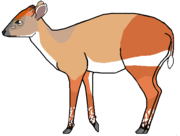
Bovidae is a family of hoofed ruminant mammals in the order Artiodactyla. A member of this family is called a bovid. They are widespread throughout Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America, and are found in a variety of biomes, most typically forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland. Bovids range in size from the 38 cm (15 in) long royal antelope to the 3.3 m (11 ft) long gaur, which can reach 1,500 kg (3,300 lb) in weight.[1] Over a billion each of domesticated sheep, cattle, and goats, and over 200 million domesticated water buffalo, 14 million domestic yak, and 300,000 domesticated gayal are used in farming worldwide. Many wild species do not have population estimates, though the impala, springbok, and harnessed bushbuck have population sizes of over one million, while several species of bovid are considered endangered or critically endangered with populations as low as 25. One species, the scimitar oryx, was once extinct in the wild, though populations are now recovering. The bluebuck went extinct in the last 200 years, and the aurochs went extinct 400 years ago. A third extinct species, the red gazelle, potentially never existed,[2] and the kouprey is potentially extinct, with no sightings since 1969.[3]

The 146 extant species of Bovidae are split into 53 genera within 9 subfamilies: Aepycerotinae, or the impala; Alcelaphinae, containing the bontebok, hartebeest, wildebeest, and relatives; Antilopinae, containing several antelope, gazelles, and relatives; Bovinae, containing cattle, buffalos, bison, and other antelopes; Caprinae, containing goats, sheep, ibex, serows and relatives; Cephalophinae, or duikers; Hippotraginae, containing the addax, oryx, and relatives; Nesotraginae, or dwarf antelopes; and Reduncinae, or reedbuck and kob antelopes. Extinct species have also been placed into these subfamilies, as well as the extinct Hypsodontinae, Oiocerinae, and Tethytraginae subfamilies. Over one hundred extinct Bovidae species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.[4]
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (2 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (6 species) |
| EN | Endangered (19 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (24 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (25 species) |
| LC | Least concern (59 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (3 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (10 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the bovid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted. All extinct species or subspecies listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†".
Classification
The family Bovidae consists of 146 extant species belonging to 53 genera in 9 subfamilies and divided into hundreds of extant subspecies. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species. Additionally, the bluebuck went extinct in the last 200 years, and the aurochs went extinct 400 years ago.
- Subfamily Aepycerotinae
- Genus Aepyceros: one species
- Subfamily Alcelaphinae
- Genus Alcelaphus: one species
- Genus Beatragus: one species
- Genus Connochaetes: two species
- Genus Damaliscus: two species
- Subfamily Antilopinae
- Genus Ammodorcas: one species
- Genus Antidorcas: one species
- Genus Antilope: one species
- Genus Dorcatragus: one species
- Genus Eudorcas: five species
- Genus Gazella: ten species
- Genus Litocranius: one species
- Genus Madoqua: four species
- Genus Nanger: three species
- Genus Neotragus: three species
- Genus Oreotragus: one species
- Genus Ourebia: one species
- Genus Procapra: three species
- Genus Raphicerus: three species
- Genus Saiga: one species
- Subfamily Bovinae
- Genus Bison: two species
- Genus Bos: ten species (one extinct)
- Genus Boselaphus: one species
- Genus Bubalus: five species
- Genus Pseudoryx: one species
- Genus Syncerus: one species
- Genus Taurotragus: two species
- Genus Tetracerus: one species
- Genus Tragelaphus: seven species
- Subfamily Caprinae
- Genus Ammotragus: one species
- Genus Arabitragus: one species
- Genus Budorcas: one species
- Genus Capra: nine species
- Genus Capricornis: four species
- Genus Hemitragus: one species
- Genus Naemorhedus: four species
- Genus Nilgiritragus: one species
- Genus Oreamnos: one species
- Genus Ovibos: one species
- Genus Ovis: seven species
- Genus Pantholops: one species
- Genus Pseudois: one species
- Genus Rupicapra: two species
- Subfamily Cephalophinae
- Genus Cephalophus: fifteen species
- Genus Philantomba: three species
- Genus Sylvicapra: one species
- Subfamily Hippotraginae
- Genus Addax: one species
- Genus Hippotragus: three species (one extinct)
- Genus Oryx: four species
- Subfamily Nesotraginae
- Genus Nesotragus: two species
- Subfamily Reduncinae
Bovids
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis.
