | 2,075,258 | 0.200 |
| 23 | Kurukh | 1,751,489 | 0.170 |
| 24 | Tulu | 1,722,768 | 0.170 |
| 25 | Meitei (Manipuri) | 1,466,705 | 0.140 |
| 26 | Bodo | 1,350,478 | 0.130 |
| 27 | Khasi – Garo | 1,128,575 | 0.112 |
| 28 | Mundari | 1,061,352 | 0.105 |
| 29 | Ho | 1,042,724 | 0.103 |
| 30 | Tripuri | 1,011,294 | 0.103 |
Largest cities of India
| Rank | Name | State/UT | Pop. | Rank | Name | State/UT | Pop. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Mumbai  Delhi | 1 | Mumbai | Maharashtra | 12,478,447 | 11 | Kanpur | Uttar Pradesh | 2,920,067 |  Chennai  Bangalore |
| 2 | Delhi | Delhi | 11,007,835 | 12 | Lucknow | Uttar Pradesh | 2,901,474 | ||
| 3 | Chennai | Tamil Nadu | 8,696,010 | 13 | Nagpur | Maharashtra | 2,405,421 | ||
| 4 | Bangalore | Karnataka | 8,425,970 | 14 | Indore | Madhya Pradesh | 1,960,521 | ||
| 5 | Hyderabad | Telangana | 6,809,970 | 15 | Thane | Maharashtra | 1,818,872 | ||
| 6 | Ahmedabad | Gujarat | 5,570,585 | 16 | Bhopal | Madhya Pradesh | 1,795,648 | ||
| 7 | Kolkata | West Bengal | 4,486,679 | 17 | Visakhapatnam | Andhra Pradesh | 1,730,320 | ||
| 8 | Surat | Gujarat | 4,462,002 | 18 | Pimpri-Chinchwad | Maharashtra | 1,729,359 | ||
| 9 | Pune | Maharashtra | 3,115,431 | 19 | Patna | Bihar | 1,683,200 | ||
| 10 | Jaipur | Rajasthan | 3,073,350 | 20 | Ludhiana | Punjab | 1,613,878 | ||
Vital statistics
UN estimates
| Year | Mid-year population | Births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Total Fertility rate | Infant mortality (per 1000) | Life expectancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 357,021,000 | 15,651,000 | 7,942,000 | 7,709,000 | 43.8 | 22.2 | 21.6 | 5.73 | 181.2 | 41.7 |
| 1951 | 364,922,000 | 16,042,000 | 8,171,000 | 7,871,000 | 44.0 | 22.4 | 21.6 | 5.77 | 180.1 | 41.7 |
| 1952 | 372,997,000 | 16,458,000 | 8,293,000 | 8,165,000 | 44.1 | 22.2 | 21.9 | 5.82 | 177.5 | 42.0 |
| 1953 | 381,228,000 | 16,857,000 | 8,442,000 | 8,415,000 | 44.2 | 22.1 | 22.1 | 5.87 | 175.3 | 42.2 |
| 1954 | 389,731,000 | 17,247,000 | 8,414,000 | 8,833,000 | 44.2 | 21.6 | 22.7 | 5.91 | 172.2 | 43.0 |
| 1955 | 398,578,000 | 17,549,000 | 8,468,000 | 9,081,000 | 44.0 | 21.2 | 22.8 | 5.91 | 169.7 | 43.4 |
| 1956 | 407,657,000 | 17,844,000 | 8,533,000 | 9,310,000 | 43.8 | 20.9 | 22.8 | 5.91 | 167.3 | 43.8 |
| 1957 | 416,935,000 | 18,128,000 | 8,618,000 | 9,510,000 | 43.5 | 20.7 | 22.8 | 5.91 | 165.0 | 44.1 |
| 1958 | 426,296,000 | 18,370,000 | 8,673,000 | 9,696,000 | 43.1 | 20.3 | 22.7 | 5.90 | 162.7 | 44.4 |
| 1959 | 435,900,000 | 18,593,000 | 8,688,000 | 9,905,000 | 42.6 | 19.9 | 22.7 | 5.89 | 160.3 | 44.9 |
| 1960 | 445,955,000 | 18,958,000 | 8,756,000 | 10,201,000 | 42.5 | 19.6 | 22.9 | 5.92 | 158.2 | 45.2 |
| 1961 | 456,352,000 | 19,301,000 | 8,874,000 | 10,427,000 | 42.3 | 19.4 | 22.8 | 5.94 | 156.4 | 45.4 |
| 1962 | 467,024,000 | 19,663,000 | 8,969,000 | 10,693,000 | 42.1 | 19.2 | 22.9 | 5.95 | 154.5 | 45.7 |
| 1963 | 477,934,000 | 20,031,000 | 9,064,000 | 10,966,000 | 41.9 | 19.0 | 22.9 | 5.97 | 152.7 | 45.9 |
| 1964 | 489,059,000 | 20,407,000 | 9,177,000 | 11,230,000 | 41.7 | 18.8 | 23.0 | 5.98 | 151.1 | 46.2 |
| 1965 | 500,114,000 | 20,679,000 | 9,824,000 | 10,855,000 | 41.3 | 19.6 | 21.7 | 5.94 | 156.4 | 45.0 |
| 1966 | 510,993,000 | 20,913,000 | 9,886,000 | 11,027,000 | 40.9 | 19.3 | 21.6 | 5.88 | 154.7 | 45.3 |
| 1967 | 521,987,000 | 21,193,000 | 9,963,000 | 11,231,000 | 40.6 | 19.1 | 21.5 | 5.83 | 153.1 | 45.7 |
| 1968 | 533,432,000 | 21,454,000 | 9,486,000 | 11,968,000 | 40.2 | 17.8 | 22.4 | 5.76 | 145.0 | 47.5 |
| 1969 | 545,315,000 | 21,704,000 | 9,551,000 | 12,154,000 | 39.8 | 17.5 | 22.3 | 5.68 | 143.3 | 47.9 |
| 1970 | 557,501,000 | 22,043,000 | 9,606,000 | 12,437,000 | 39.5 | 17.2 | 22.3 | 5.62 | 141.7 | 48.2 |
| 1971 | 569,999,000 | 22,483,000 | 9,658,000 | 12,825,000 | 39.4 | 16.9 | 22.5 | 5.57 | 139.9 | 48.6 |
| 1972 | 582,838,000 | 22,835,000 | 9,702,000 | 13,133,000 | 39.2 | 16.6 | 22.5 | 5.48 | 138.5 | 49.0 |
| 1973 | 596,107,000 | 23,230,000 | 9,701,000 | 13,529,000 | 39.0 | 16.3 | 22.7 | 5.40 | 136.3 | 49.5 |
| 1974 | 609,722,000 | 23,559,000 | 9,628,000 | 13,931,000 | 38.6 | 15.8 | 22.8 | 5.33 | 133.3 | 50.2 |
| 1975 | 623,524,000 | 23,660,000 | 9,592,000 | 14,068,000 | 37.9 | 15.4 | 22.6 | 5.20 | 130.7 | 50.8 |
| 1976 | 637,451,000 | 24,021,000 | 9,572,000 | 14,449,000 | 37.7 | 15.0 | 22.7 | 5.13 | 127.9 | 51.4 |
| 1977 | 651,686,000 | 24,042,000 | 9,555,000 | 14,487,000 | 36.9 | 14.7 | 22.2 | 5.01 | 124.9 | 51.9 |
| 1978 | 666,268,000 | 24,243,000 | 9,520,000 | 14,723,000 | 36.4 | 14.3 | 22.1 | 4.89 | 121.7 | 52.5 |
| 1979 | 681,248,000 | 24,699,000 | 9,515,000 | 15,184,000 | 36.3 | 14.0 | 22.3 | 4.81 | 118.4 | 53.1 |
| 1980 | 696,828,000 | 25,235,000 | 9,530,000 | 15,705,000 | 36.2 | 13.7 | 22.5 | 4.78 | 115.2 | 53.6 |
