The Legislative Assembly of Rio Grande do Sul (Portuguese: Assembleia Legislativa do Rio Grande do Sul) is the regional parliament of Rio Grande do Sul, a federative unit in Brazil. It has 55 state deputies elected every 4 years.
Legislative Assembly of Rio Grande do Sul Assembleia Legislativa do Rio Grande do Sul | |
|---|---|
| 56th Legislature | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 1828 |
| Leadership | |
President | Vilmar Zanchin, MDB |
1st Vice President | Nadine Anflor, PSDB |
2nd Vice President | Valdeci Oliveira, PT |
1st Secretary | Adolfo Brito, PP |
2nd Secretary | Eliana Bayer, Republicanos |
3rd Secretary | Paparico Bacchi, PL |
4th Secretary | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 55 |
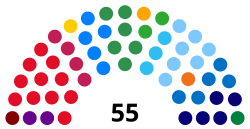 | |
Political groups | Government (28)[1] PP (7) MDB (6) PSDB (5) PDT (4) UNIÃO (3) PODE (2) PSD (1) Opposition (14) PT (11) PSOL (2) PCdoB (1) Independent (13) PL (5) Republicanos (5) NOVO (1) PSB (1) PRD (1) |
Length of term | 4 years |
| Salary | R$ 31,238.19 monthly[2] |
| Elections | |
| Open list proportional representation | |
Last election | 2 October 2022 |
Next election | 4 October 2026 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Farroupilha Palace, Porto Alegre | |
| Website | |
| ww4 | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of the State of Rio Grande do Sul[3][4] | |
History
Imperial Brazil
The Assembly originated in 1828 as the General Council of the Province in the Casa da Junta, which had limited legislative power. After the creation of the Provincial Legislative Assemblies by Law No. 16 of 12 August 1834, the Legislative Assembly of São Pedro do Rio Grande do Sul began to operate on 20 April 1835. However, the Ragamuffin War, which initiated in September of the same year, prompted the Assembly to go into recess until 1 March 1845, briefly reactivating between October and November 1837. It was closed again from 1865 to 1871, during the Paraguayan War, when the imperial government suspended constitutional guarantees.[5][6]
Republican Brazil
The Assembly was deactivated with the Proclamation of the Republic in 1889 until 25 June 1891. With the 1935 State Constitution, it was reduced to a Permanent Commission of 7 members, and on 10 November 1937, Getúlio Vargas decreed the Estado Novo and closed all the legislative houses. It remained in this condition until 1947, when the new deputies met for the third State Constituent Assembly.[5][6]
On 20 September 1967, the legislature's new building, the Farroupilha Palace, was inaugurated.[6][7]
Present composition
| Party | Floor leader | Seats |
|---|---|---|
| Workers' Party | Luiz Fernando Mainardi | 11 |
| Progressives | Guilherme Pasin | 7 |
| Brazilian Democratic Movement | Edivilson Brum | 6 |
| Brazilian Social Democracy Party | Valdir Bonatto | 5 |
| Liberal Party | Rodrigo Lorenzoni | 5 |
| Republicans | Rodrigo Zucco | 5 |
| Democratic Labour Party | Eduardo Loureiro | 4 |
| Brazil Union | Aloísio Classmann | 3 |
| Socialism and Liberty Party | Luciana Genro | 2 |
| We Can | Airton Lima | 2 |
| Communist Party of Brazil | Bruna Rodrigues | 1 |
| New Party | Felipe Camozzato | 1 |
| Social Democratic Party | Juliano Franczak | 1 |
| Brazilian Socialist Party | Elton Weber | 1 |
| Brazilian Labour Party | Elizandro Sabino | 1 |
Committees
The Legislative Assembly has Standing and Temporary Committees, technical bodies destined to conduct studies and provide specialised reports. Below is the list of Standing Committees:[8]
| Committee | President |
|---|---|
| Committee on Agriculture, Animal Husbandry, Fishing and Cooperativism | Luciano Silveira (MDB) |
| Committee on Municipal Affairs | Joel Wilhelm (PP) |
| Committee on Citizenship and Human Rights | Laura Sito (PT) |
| Committee on Constitution and Justice | Frederico Antunes (PP) |
| Committee on Economy, Sustainable Development and Tourism | Gustavo Victorino (Republicanos) |
| Committee on Education, Culture, Sport, Science and Technology | Sofia Cavedon (PT) |
| Committee on Finance, Planning, Inspection and Control | Patrícia Alba (MDB) |
| Committee on Health and the Environment | Neri Júnior (PSDB) |
| Committee on Security, Public Services and State Modernization | Stela Farias (PT) |
| Joint Standing Committee on Consumer and Taxpayer Protection and Popular Legislative Participation | Thiago Duarte (UNIÃO) |
| Joint Standing Committee on Mercosur and International Affairs | Adriana Lara (PL) |
Historical composition
| Legislature (election) | Parliamentary groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Non-aligned | Opposition | ||
| Vargas Era | ||||
| XXXVI (1935) |  |
|
| |
| Fourth Republic | ||||
| XXXVII (1947) |  |
| ||
| XXXVIII (1950) | 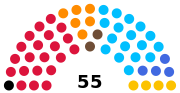 |
|
| |
| XXXIX (1954) |  |
| ||
| XL (1958) |  | |||
| XLI (1962) |  |
|
| |
| Military dictatorship | ||||
| XLII (1966) |  |
| — |
|
| XLIII (1970) |  |
| — |
|
| XLIV (1974) |  |
| — |
|
| XLV (1978) |  |
| — |
|
| XLVI (1982) |  |
|
|
|
| Sixth Republic | ||||
| XLVII (1986) |  |
|
| |
| XLVIII (1990) |  | |||
| XLIX (1994) |  | |||
| L (1998) |  |
| ||
| LI (2002) |  | |||
| LII (2006) |  | |||
| LIII (2010) | 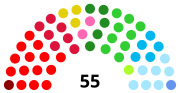 | |||
| LIV (2014) |  | |||
| LV (2018) |  | |||
| References: [9][10][11][12] | ||||