Subfamily Aepycerotinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impala | A. melampus (Lichtenstein, 1812) Two subspecies
| Southern Africa (Common impala in green) | Size: 120–160 cm (47–63 in) long, plus 30–45 cm (12–18 in) tail[5] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[6] Diet: Grass and shrubs[6][7] | LC
|
Subfamily Alcelaphinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hartebeest | A. buselaphus (Pallas, 1766) Eight subspecies
| Scattered sub-Saharan Africa | Size: 150–245 cm (59–96 in) long, plus 30–70 cm (12–28 in) tail[8] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[9] Diet: Grass[9] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hirola | B. hunteri (P. L. Sclater, 1889) | Border between Kenya and Somalia | Size: 120–205 cm (47–81 in) long, plus 30–45 cm (12–18 in) tail[10] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[11] Diet: Grass, as well as forbs[10][11] | CR
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black wildebeest | C. gnou (Zimmermann, 1780) | Southern Africa | Size: 212–242 cm (83–95 in) long, plus 31–45 cm (12–18 in) tail[12] Habitat: Shrubland and grassland[13] Diet: Grass[13] | LC
|
| Blue wildebeest | C. taurinus (Burchell, 1824) Five subspecies
| Southern and eastern Africa | Size: 170–240 cm (67–94 in) long, plus 60–100 cm (24–39 in) tail[5] Habitat: Savanna and grassland[14] Diet: Grass[14] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bontebok | D. pygargus (Pallas, 1767) Two subspecies
| Southern Africa | Size: 140–160 cm (55–63 in) long, plus 30–45 cm (12–18 in) tail[15] Habitat: Shrubland and grassland[16] Diet: Grass and burnt veldt shrubs[16] | LC
|
| Tsessebe | D. lunatus (Burchell, 1823) Six subspecies
| Scattered sub-Saharan Africa | Size: 150–230 cm (59–91 in) long, plus 36–42 cm (14–17 in) tail[17] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[18] Diet: Grass[18] | LC
|
Subfamily Antilopinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dibatag | A. clarkei (Thomas, 1891) | Horn of Africa | Size: 152–168 cm (60–66 in) long, plus 25–35 cm (10–14 in) tail[19] Habitat: Shrubland and grassland[20] Diet: Leaves and shoots[19][20] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Springbok | A. marsupialis (Zimmermann, 1780) Three subspecies
| Southwestern Africa | Size: 120–150 cm (47–59 in) long, plus 14–28 cm (6–11 in) tail[21] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[22] Diet: Shrubs and grass[22] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blackbuck | A. cervicapra (Linnaeus, 1758) Two subspecies
| India (former range in light green) | Size: Up to 120 cm (47 in) long[23] Habitat: Forest, grassland, and desert[24] Diet: Grass, as well as leaf litter, flowers, and fruit[24] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beira | D. megalotis (Menges, 1894) | Horn of Africa | Size: 76–87 cm (30–34 in) long, plus 5–8 cm (2–3 in) tail[25] Habitat: Shrubland, and rocky areas[26] Diet: Shrubs[26] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heuglin's gazelle | E. tilonura (Heuglin, 1863) | Northeastern Africa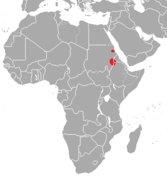 | Size: 55–120 cm (22–47 in) long, plus 15–27 cm (6–11 in) tail[27] Habitat: Savanna and shrubland[28] Diet: Grass and shrubs[27] | EN
|