| 1981 | 712,869,000 | 25,683,000 | 9,532,000 | 16,151,000 | 36.0 | 13.4 | 22.7 | 4.70 | 112.1 | 54.2 |
| 1982 | 729,169,000 | 25,964,000 | 9,512,000 | 16,452,000 | 35.6 | 13.0 | 22.6 | 4.62 | 109.3 | 54.7 |
| 1983 | 745,827,000 | 26,329,000 | 9,487,000 | 16,842,000 | 35.3 | 12.7 | 22.6 | 4.57 | 106.7 | 55.3 |
| 1984 | 762,890,005 | 26,777,000 | 9,471,000 | 17,307,000 | 35.1 | 12.4 | 22.7 | 4.52 | 104.2 | 55.8 |
| 1985 | 780,242,000 | 27,001,000 | 9,444,000 | 17,558,000 | 34.6 | 12.1 | 22.5 | 4.43 | 101.8 | 56.3 |
| 1986 | 797,879,000 | 27,522,000 | 9,434,000 | 18,088,000 | 34.5 | 11.8 | 22.7 | 4.40 | 99.4 | 56.8 |
| 1987 | 815,716,000 | 27,478,000 | 9,400,000 | 18,077,000 | 33.7 | 11.5 | 22.2 | 4.31 | 97.0 | 57.3 |
| 1988 | 833,730,000 | 27,654,000 | 9,369,000 | 18,286,000 | 33.2 | 11.2 | 21.9 | 4.22 | 94.6 | 57.8 |
| 1989 | 852,013,000 | 27,733,000 | 9,335,000 | 18,398,000 | 32.5 | 11.0 | 21.6 | 4.13 | 92.2 | 58.2 |
| 1990 | 870,452,000 | 27,692,000 | 9,306,000 | 18,386,000 | 31.8 | 10.7 | 21.1 | 4.05 | 89.8 | 58.7 |
| 1991 | 888,942,000 | 27,937,000 | 9,295,000 | 18,642,000 | 31.4 | 10.5 | 21.0 | 3.96 | 87.6 | 59.1 |
| 1992 | 907,574,000 | 28,057,000 | 9,285,000 | 18,772,000 | 30.9 | 10.2 | 20.7 | 3.88 | 85.5 | 59.5 |
| 1993 | 926,351,000 | 28,055,000 | 9,283,000 | 18,772,000 | 30.3 | 10.0 | 20.3 | 3.80 | 83.5 | 59.8 |
| 1994 | 945,262,000 | 28,207,000 | 9,270,000 | 18,937,000 | 29.8 | 9.8 | 20.0 | 3.72 | 81.4 | 60.2 |
| 1995 | 964,279,000 | 28,314,000 | 9,269,000 | 19,044,000 | 29.4 | 9.6 | 19.7 | 3.65 | 79.3 | 60.6 |
| 1996 | 983,281,000 | 28,305,000 | 9,262,000 | 19,043,000 | 28.8 | 9.4 | 19.4 | 3.58 | 77.1 | 61.0 |
| 1997 | 1,002,335,000 | 28,341,000 | 9,251,000 | 19,090,000 | 28.3 | 9.2 | 19.0 | 3.51 | 74.8 | 61.4 |
| 1998 | 1,021,435,000 | 28,381,000 | 9,245,000 | 19,136,000 | 27.8 | 9.1 | 18.7 | 3.45 | 72.5 | 61.8 |
| 1999 | 1,040,500,000 | 28,365,000 | 9,235,000 | 19,130,000 | 27.3 | 8.9 | 18.4 | 3.38 | 70.2 | 62.2 |
| 2000 | 1,059,634,000 | 28,615,000 | 9,221,000 | 19,394,000 | 27.0 | 8.7 | 18.3 | 3.35 | 67.8 | 62.7 |
| 2001 | 1,078,971,000 | 28,843,000 | 9,235,000 | 19,608,000 | 26.7 | 8.6 | 18.2 | 3.30 | 65.4 | 63.1 |
| 2002 | 1,098,313,000 | 28,648,000 | 9,186,000 | 19,462,000 | 26.1 | 8.4 | 17.7 | 3.22 | 63.1 | 63.6 |
| 2003 | 1,117,415,000 | 28,356,000 | 9,150,000 | 19,206,000 | 25.4 | 8.2 | 17.2 | 3.12 | 60.8 | 64.1 |
| 2004 | 1,136,265,000 | 28,099,000 | 9,136,000 | 18,963,000 | 24.7 | 8.0 | 16.7 | 3.05 | 58.6 | 64.5 |
| 2005 | 1,154,639,000 | 27,646,000 | 9,096,000 | 18,550,000 | 23.9 | 7.9 | 16.1 | 2.96 | 56.3 | 65.0 |
| 2006 | 1,172,374,000 | 27,229,000 | 9,080,000 | 18,149,000 | 23.2 | 7.7 | 15.5 | 2.86 | 54.1 | 65.4 |
| 2007 | 1,189,692,000 | 27,030,000 | 9,095,000 | 17,935,000 | 22.7 | 7.6 | 15.1 | 2.78 | 51.9 | 65.8 |
| 2008 | 1,206,735,000 | 26,890,000 | 9,123,000 | 17,767,000 | 22.3 | 7.6 | 14.7 | 2.72 | 49.6 | 66.1 |
| 2009 | 1,223,640,000 | 26,848,000 | 9,154,000 | 17,694,000 | 21.9 | 7.5 | 14.5 | 2.67 | 47.4 | 66.5 |
| 2010 | 1,240,614,000 | 26,599,000 | 9,162,000 | 17,437,000 | 21.4 | 7.4 | 14.1 | 2.60 | 45.2 | 66.9 |
| 2011 | 1,257,621,191 | 26,342,000 | 9,139,000 | 17,203,000 | 20.9 | 7.3 | 13.7 | 2.54 | 43.0 | 67.4 |
| 2012 | 1,274,487,215 | 26,027,000 | 9,072,000 | 16,954,000 | 20.4 | 7.1 | 13.3 | 2.47 | 40.8 | 67.9 |
| 2013 | 1,291,132,063 | 25,740,000 | 8,987,000 | 16,753,000 | 19.9 | 7.0 | 13.0 | 2.41 | 38.7 | 68.5 |
| 2014 | 1,307,246,509 | 24,899,000 | 8,876,000 | 16,023,000 | 19.0 | 6.8 | 12.3 | 2.31 | 36.7 | 69.1 |
| 2015 | 1,322,866,505 | 24,828,000 | 8,826,000 | 16,003,000 | 18.8 | 6.7 | 12.1 | 2.29 | 34.7 | 69.6 |
| 2016 | 1,338,636,340 | 24,783,000 | 8,839,000 | 15,944,000 | 18.5 | 6.6 | 11.9 | 2.27 | 32.8 | 70.1 |
| 2017 | 1,354,195,680 | 24,254,000 | 8,928,000 | 15,326,000 | 17.9 | 6.6 | 11.3 | 2.20 | 31.1 | 70.5 |
| 2018 | 1,369,003,306 | 24,168,000 | 9,098,000 | 15,070,000 | 17.7 | 6.6 | 11.0 | 2.18 | 29.4 | 70.7 |
| 2019 | 1,383,112,050 | 23,583,000 | 9,281,000 | 14,302,000 | 17.0 | 6.7 | 10.3 | 2.11 | 27.9 | 70.9 |
| 2020 | 1,396,387,127 | 23,139,000 | 10,262,000 | 12,876,000 | 16.6 | 7.4 | 9.2 | 2.05 | 26.6 | 70.1 |
| 2021 | 1,407,563,842 | 23,114,000 | 13,300,000 | 9,814,000 | 16.4 | 9.4 | 7.0 | 2.03 | 25.5 | 67.2 |
| 2022 | 1,417,173,173 | 23,056,027 | 12,862,015 | 10,194,012 | 16.3 | 9.1 | 7.2 | 2.01 |
Census of India: sample registration system


| Year | Average population | Live births1 | Deaths1 | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Total fertility rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 | 716,493,000 | 24,289,000 | 8,956,000 | 15,333,000 | 33.9 | 12.5 | 21.4 | 4.52 |
| 1982 | 733,152,000 | 24,781,000 | 8,725,000 | 16,056,000 | 33.8 | 11.9 | 21.9 | 4.5 |