| Mongalla gazelle | E. albonotata (W. Rothschild, 1903) | South Sudan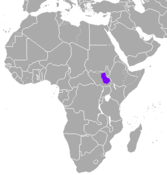 | Size: 80–120 cm (31–47 in) long, plus 15–27 cm (6–11 in) tail[29] Habitat: Savanna and grassland[30] Diet: Grass and shrubs[29] | LC
|
| Red gazelle† | E. rufina Thomas, 1894 | North Africa | Size: Unknown Habitat: Unknown Diet: Unknown | DD
|
| Red-fronted gazelle | E. rufifrons (Gray, 1846) Five subspecies
| Sahel zone in central and western Africa | Size: 80–120 cm (31–47 in) long, plus 15–27 cm (6–11 in) tail[31] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[32] Diet: Grass and shrubs[31] | VU
|
| Thomson's gazelle | E. thomsonii (Günther, 1884) Two subspecies
| Eastern Africa | Size: 80–120 cm (31–47 in) long, plus 15–27 cm (6–11 in) tail[33] Habitat: Savanna and grassland[34] Diet: Grass, as well as forbs and fruit[34] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabian gazelle | G. arabica (Lichtenstein, 1827) Two subspecies
| Arabian Peninsula | Size: About 100 cm (39 in) long, plus 9 cm (4 in) tail[35] Habitat: Shrubland and grassland[36] Diet: Cyperus sedges[36] | VU
|
| Arabian sand gazelle | G. marica Thomas, 1897 | Arabian Peninsula | Size: About 97 cm (38 in) long, plus 15 cm (6 in) tail[37] Habitat: Desert[38] Diet: Grass and forbs[37] | VU
|
| Chinkara | G. bennettii (Sykes, 1831) Six subspecies
| South Asia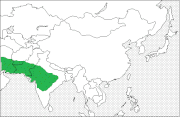 | Size: 90–120 cm (35–47 in) long[39] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and desert[40] Diet: Grass, leaves, crops, and fruit[39] | LC
|
| Cuvier's gazelle | G. cuvieri (Ogilby, 1841) | Northwestern Africa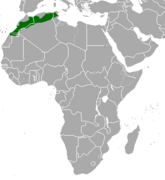 | Size: 95–105 cm (37–41 in) long, plus 15–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[41] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, rocky areas, and desert[42] Diet: Leaves and grass[41] | VU
|
| Dorcas gazelle | G. dorcas (Linnaeus, 1758) Six subspecies
| Northern Africa | Size: 90–110 cm (35–43 in) long, plus 15–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[43] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert[44] Diet: Acacia tree flowers, leaves, and pods, as well as other fruit and leaves[45] | VU
|
| Erlanger's gazelle | G. erlangeri Neumann, 1906 | Arabian Peninsula | Size: 110–125 cm (43–49 in) long, plus 15–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[46] Habitat: Desert[46] Diet: Grass[46] | NE
|
| Goitered gazelle | G. subgutturosa (Güldenstädt, 1780) Three subspecies
| Western and central Asia | Size: 90–115 cm (35–45 in) long, plus 15–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[47] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert[48] Diet: Grass and low plants[49] | VU
|
| Mountain gazelle | G. gazella (Pallas, 1766) Six subspecies
| Mediterranean western Asia | Size: 100–125 cm (39–49 in) long, plus 8–13 cm (3–5 in) tail[50] Habitat: Desert and coastal marine[51] Diet: Grass, herbs, and shrubs[52] | EN
|
| Rhim gazelle | G. leptoceros (F. Cuvier, 1842) Two subspecies
| Scattered northern Africa | Size: 100–110 cm (39–43 in) long, plus 15–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[53] Habitat: Desert[54] Diet: Desert vegetation[54] | EN
|
| Speke's gazelle | G. spekei Blyth, 1863 | Horn of Africa | Size: 95–105 cm (37–41 in) long, plus 15–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[55] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert[56] Diet: Grass and leaves[55] | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gerenuk | L. walleri (Brooke, 1878) Two subspecies
| Horn of Africa | Size: 140–160 cm (55–63 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[57] Habitat: Savanna and shrubland[58] Diet: Shrubs[58] | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Günther's dik-dik | M. guentheri Thomas, 1894 Two subspecies
| Horn of Africa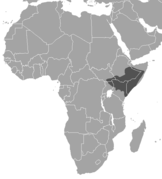 | Size: 55–65 cm (22–26 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[59] Habitat: Shrubland[60] Diet: Shrubs, leaves, and flowers[61] | LC
|
| Kirk's dik-dik | M. kirkii (Günther, 1880) Four subspecies
| Southeastern and southwestern Africa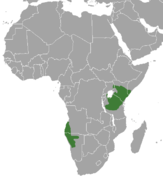 | Size: 52–67 cm (20–26 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail[62] Habitat: Shrubland[63] Diet: Leaves, as well as grass, herbs, and sedge[63] | LC
|
| Salt's dik-dik | M. saltiana (Desmarest, 1816) Five subspecies
| Horn of Africa | Size: 52–67 cm (20–26 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail[64] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[65] Diet: Acacia bushes, as well as leaves, buds, flowers, fruit, and herbs[64][65] | LC
|
| Silver dik-dik | M. piacentinii Drake-Brockman, 1911 | Horn of Africa | Size: 45–50 cm (18–20 in) long, plus 3–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[66] Habitat: Shrubland[67] Diet: Grass and shrubs[66] | DD
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dama gazelle | N. dama (Pallas, 1766) Three subspecies
| Scattered Saharan Desert and Sahel | Size: 140–168 cm (55–66 in) long[68] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and desert[69] Diet: Shrubs and grass[69] | CR
|
| Grant's gazelle | N. granti (Brooke, 1872) Five subspecies
| Eastern Africa | Size: 140–166 cm (55–65 in) long, plus 20–28 cm (8–11 in) tail[70] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[71] Diet: Leaves and stems, as well as grass[72][71] | LC
|
| Soemmerring's gazelle | N. soemmerringii (Cretzschmar, 1828) Three subspecies
| Horn of Africa | Size: 125–150 cm (49–59 in) long, plus 18–23 cm (7–9 in) tail[73] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[74] Diet: Leaves, grass, and herbs[73] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Royal antelope | N. pygmaeus (Linnaeus, 1758) | Western Africa | Size: 38–51 cm (15–20 in) long, plus 5–8 cm (2–3 in) tail[75] Habitat: Forest[76] Diet: Leaves and shoots, as well as fruit and fungi[75] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Klipspringer | O. oreotragus (Zimmermann, 1783) Five subspecies
| Southern and Eastern Africa | Size: 75–115 cm (30–45 in) long[77] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, rocky areas, and desert[78] Diet: Shrubs[78] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oribi | O. ourebi (Zimmermann, 1782) Eight subspecies
| Sub-Saharan Africa | Size: 92–110 cm (36–43 in) long[79] Habitat: Savanna and grassland[80] Diet: Grass and shrubs[79] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goa | P. picticaudata Hodgson, 1846 | Western China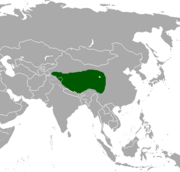 | Size: 91–105 cm (36–41 in) long, plus 8–9 cm (3–4 in) tail[81] Habitat: Grassland and inland wetlands[82] Diet: Forbs and legumes, as well as grass and sedges[81] | NT
|