| 1983 | 750,034,000 | 25,276,000 | 8,925,000 | 16,351,000 | 33.7 | 11.9 | 21.8 | 4.5 |
| 1984 | 767,147,000 | 26,006,000 | 9,666,000 | 16,340,000 | 33.9 | 12.6 | 21.3 | 4.5 |
| 1985 | 784,491,000 | 25,810,000 | 9,257,000 | 16,553,000 | 32.9 | 11.8 | 21.1 | 4.3 |
| 1986 | 802,052,000 | 26,147,000 | 8,903,000 | 17,244,000 | 32.6 | 11.1 | 21.5 | 4.15 |
| 1987 | 819,800,000 | 26,316,000 | 8,936,000 | 17,380,000 | 32.1 | 10.9 | 21.2 | 4.1 |
| 1988 | 837,700,000 | 26,388,000 | 9,215,000 | 17,173,000 | 31.5 | 11.0 | 20.5 | 4.0 |
| 1989 | 855,707,000 | 26,185,000 | 8,814,000 | 17,371,000 | 30.6 | 10.3 | 20.3 | 3.9 |
| 1990 | 873,785,000 | 26,388,000 | 8,476,000 | 17,912,000 | 30.2 | 9.7 | 20.5 | 3.8 |
| 1991 | 891,910,000 | 26,133,000 | 8,741,000 | 17,392,000 | 29.3 | 9.8 | 19.5 | 3.64 |
| 1992 | 910,065,000 | 26,392,000 | 9,192,000 | 17,200,000 | 29.0 | 10.1 | 18.9 | 3.6 |
| 1993 | 928,226,000 | 26,640,000 | 8,633,000 | 18,007,000 | 0 | 9.3 | 19.4 | 3.5 |
| 1994 | 946,373,000 | 27,161,000 | 8,801,000 | 18,360,000 | 28.7 | 9.3 | 19.4 | 3.5 |
| 1995 | 964,486,000 | 27,295,000 | 8,680,000 | 18,615,000 | 28.3 | 9.0 | 19.3 | 3.5 |
| 1996 | 982,553,000 | 26,824,000 | 8,745,000 | 18,079,000 | 27.3 | 8.9 | 18.4 | 3.40 |
| 1997 | 1,000,558,000 | 27,215,000 | 8,905,000 | 18,310,000 | 27.2 | 8.9 | 18.3 | 3.3 |
| 1998 | 1,018,471,000 | 26,989,000 | 9,166,000 | 17,823,000 | 26.5 | 9.0 | 17.5 | 3.2 |
| 1999 | 1,036,259,000 | 26,943,000 | 9,015,000 | 17,928,000 | 26.0 | 8.7 | 17.3 | 3.2 |
| 2000 | 1,053,898,000 | 27,191,000 | 8,958,000 | 18,233,000 | 25.8 | 8.5 | 17.3 | 3.2 |
| 2001 | 1,071,374,000 | 27,213,000 | 9,000,000 | 18,213,000 | 25.4 | 8.4 | 17.0 | 3.10 |
| 2002 | 1,088,694,000 | 27,217,000 | 8,818,000 | 18,399,000 | 25.0 | 8.1 | 16.9 | 3.0 |
| 2003 | 1,105,886,000 | 27,426,000 | 8,847,000 | 18,579,000 | 24.8 | 8.0 | 16.8 | 3.0 |
| 2004 | 1,122,991,000 | 27,064,000 | 8,422,000 | 18,642,000 | 24.1 | 7.5 | 16.6 | 2.9 |
| 2005 | 1,140,043,000 | 27,133,000 | 8,664,000 | 18,469,000 | 23.8 | 7.6 | 16.2 | 2.9 |
| 2006 | 1,157,039,000 | 27,190,000 | 8,678,000 | 18,512,000 | 23.5 | 7.5 | 16.0 | 2.79 |
| 2007 | 1,134,024,000 | 26,195,954 | 8,391,778 | 17,804,176 | 23.1 | 7.4 | 15.7 | 2.7 |
| 2008 | 1,150,196,000 | 26,224,469 | 8,511,450 | 17,713,019 | 22.8 | 7.4 | 15.4 | 2.6 |
| 2009 | 1,166,228,000 | 26,240,130 | 8,513,464 | 17,726,666 | 22.5 | 7.3 | 15.2 | 2.6 |
| 2010 | 1,182,108,000 | 26,124,587 | 8,511,178 | 17,613,409 | 22.1 | 7.2 | 14.9 | 2.5 |
| 2011 | 1,197,658,000 | 26,108,944 | 8,503,372 | 17,605,572 | 21.8 | 7.1 | 14.7 | 2.44 |
| 2012 | 1,212,827,000 | 26,197,063 | 8,489,789 | 17,707,274 | 21.6 | 7.0 | 14.6 | 2.38 |
| 2013 | 1,227,012,000 | 26,258,057 | 8,589,084 | 17,668,973 | 21.4 | 7.0 | 14.4 | 2.34 |
| 2014 | 1,243,542,000 | 25,904,377 | 8,264,730 | 17,639,647 | 21.0 | 6.7 | 14.3 | 2.32 |
| 2015 | 1,259,108,000 | 26,189,446 | 8,184,202 | 18,005,244 | 20.8 | 6.5 | 14.3 | 2.27 |
| 2016 | 1,273,986,000 | 25,989,314 | 8,153,510 | 17,835,804 | 20.4 | 6.4 | 14.0 | 2.26 |
| 2017[93] | 1,288,522,000 | 26,028,144 | 8,117,689 | 17,910,455 | 20.2 | 6.3 | 13.9 | 2.18 |
| 2018 | 1,324,609,000 | 26,492,180 | 8,212,576 | 18,279,604 | 20.0 | 6.2 | 13.8 | 2.15 |
| 2019 | 1,338,995,000 | 24,820,886 | 7,641,076 | 17,179,810 | 18.5 | 5.7 | 12.8 | 2.08[94] |
| 2020 | 1,353,378,000 | 24,222,444 | 8,115,882 | 16,106,562 | 17.9 | 6.0 | 11.9 | 2.03 |
| 1 The numbers of births and deaths were calculated from the birth and death rates and the average population. | ||||||||
Life expectancy


with calculated sex gap[96]
| Period | Life expectancy in Years |
|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 36.6 |
| 1955–1960 | 39.7 |
| 1960–1965 | 42.7 |
| 1965–1970 | 46.0 |
| 1970–1975 | 49.4 |
| 1975–1980 | 52.5 |
| 1980–1985 | 54.9 |
| 1985–1990 | 56.7 |
| 1990–1995 | 59.1 |
| 1995–2000 | 61.5 |
| 2000–2005 | 63.5 |
| 2005–2010 | 65.6 |
| 2010–2015 | 67.6 |
Source: UN World Population Prospects[97]
Structure of the population
Structure of the population (Census 9.II.2011)
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percentage (%) | Cumulative Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–4 | 58,632,074 | 54,174,704 | 112,806,778 | 9.32 | 9.32 |
| 5–9 | 66,300,466 | 60,627,660 | 126,928,126 | 10.48 | 19.8 |
| 10–14 | 69,418,835 | 63,290,377 | 132,709,212 | 10.96 | 30.76 |
| 15–19 | 63,982,396 | 56,544,053 | 120,526,449 | 9.95 | 40.71 |
| 20–24 | 57,584,693 | 53,839,529 | 111,424,222 | 9.20 | 49.91 |
| 25–29 | 51,344,208 | 50,069,757 | 101,413,965 | 8.38 | 58.29 |
| 30–34 | 44,660,674 | 43,934,277 | 88,594,951 | 7.32 | 65.61 |
| 35–39 | 42,919,381 | 42,221,303 | 85,140,684 | 7.03 | 72.64 |
| 40–44 | 37,545,386 | 34,892,726 | 72,438,112 | 5.98 | 78.62 |
| 45–49 | 32,138,114 | 30,180,213 | 62,318,327 | 5.15 | 83.77 |
| 50–54 | 25,843,266 | 23,225,988 | 49,069,254 | 4.05 | 87.82 |
| 55–59 | 19,456,012 | 19,690,043 | 39,146,055 | 3.23 | 91.05 |
| 60–64 | 18,701,749 | 18,961,958 | 37,663,707 | 3.11 | 94.16 |
| 65–69 | 12,944,326 | 13,510,657 | 26,454,983 | 2.18 | 96.34 |
| 70–74 | 9,651,499 | 9,557,343 | 19,208,842 | 1.59 | 97.93 |
| 75–79 | 4,490,603 | 4,741,900 | 9,232,503 | 0.76 | 98.69 |
| 80–84 | 2,927,040 | 3,293,189 | 6,220,229 | 0.51 | 99.2 |
| 85–89 | 1,120,106 | 1,263,061 | 2,383,167 | 0.20 | 99.4 |
| 90–94 | 652,465 | 794,069 | 1,446,534 | 0.12 | 99.52 |
| 95–99 | 294,759 | 338,538 | 633,297 | 0.05 | 99.57 |
| 100+ | 289,325 | 316,453 | 605,778 | 0.05 | 99.62 |
| Unknown | 2,372,881 | 2,116,921 | 4,489,802 | 0.37 | 99.99 |
| Total | 623,270,258 | 587,584,719 | 1,210,854,977 | 100.00 | |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent | |
| 0–14 | 194,351,375 | 178,092,741 | 372,444,116 | 30.76 | |
| 15–64 | 394,175,879 | 373,559,847 | 767,735,726 | 63.40 | |
| 65+ | 32,370,123 | 33,815,210 | 66,185,333 | 5.47 |
Population Estimates by Sex and Age Group (03.III.2016) (Data are projections based on the 2011 Population Census.):[98]
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 664,184,000 | 626,890,000 | 1,291,074,000 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 62,872,000 | 56,038,000 | 118,910,000 | 9.21 |
| 5–9 | 61,499,000 | 56,969,000 | 118,468,000 | 9.18 |
| 10–14 | 65,142,000 | 59,682,000 | 124,824,000 | 9.67 |
| 15–19 | 67,223,000 | 60,871,000 | 128,094,000 | 9.92 |
| 20–24 | 63,521,000 | 57,356,000 | 120,877,000 | 9.36 |
| 25–29 | 57,272,000 | 53,357,000 | 110,629,000 | 8.57 |
| 30–34 | 50,782,000 | 49,250,000 | 100,032,000 | 7.75 |
| 35–39 | 45,318,000 | 44,787,000 | 90,105,000 | 6.98 |
| 40–44 | 41,280,000 | 40,497,000 | 81,777,000 | 6.33 |
| 45–49 | 36,602,000 | 35,107,000 | 71,709,000 | 5.55 |
| 50–54 | 30,738,000 | 29,016,000 | 59,754,000 | 4.63 |
| 55–59 | 24,403,000 | 23,307,000 | 47,710,000 | 3.70 |
| 60–64 | 19,133,000 | 19,288,000 | 38,421,000 | 2.98 |
| 65–69 | 15,198,000 | 16,114,000 | 31,312,000 | 2.43 |
| 70–74 | 11,002,000 | 11,723,000 | 22,725,000 | 1.76 |
| 75–79 | 7,703,000 | 8,367,000 | 16,070,000 | 1.24 |
| 80+ | 4,496,000 | 5,161,000 | 9,657,000 | 0.75 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0–14 | 189,513,000 | 172,689,000 | 362,202,000 | 28.05 |
| 15–64 | 436,272,000 | 412,836,000 | 849,108,000 | 65.77 |
| 65+ | 38,399,000 | 41,365,000 | 79,764,000 | 6.18 |
Population Estimates by Sex and Age Group (01.III.2021) (Includes data for the Indian-held part of Jammu and Kashmir, the final status of which has not yet been determined. Data are projections based on the 2011 Population Census.):[99]
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 700 623 000 | 662 383 000 | 1 363 006 000 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 60 153 000 | 54 120 000 | 114 273 000 | 8.38 |
| 5–9 | 62 276 000 | 55 390 000 | 117 666 000 | 8.63 |
| 10–14 | 61 266 000 | 56 785 000 | 118 051 000 | 8.66 |
| 15–19 | 64 862 000 | 59 420 000 | 124 282 000 | 9.12 |
| 20–24 | 66 770 000 | 60 474 000 | 127 244 000 | 9.34 |
| 25–29 | 62 944 000 | 56 956 000 | 119 900 000 | 8.80 |
| 30–34 | 56 614 000 | 52 961 000 | 109 575 000 | 8.04 |
| 35–39 | 50 027 000 | 48 836 000 | 98 863 000 | 7.25 |
| 40–44 | 44 450 000 | 44 315 000 | 88 765 000 | 6.51 |
| 45–49 | 40 204 000 | 39 903 000 | 80 107 000 | 5.88 |
| 50–54 | 35 235 000 | 34 331 000 | 69 566 000 | 5.10 |
| 55–59 | 29 082 000 | 28 062 000 | 57 144 000 | 4.19 |
| 60–64 | 22 465 000 | 22 079 000 | 44 544 000 | 3.27 |
| 65–69 | 16 823 000 | 17 583 000 | 34 406 000 | 2.52 |
| 70–74 | 12 546 000 | 13 904 000 | 26 450 000 | 1.94 |
| 75–79 | 8 269 000 | 9 294 000 | 17 563 000 | 1.29 |
| 80+ | 6 637 000 | 7 970 000 | 14 607 000 | 1.07 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0–14 | 183 695 000 | 166 295 000 | 349 990 000 | 25.68 |
| 15–64 | 472 653 000 | 447 337 000 | 919 990 000 | 67.50 |
| 65+ | 44 275 000 | 48 751 000 | 93 026 000 | 6.83 |
Fertility rate
From the Demographic Health Survey:[100]

| Year | CBR – Total | TFR – Total1 | CBR – Urban | TFR – Urban1 | CBR – Rural | TFR – Rural1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992–1993 | 28.7 | 3.39 (2.64) | 24.1 | 2.70 (2.09) | 30.4 | 3.67 (2.86) |
| 1998–1999 | 24.8 | 2.85 (2.13) | 20.9 | 2.27 (1.73) | 26.2 | 3.07 (2.28) |
| 2005–2006 | 23.1 | 2.68 (1.90) | 18.8 | 2.06 (1.60) | 25.0 | 2.98 (2.10) |
| 2015–2016 | 19.0 | 2.18 (1.8) | 15.8 | 1.75 (1.5) | 20.7 | 2.41 (1.9) |
| 2019–2021 | 17.1 | 1.99 (1.6) | 14.0 | 1.63 (1.4) | 18.6 | 2.14 (1.7) |
| CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman). 1Number in parentheses represents the wanted fertility rate. | ||||||