| Mongolian gazelle | P. gutturosa (Pallas, 1777) | Mongolia and nearby central Asia (historical range in light green)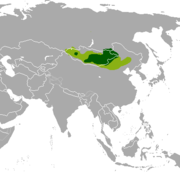 | Size: 100–130 cm (39–51 in) long[83] Habitat: Grassland and desert[84] Diet: Grass, onions, and shrubs[83] | LC
|
| Przewalski's gazelle | P. przewalskii (Büchner, 1891) Two subspecies
| Central China | Size: 105–110 cm (41–43 in) long, plus up to 11 cm (4 in) tail[85] Habitat: Grassland and desert[86] Diet: Shrubs and grass[85] | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cape grysbok | R. melanotis (Thunberg, 1811) | Southern Africa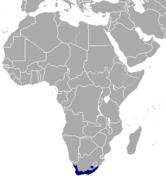 | Size: 65–80 cm (26–31 in) long, plus up to 4–8 cm (2–3 in) tail[87] Habitat: Shrubland and grassland[88] Diet: Shrubs and grass[88] | LC
|
| Sharpe's grysbok | R. sharpei Thomas, 1897 | Southeastern Africa | Size: 65–75 cm (26–30 in) long, plus 4–8 cm (2–3 in) tail[89] Habitat: Savanna and shrubland[90] Diet: Shrubs and grass[90] | LC
|
| Steenbok | R. campestris (Thunberg, 1811) Four subspecies
| Southern and southeastern Africa | Size: 70–95 cm (28–37 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (2–2 in) tail[91] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[92] Diet: Shrubs, geophytes, berries, flowers, and fruit[92] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saiga antelope | S. tatarica (Linnaeus, 1766) Two subspecies
| Central Asia (historical range in white) | Size: 108–146 cm (43–57 in) long, plus 6–13 cm (2–5 in) tail[93] Habitat: Grassland and desert[94] Diet: Grass[94] | NT
|
Subfamily Bovinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American bison | B. bison Linnaeus, 1758 | Scattered North America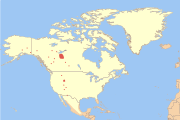 | Size: 210–380 cm (83–150 in) long, plus 43–90 cm (17–35 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, and desert[95] Diet: Grass, leaves, and roots, as well as sagebrush[5][95] | NT |
| European bison | B. bonasus Linnaeus, 1758 Three subspecies
| Scattered Europe and western Asia | Size: 280–330 cm (110–130 in) long, plus 30–92 cm (12–36 in) tail[97] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and unknown[98] Diet: Grass, sedges and herbs, as well as trees and shrubs[99] | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aurochs† | B. primigenius Bojanus, 1827 | Formerly Europe, Asia, and North Africa | Size: Unknown Habitat: Unknown Diet: Grass[100] | EX
|
| Banteng | B. javanicus d'Alton, 1823 Two subspecies
| Southeast Asia (possible range in red)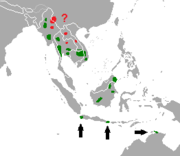 | Size: 190–225 cm (75–89 in) long, plus 65–70 cm (26–28 in) tail[101] Habitat: Forest and grassland[102] Diet: Grass, sedges, herbs, and bamboo, as well as leaves, fruit, flowers, bark, and young branches of shrubs and trees[102] | EN
|
| Bali cattle | B. domesticus Wilckens, 1905 | Southeast Asia | Size: 190–225 cm (75–89 in) long, plus 65–70 cm (26–28 in) tail[101] Habitat: Forest and grassland[102] Diet: Grass, sedges, herbs, and bamboo, as well as leaves, fruit, flowers, bark, and young branches of shrubs and trees[102] | NE
|
| Cattle | B. taurus Linnaeus, 1758 | Worldwide | Size: 150–250 cm (59–98 in) long[103] Habitat: Grassland, shrubland, forest, and desert[100] Diet: Grass[100] | NE
|
| Gaur | B. gaurus Smith, 1827 Two subspecies