| Year | Hindu | Muslim | Christian | Sikh | Buddhist/Neo-Buddhist | Jain | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019–2021 | 1.94 (1.6) | 2.36 (1.8) | 1.88 (1.7) | 1.61 (1.4) | 1.39 (1.2) | 1.60 (1.5) | 2.15 (1.7) |
| CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman). 1Number in parentheses represents the wanted fertility rate. | |||||||
| State (Population 2011) | CBR – Total | TFR – Total1 | CBR – Urban | TFR – Urban1 | CBR – Rural | TFR – Rural1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uttar Pradesh (199 812 341) | 22.6 | 2.74 (2.06) | 18.6 | 2.08 (1.62) | 24.0 | 2.99 (2.22) |
| Maharashtra (112 374 333) | 16.6 | 1.87 (1.57) | 15.5 | 1.68 (1.41) | 17.5 | 2.06 (1.73) |
| Bihar (104 099 452) | 27.1 | 3.41 (2.48) | 20.4 | 2.42 (1.83) | 28.0 | 3.56 (2.58) |
| West Bengal (91 276 115) | 16.6 | 1.77 (1.53) | 14.0 | 1.57 (1.38) | 18.0 | 1.85 (1.58) |
| Madhya Pradesh (72 626 809) | 20.2 | 2.32 (1.82) | 17.7 | 1.95 (1.61) | 21.3 | 2.48 (1.91) |
| Tamil Nadu (72 147 030) | 15.5 | 1.70 (1.51) | 13.9 | 1.54 (1.38) | 17.2 | 1.86 (1.63) |
| Rajasthan (68 548 437) | 20.8 | 2.40 (1.81) | 17.5 | 1.94 (1.52) | 22.0 | 2.56 (1.91) |
| Karnataka (61 095 297) | 15.9 | 1.81 (1.42) | 15.2 | 1.65 (1.30) | 16.5 | 1.92 (1.50) |
| Gujarat (60 439 692) | 16.7 | 2.03 (1.54) | 15.3 | 1.82 (1.39) | 17.9 | 2.19 (1.64) |
| Andhra Pradesh (49 386 799) | 16.1 | 1.83 (1.64) | 13.9 | 1.53 (1.39) | 17.0 | 1.96 (1.75) |
| Odisha (41 974 218) | 18.1 | 2.05 (1.69) | 15.6 | 1.73 (1.50) | 18.7 | 2.12 (1.72) |
| Telangana (35 193 978) | 17.1 | 1.79 (1.59) | 17.1 | 1.67 (1.53) | 17.2 | 1.88 (1.64) |
| Kerala (33 406 061) | 11.2 | 1.56 (1.47) | 11.4 | 1.57 (1.47) | 11.0 | 1.55 (1.46) |
| Jharkhand (32 988 134) | 21.7 | 2.55 (2.06) | 16.3 | 1.78 (1.47) | 23.5 | 2.83 (2.27) |
| Assam (31 205 576) | 19.5 | 2.21 (1.78) | 13.2 | 1.45 (1.25) | 20.5 | 2.34 (1.87) |
| Punjab (27 743 338) | 13.8 | 1.62 (1.37) | 13.5 | 1.59 (1.32) | 14.0 | 1.63 (1.39) |
| Chhattisgarh (25 545 198) | 20.7 | 2.23 (1.88) | 17.9 | 1.78 (1.58) | 21.5 | 2.37 (1.97) |
| Haryana (25 351 462) | 18.7 | 2.05 (1.63) | 16.3 | 1.78 (1.44) | 20.2 | 2.22 (1.75) |
| Jammu and Kashmir (12 541 302) | 17.7 | 2.01 (1.67) | 13.9 | 1.58 (1.39) | 19.4 | 2.18 (1.77) |
| Uttarakhand (10 086 292) | 19.0 | 2.07 (1.60) | 17.1 | 1.80 (1.43) | 20.0 | 2.24 (1.71) |
| Himachal Pradesh (6 864 602) | 15.3 | 1.88 (1.55) | 12.0 | 1.43 (1.15) | 15.7 | 1.92 (1.59) |
| Tripura (3 673 917) | 15.3 | 1.69 (1.55) | 12.7 | 1.40 (1.34) | 16.4 | 1.80 (1.62) |
| Meghalaya (2 966 889) | 24.6 | 3.04 (2.79) | 16.1 | 1.67 (1.57) | 26.7 | 3.47 (3.18) |
| Manipur (2 855 794) | 21.2 | 2.61 (2.33) | 17.5 | 2.14 (1.96) | 23.7 | 2.92 (2.57) |
| Nagaland (1 978 502) | 21.4 | 2.74 (2.35) | 16.3 | 1.78 (1.58) | 24.1 | 3.38 (2.86) |
| Goa (1 458 545) | 12.8 | 1.66 (1.37) | 13.4 | 1.72 (1.37) | 11.7 | 1.55 (1.37) |
| Arunachal Pradesh (1 383 727) | 17.9 | 2.12 (1.64) | 17.0 | 1.69 (1.26) | 18.2 | 2.29 (1.79) |
| Mizoram (1 097 206) | 18.7 | 2.26 (2.15) | 16.9 | 1.97 (1.89) | 21.2 | 2.71 (2.54) |
| Sikkim (610 577) | 11.4 | 1.17 (0.88) | 12.1 | 1.11 (0.82) | 11.1 | 1.21 (0.91) |
| CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman). 1Number in parentheses represents the wanted fertility rate. | ||||||
| State (Population 2011) | CBR – Total | TFR – Total1 | CBR – Urban | TFR – Urban1 | CBR – Rural | TFR – Rural1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uttar Pradesh (199 812 341) | 20.5 | 2.35 (1.77) | 16.7 | 1.88 (1.49) | 21.8 | 2.50 (1.86) |
| Maharashtra (112 374 333) | 13.8 | 1.71 (1.43) | 12.6 | 1.50 (1.27) | 15.0 | 1.89 (1.58) |
| Bihar (104 099 452) | 25.9 | 2.98 (2.25) | 20.4 | 2.35 (1.88) | 27.0 | 3.11 (2.31) |
| West Bengal (91 276 115) | 15.5 | 1.64 (1.42) | 12.4 | 1.39 (1.24) | 17.0 | 1.73 (1.48) |
| Madhya Pradesh (72 626 809) | 17.2 | 1.99 (1.61) | 13.7 | 1.61 (1.34) | 18.5 | 2.12 (1.69) |
| Tamil Nadu (72 147 030) | 13.7 | 1.76 (1.59) | 12.7 | 1.61 (1.50) | 14.6 | 1.89 (1.66) |
| Rajasthan (68 548 437) | 18.7 | 2.01 (1.61) | 15.3 | 1.67 (1.42) | 19.8 | 2.11 (1.65) |
| Karnataka (61 095 297) | 14.2 | 1.67 (1.38) | 13.2 | 1.50 (1.25) | 14.9 | 1.79 (1.46) |
| Gujarat (60 439 692) | 15.0 | 1.86 (1.53) | 13.3 | 1.65 (1.39) | 16.3 | 2.0 (1.60) |
| Andhra Pradesh (49 386 799) | 13.8 | 1.68 (1.55) | 12.5 | 1.47 (1.36) | 14.3 | 1.78 (1.64) |
| Odisha (41 974 218) | 15.9 | 1.82 (1.52) | 13.1 | 1.48 (1.26) | 16.5 | 1.89 (1.57) |
| Telangana (35 193 978) | 15.3 | 1.75 (1.55) | 16.0 | 1.75 (1.57) | 15.3 | 1.74 (1.54) |
| Kerala (33 406 061) | 11.8 | 1.79 (1.68) | 11.9 | 1.82 (1.71) | 11.6 | 1.76 (1.65) |
| Jharkhand (32 988 134) | 20.2 | 2.26 (1.87) | 14.2 | 1.56 (1.32) | 22.0 | 2.48 (2.04) |
| Assam (31 205 576) | 16.8 | 1.87 (1.56) | 13.1 | 1.50 (1.37) | 17.4 | 1.93 (1.59) |
| Punjab (27 743 338) | 13.3 | 1.63 (1.35) | 12.1 | 1.55 (1.29) | 14.0 | 1.68 (1.38) |
| Chhattisgarh (25 545 198) | 16.4 | 1.82 (1.57) | 13.6 | 1.42 (1.28) | 17.2 | 1.94 (1.66) |
| Haryana (25 351 462) | 16.4 | 1.91 (1.54) | 14.1 | 1.65 (1.38) | 17.5 | 2.04 (1.62) |
| Jammu and Kashmir (12 541 302) | 13.1 | 1.41 (1.3) | ||||
| Uttarakhand (10 086 292) | 16.7 | 1.85 (1.46) | 16.8 | 1.84 (1.47) | 16.6 | 1.86 (1.47) |
| Himachal Pradesh (6 864 602) | 12.7 | 1.66 (1.43) | 11.2 | 1.43 (1.36) | 12.9 | 1.69 (1.44) |
| Tripura (3 673 917) | 14.5 | 1.70 (1.49) | 11.0 | 1.39 (1.29) | 15.8 | 1.81 (1.56) |
| Meghalaya (2 966 889) | 24.2 | 2.91 (2.66) | 14.8 | 1.57 (1.43) | 26.5 | 3.31 (3.04) |
| Manipur (2 855 794) | 17.4 | 2.17 (1.98) | 14.7 | 1.84 (1.73) | 19.1 | 2.38 (2.13) |
| Nagaland (1 978 502) | 15.4 | 1.72 (1.57) | 12.5 | 1.21 (1.13) | 16.8 | 2.00 (1.82) |
| Goa (1 458 545) | 10.3 | 1.30 (1.21) | 10.3 | 1.26 (1.19) | 10.3 | 1.36 (1.24) |
| Arunachal Pradesh (1 383 727) | 16.0 | 1.80 (1.49) | 14.8 | 1.44 (1.24) | 16.2 | 1.88 (1.54) |
| Mizoram (1 097 206) | 15.0 | 1.87 (1.78) | 13.9 | 1.63 (1.56) | 16.4 | 2.19 (2.08) |
| Sikkim (610 577) | 10.2 | 1.05 (0.85) | 7.8 | 0.71 (0.54) | 11.7 | 1.32 (1.11) |
| Delhi | 14.8 | 1.62 (1.29) | 14.6 | 1.60 (1.27) | 23.4 | 2.47 (2.06) |
| CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman). 1Number in parentheses represents the wanted fertility rate. | ||||||
Regional vital statistics
| State or UT | Birth rate | Death rate | Natural growth rate | Infant mortality rate | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Rural | Urban | Total | Rural | Urban | Total | Rural | Urban | Total | Rural | Urban | |
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 15.6 | 15.5 | 15.8 | 4.3 | 4.8 | 3.3 | 11.3 | 10.7 | 12.6 | 25 | 29 | 18 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 17.9 | 18.3 | 16.7 | 7.6 | 8.6 | 5.4 | 10.2 | 9.7 | 11.3 | 46 | 51 | 33 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | 20.5 | 22.1 | 14.6 | 5.9 | 6.9 | 2.3 | 14.6 | 15.2 | 12.3 | 31 | 34 | 12 |
| Assam | 23.2 | 24.4 | 15.8 | 8.2 | 8.6 | 5.8 | 14.9 | 15.8 | 10.1 | 58 | 60 | 36 |
| Bihar | 28.1 | 28.8 | 22.0 | 6.8 | 7.0 | 5.6 | 21.3 | 21.8 | 16.4 | 48 | 49 | 38 |
| Chandigarh | 15.6 | 21.6 | 15.0 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 11.6 | 17.9 | 11.0 | 22 | 20 | 23 |
| Chhattisgarh | 25.3 | 26.8 | 18.6 | 8.0 | 8.4 | 6.2 | 17.3 | 18.4 | 12.4 | 51 | 52 | 44 |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli | 26.6 | 26.0 | 28.6 | 4.7 | 5.1 | 3.3 | 21.9 | 20.9 | 25.3 | 38 | 43 | 22 |
| Daman and Diu | 18.8 | 19.1 | 18.3 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 4.8 | 13.9 | 14.2 | 13.6 | 23 | 19 | 29 |
| Delhi | 17.8 | 19.7 | 17.5 | 4.2 | 4.6 | 4.1 | 13.6 | 15.0 | 13.4 | 30 | 37 | 29 |
| Goa | 13.2 | 12.6 | 13.7 | 6.6 | 8.1 | 5.7 | 6.6 | 4.5 | 8.0 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Gujarat | 21.8 | 23.3 | 19.4 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 15.1 | 15.8 | 14.0 | 44 | 51 | 30 |
| Haryana | 22.3 | 23.3 | 19.8 | 6.6 | 7.0 | 5.6 | 15.7 | 16.3 | 14.3 | 48 | 51 | 38 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 16.9 | 17.5 | 11.5 | 6.9 | 7.2 | 4.2 | 10.0 | 10.3 | 7.3 | 40 | 41 | 29 |
| Jammu and Kashmir | 18.3 | 19.5 | 13.5 | 5.7 | 5.9 | 4.7 | 12.6 | 13.6 | 8.8 | 43 | 45 | 32 |
| Jharkhand | 25.3 | 26.7 | 19.3 | 7.0 | 7.4 | 5.4 | 18.3 | 19.3 | 13.9 | 42 | 44 | 30 |
| Karnataka | 19.2 | 20.2 | 17.5 | 7.1 | 8.1 | 5.4 | 12.1 | 12.1 | 12.1 | 38 | 43 | 28 |
| Kerala | 14.8 | 14.8 | 14.8 | 7.0 | 7.1 | 6.7 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 8.1 | 13 | 14 | 10 |
| Lakshadweep | 14.3 | 15.5 | 13.2 | 6.4 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 8.0 | 9.5 | 6.5 | 25 | 23 | 27 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 27.3 | 29.2 | 20.5 | 8.3 | 9.0 | 6.0 | 18.9 | 20.2 | 14.5 | 62 | 67 | 42 |
| Maharashtra | 17.1 | 17.6 | 16.4 | 6.5 | 7.5 | 5.3 | 10.6 | 10.2 | 11.1 | 28 | 34 | 20 |
| Manipur | 14.9 | 14.8 | 15.3 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 4.0 | 10.7 | 10.5 | 11.3 | 14 | 15 | 9 |
| Meghalaya | 24.5 | 26.6 | 14.8 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 5.6 | 16.6 | 18.2 | 9.2 | 55 | 58 | 37 |
| Mizoram | 17.1 | 21.1 | 13.0 | 4.5 | 5.4 | 3.7 | 12.5 | 15.7 | 9.3 | 37 | 47 | 21 |
| Nagaland | 16.8 | 17.0 | 16.0 | 3.6 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 12.7 | 23 | 24 | 20 |
| Odisha | 20.5 | 21.4 | 15.2 | 8.6 | 9.0 | 6.6 | 11.9 | 12.4 | 8.6 | 61 | 63 | 43 |
| Puducherry | 16.7 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 7.4 | 8.2 | 7.0 | 9.3 | 8.5 | 9.6 | 22 | 25 | 21 |
| Punjab | 16.6 | 17.2 | 15.6 | 7.0 | 7.7 | 5.8 | 9.6 | 9.5 | 9.8 | 34 | 37 | 28 |