| Southern and southeastern Asia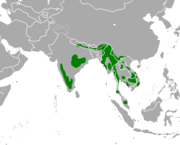 | Size: 250–330 cm (98–130 in) long, plus 70–100 cm (28–39 in) tail[1] Habitat: Forest, savanna, grassland, and shrubland[105] Diet: Grass as well as leaves, fruit, twigs, bark, and bamboo[105] | VU
|
| Gayal | B. frontalis Lambert, 1804 Four subspecies
| South Asia | Size: 250–330 cm (98–130 in) long, plus 70–105 cm (28–41 in) tail[106] Habitat: Forest and grassland[106] Diet: Grass, forbs, and leaves[106] | NE |
| Kouprey | B. sauveli Urbain, 1937 | Southeast Asia | Size: 210–223 cm (83–88 in) long, plus up to 100 cm (39 in) tail[108] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and grassland[3] Diet: Grass, sedges, and shrubs[3] | CR
|
| Wild yak | B. mutus (Przhevalsky, 1883) | Central Asia | Size: 306–385 cm (120–152 in) long, plus up to 60 cm (24 in) tail[109] Habitat: Grassland and desert[110] Diet: Grass and sedges, as well as forbs[110] | VU
|
| Yak | B. grunniens Linnaeus, 1766 | Central Asia | Size: 145–218 cm (57–86 in) long, plus 60 cm (24 in) tail[111] Habitat: Rocky areas and grassland[112] Diet: Grass, shrubs, and forbs, as well as lichen and moss[112] | NE
|
| Zebu | B. indicus Linnaeus, 1758 | Asia | Size: 150–250 cm (59–98 in) long[103] Habitat: Grassland, shrubland, forest, and desert[100] Diet: Grass[100] | NE
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nilgai | B. tragocamelus (Pallas, 1766) | Indian subcontinent | Size: 180–200 cm (71–79 in) long[114] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[115] Diet: Grass and shrubs[115] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lowland anoa | B. depressicornis (H. Smith, 1827) | Island of Sulawesi in Indonesia | Size: 122–188 cm (48–74 in) long, plus up to 41 cm (16 in) tail[116] Habitat: Forest[117] Diet: Shrubs[117] | EN
|
| Mountain anoa | B. quarlesi (Ouwens, 1910) | Island of Sulawesi in Indonesia | Size: 122–153 cm (48–60 in) long[118] Habitat: Forest[119] Diet: Grass and shrubs[119] | EN
|
| Tamaraw | B. mindorensis Heude, 1888 | Island of Mindoro in the Philippines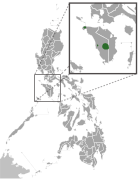 | Size: Around 220 cm (87 in) long, plus 60 cm (24 in) tail[120] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[121] Diet: Grass and young bamboo shoots[121] | CR
|
| Water buffalo | B. bubalis (Linnaeus, 1758) Three subspecies
| Scattered Asia, Egypt, and South America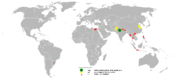 | Size: 240–300 cm (94–118 in) long, plus 60–100 cm (24–39 in) tail[122] Habitat: Forest and grassland[122] Diet: Grass, as well as herbs, shrubs, and leaves[122] | NE
|
| Wild water buffalo | B. arnee (Kerr, 1792) Four subspecies
| Scattered Southeast Asia | Size: 240–300 cm (94–118 in) long, plus up to 60–100 cm (24–39 in) tail[124] Habitat: Forest, savanna, grassland, and inland wetlands[125] Diet: Grass and sedges, as well as fruit and shrubs[124] | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saola | P. nghetinhensis Dung, Giao, Chinh, Tuoc, Arctander, MacKinnon, 1993 | Annamite Range of Vietnam and Laos | Size: 143–150 cm (56–59 in) long, plus up to 25 cm (10 in) tail[126] Habitat: Forest[127] Diet: Leaves as well as shrubs[127] | CR
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| African buffalo | S. caffer (Sparrman, 1779) Five subspecies