| Rajasthan | 26.7 | 27.9 | 22.9 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 6.0 | 20.0 | 20.9 | 16.9 | 55 | 61 | 31 |
| Sikkim | 17.8 | 18.1 | 16.1 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 3.8 | 12.3 | 12.3 | 12.3 | 30 | 31 | 19 |
| Tamil Nadu | 15.9 | 16.0 | 15.8 | 7.6 | 8.2 | 6.9 | 8.3 | 7.8 | 8.9 | 24 | 25 | 22 |
| Tripura | 14.9 | 15.6 | 11.5 | 5.0 | 4.8 | 5.7 | 9.9 | 10.8 | 5.8 | 27 | 29 | 19 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 28.3 | 29.2 | 24.2 | 8.1 | 8.5 | 6.3 | 20.2 | 20.7 | 17.9 | 61 | 64 | 44 |
| Uttarakhand | 19.3 | 20.2 | 16.2 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 5.1 | 13.0 | 13.5 | 11.1 | 38 | 41 | 25 |
| West Bengal | 16.8 | 18.6 | 11.9 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 10.7 | 12.6 | 5.6 | 31 | 32 | 25 |
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
- Total population
1,166,079,217 (July 2009 est. CIA),[104] 1,210 million (2011 census),[105] 1,389,637,446 (May 2022 est.)[106]
- Rural population:
62.2%; male: 381,668,992, female: 360,948,755
- Age structure:
0–14 years: 27.34% (male 186,087,665/female 164,398,204)
15–24 years: 17.9% (male 121,879,786/female 107,583,437)
25–54 years: 41.08% (male 271,744,709/female 254,834,569)
55–64 years: 7.45% (male 47,846,122/female 47,632,532)
65+ years: 6.24% (male 37,837,801/female 42,091,086) (2017 est.)
- Median age:
Total: 28.7 years
Male: 28 years
female: 29.5 years (2020 est.)[107]
- Population growth rate :
0.67% (2022 est)[108]
- Literacy rate
74% (age 7 and above, in 2011)[109]
81.4% (total population, age 15–25, in 2006)[110]
- Per cent of population below poverty line:
22% (2006 est.)
- Unemployment rate:
7.8%
- Net migration rate:
0.00 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2020 est.)[107]
- Sex ratio:
At birth:1.12 male(s)/female
Under 10 years:1.13 male(s)/female
15–24 years:1.13 male(s)/female
24–64 years:1.06 male(s)/female
65 years and over:0.9 male(s)/female
Total population:1.08 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
- Life expectancy at birth:
Total population: 69.7 years
Male: 68.4 years
Female: 71.2 years (2020 est.)[107]
- Total fertility rate:
2.35 (2020 est.)[107][111][112]
The TFR (total number of children born per women) by religion in 2005–2006 was: Hindus, 2.7; Muslims, 3.1; Christians, 2.4; and Sikhs, 2.0.[113]
- Religious Composition:
Hindus 79.5%, Muslims 15%, Christian 2.3%, Sikh 1.7%, other and unspecified 2% (2011 est.)[107][114][115][116][117]
- Scheduled castes and tribes:
Scheduled castes: 16.6% (2011 census);[118][119]scheduled tribes: 8.6% (2011 census)
- Languages
See Languages of India and List of languages by number of native speakers in India. There are 216 languages with more than 10,000 native speakers in India. The largest of these is Hindi with some 337 million, and the second largest is Bengali with 238 million. 22 languages are recognised as official languages. In India, there are 1,652 languages and dialects in total.[120][121]
Caste/Tribe
Caste and community statistics as recorded from "Socially and Educationally Backward Classes Commission" (SEBC) or Mandal Commission of 1979. This was completed in 1983.
India has chosen not to officially count caste population since then.
The following data are from the Mandal report:[citation needed]
| Caste/Tribe | population | percentage | notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total population | 731,000,000 | 100% | *Margin of error 0.34% |
| Scheduled castes and tribes | 164,913,600 | 22.56% | |
| Scheduled castes | 110,015,500 | 15.05% | |
| Scheduled tribes | 54,898,100 | 7.51% | |
| Non OBC/SC/ST Hindu castes/communities | 128,509,800 | 17.58% | |
| Brahmin (including Bhumihar) | 40,351,200 | 5.52% | |
| Kshtriya (Rajput) | 28,509,000 | 3.90% | |
| Maratha | 16,155,100 | 2.21% | |
| Jats | 7,310,000 | 1% | |
| Vaishya, Bania, etc. | 13,742,800 | 1.88% | |
| Kayasthas | 7,821,700 | 1.07% | |
| Others | 14,620,000 | 2% | |
| Non-Hindu communities and groups | 121,346,000 | 16.6% | Non-Hindu scheduled and OBC |
| Muslim (Non S.T) | 81,798,900 | 11.19% | 0.02% |
| Christian (Non S.T) | 15,789,600 | 2.16% | 0.44% |
| Sikh (Non scheduled) | 12,207,700 | 1.67% | 0.22% |
| Buddhist (Non S.T) | 4,897,700 | 0.67% | 0.03% |
| Jain (Non scheduled) | 3,435,700 | 0.47% | |
| Other backward classes and communities (OBC) | 380,120,000 | 52% | *OBC is a derived figure |
| Hindu OBC | 318,716,000 | 43.60% | |
| Non-Hindu OBC | 61,404,000 | 8.40% | *52% of Non-Hindus |
Ethnic groups
The national Census of India does not recognise racial or ethnic groups within India,[122] but recognises many of the tribal groups as Scheduled Castes and Tribes (see list of Scheduled Tribes in India).
According to a 2009 study published by Reich et al.., the modern Indian population is composed of two genetically divergent and heterogeneous populations which mixed in ancient times (about 1,200–3,500 BP), known as Ancestral North Indians (ANI) and Ancestral South Indians (ASI). ASI corresponds to the Dravidian-speaking population of southern India, whereas ANI corresponds to the Indo-Aryan-speaking population of northern India.[123][124] 700,000 people from the United States of any race live in India.[18] Between 300,000 and 1 million Anglo-Indians live in India.[125]
For a list of ethnic groups in the Republic of India (as well as neighbouring countries), see South Asian ethnic groups.
Genetics
Y-chromosome DNA
Y-Chromosome DNA Y-DNA represents the male lineage, The Indian Y-chromosome pool may be summarised as follows where haplogroups R-M420, H, R2, L and NOP comprise generally more than 80% of the total chromosomes.[129]
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA mtDNA represents the female lineage. The Indian mitochondrial DNA is primarily made up of Haplogroup M[131]
- Haplogroup M ~ 60%
- Haplogroup UK ~ 15%
- Haplogroup N ~ 25% (Excluding UK)
Autosomal DNA

Numerous genomic studies have been conducted in the last 15 years to seek insights into India's demographic and cultural diversity. These studies paint a complex and conflicting picture.
- In a 2003 study, Basu, Majumder et al. have concluded on the basis of results obtained from mtDNA, Y-chromosome and autosomal markers that "(1) there is an underlying unity of female lineages in India, indicating that the initial number of female settlers may have been small; (2) the tribal and the caste populations are highly differentiated; (3) the Austroasiatic tribals are the earliest settlers in India, providing support to one anthropological hypothesis while refuting some others; (4) a major wave of humans entered India through the northeast; (5) the Tibeto-Burman tribals share considerable genetic commonalities with the Austroasiatic tribals, supporting the hypothesis that they may have shared a common habitat in southern China, but the two groups of tribals can be differentiated on the basis of Y-chromosomal haplotypes; (6) the Dravidian speaking populations were possibly widespread throughout India but are regulated to South India now; (7) formation of populations by fission that resulted in founder and drift effects have left their imprints on the genetic structures of contemporary populations; (8) the upper castes show closer genetic affinities with Central Asian populations, although those of southern India are more distant than those of northern India; (9) historical gene flow into India has contributed to a considerable obliteration of genetic histories of contemporary populations so that there is at present no clear congruence of genetic and geographical or sociocultural affinities."[132]
- In a later 2010 review article, Majumder affirms some of these conclusions, introduces and revises some other. The ongoing studies, concludes Majumder, suggest India has served as the major early corridor for geographical dispersal of modern humans from out-of-Africa. The archaeological and genetic traces of the earliest settlers in India has not provided any conclusive evidence. The tribal populations of India are older than the non-tribal populations. The autosomal differentiation and genetic diversity within India's caste populations at 0.04 is significantly lower than 0.14 for continental populations and 0.09 for 31 world population sets studied by Watkins et al., suggesting that while tribal populations were differentiated, the differentiation effects within India's caste population was less than previously thought. Majumder also concludes that recent studies suggest India has been a major contributor to the gene pool of southeast Asia.[133][134]
- Another study covering a large sample of Indian populations allowed Watkins et al. to examine eight Indian caste groups and four endogamous south Indian tribal populations. The Indian castes data show low between-group differences, while the tribal Indian groups show relatively high between-group differentiation. This suggests that people between Indian castes were not reproductively isolated, while Indian tribal populations experienced reproductive isolation and drift. Furthermore, the genetic fixation index data show historical genetic differentiation and segregation between Indian castes population is much smaller than those found in east Asia, Africa and other continental populations; while being similar to the genetic differentiation and segregation observed in European populations.[134]
- In 2006, Sahoo et al. reported their analysis of genomic data on 936 Y-chromosomes representing 32 tribal and 45 caste groups from different regions of India. These scientists find that the haplogroup frequency distribution across the country, between different caste groups, was found to be predominantly driven by geographical, rather than cultural determinants. They conclude there is clear evidence for both large-scale immigration into ancient India of Sino-Tibetan speakers and language change of former Austroasiatic speakers, in the northeast Indian region.[135][136]
- The genome studies conducted up until 2010 have been on relatively small population sets. Many are from just one southeastern state of Andhra Pradesh (including Telangana, which was part of the state until June 2014). Thus, any conclusions on demographic history of India must be interpreted with caution. A larger national genome study with demographic growth and sex ratio balances may offer further insights on the extent of genetic differentiation and segregation in India over the millenniums.[133]
Charts
See also
Government
Lists
Notes
References
Bibliography
- Arnold, David. Pandemic India: From Cholera to Covid-19 (Oxford University Press, 2022). Venkatesh, Archana (January 2023). "Review of Arnold, David, Pandemic India: From Cholera to Covid-19". H-Net Reviews.
- Chakravorty, Swastika, Srinivas Goli, and Kuriath S. James. "Family demography in India: Emerging patterns and its challenges". Sage Open 11.2 (2021): doi:10.1177/2158244021100817.
- Chamie, Joseph; Mirkin, Barry (August 2017), "Busting at the seams: India is unprepared for a near future when it will be the world's most populous country", Quartz. Joseph Chamie is former director of the United Nations Population Division and Barry Mirkin is former chief of the Population Policy Section of the United Nations Population Division.
- Chandrasekhar, S., and Ajay Sharma. "Urbanization and spatial patterns of internal migration in India". Spatial demography 3.2 (2015): 63–89.
- Sekher, T. V. "Rural demography of India". in International handbook of rural demography (Springer, Dordrecht, 2012) pp. 169–189.
- Smith, Robert D., and Mohandas K. Mallath. "History of the growing burden of cancer in India: from antiquity to the 21st century". Journal of Global Oncology 5 (2019): 1–15.
- Medieval India
- Lal, K. S. (1978). Growth of Muslim population in medieval India (A.D. 1000–1800). Delhi, Research Publications.
- Lal, K. S. (1995). Growth of scheduled tribes and castes in medieval India. New Delhi: Aditya Prakashan.
External links

- Census of India; government site with detailed data from 2001 census
- Population of India as per Census India 2011
- Census of India map generator; generates maps based on 2001 census figures
- Demographic data for India; provides sources of demographic data for India
- 2001 maps; provides maps of social, economic and demographic data of India in 2001
- Population of India 2011 map; distribution of population amongst states and union territories
- India's Demographic Outlook: Implications and Trends
- "World Population Prospects Archived 1 January 2023 at the Wayback Machine": Country Profile – India
- Aggregated demographic statistics from Indian and global data sources
- Demographic statistics for India – online on Bluenomics
- India comparing with China population projection graph Based on data from database of UN Population Division.