| Sub-Saharan Africa | Size: 240–340 cm (94–134 in) long, plus 75–110 cm (30–43 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[128] Diet: Grass[5] | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common eland | T. oryx (Pallas, 1766) Three subspecies
| Eastern and southern Africa | Size: 200–345 cm (79–136 in) long, plus 50–72 cm (20–28 in) tail[129] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[130] Diet: Shrubs[130] | LC
|
| Giant eland | T. derbianus (Gray, 1847) Two subspecies
| Western and central Africa | Size: 210–345 cm (83–136 in) long, plus 55–70 cm (22–28 in) tail[131][132] Habitat: Forest and savanna[133] Diet: Leaves, shoots, herbs and fruit, as well as grass[133] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Four-horned antelope | T. quadricornis (Blainville, 1816) Three subspecies
| Indian subcontinent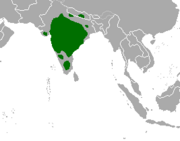 | Size: 80–110 cm (31–43 in) long, plus 10–15 cm (4–6 in) tail[134] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[135] Diet: Grass and shrubs[135] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bongo | T. eurycerus (Ogilby, 1837) | Western and central Africa | Size: 170–250 cm (67–98 in) long, plus 45–65 cm (18–26 in) tail[136] Habitat: Forest and savanna[137] Diet: Shrubs as well as grass[137] | NT
|
| Greater kudu | T. strepsiceros (Pallas, 1766) Three subspecies
| Central, eastern, and southern Africa | Size: 180–250 cm (71–98 in) long[5] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and desert[138] Diet: Shrubs[138] | LC
|
| Harnessed bushbuck | T. scriptus (Pallas, 1766) Eight subspecies
| Western and central Africa | Size: 105–150 cm (41–59 in) long, plus 19–25 cm (7–10 in) tail[139] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[140] Diet: Shrubs[140] | LC
|
| Lesser kudu | T. imberbis (Blyth, 1869) | Eastern Africa | Size: 110–175 cm (43–69 in) long, plus 26–30 cm (10–12 in) tail[141] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[142] Diet: Tree leaves, shrubs, and herbs[142] | NT
|
| Mountain nyala | T. buxtoni (Lydekker, 1910) | Central Ethiopia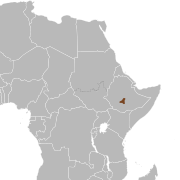 | Size: 190–260 cm (75–102 in) long[143] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[144] Diet: Grass, herbs, and shrubs[143] | EN
|
| Nyala | T. angasii Angas, 1849 | Southeastern Africa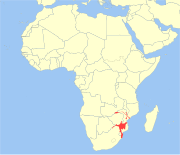 | Size: 132–198 cm (52–78 in) long, plus 35–55 cm (14–22 in) tail[145] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[146] Diet: Leaves and fruit as well as grass[146] | LC
|
| Sitatunga | T. spekii P. L. Sclater, 1863 Five subspecies
| Central Africa | Size: 115–170 cm (45–67 in) long, plus 18–30 cm (7–12 in) tail[147] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[148] Diet: Grass, sedges, and shrubs[148] | LC
|
Subfamily Caprinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barbary sheep | A. lervia (Pallas, 1777) Six subspecies
| Northern Africa | Size: 130–165 cm (51–65 in) long, plus 12–25 cm (5–10 in) tail[149] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and desert[150] Diet: Grass, shrubs, and forbs[150] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabian tahr | A. jayakari Thomas, 1894 | Eastern Arabia | Size: 93–95 cm (37–37 in) long, plus up to 8–10 cm (3–4 in) tail[151] Habitat: Shrubland, rocky areas, and desert[152] Diet: Grass, forbs, shrubs, and trees[152] | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Takin | B. taxicolor Hodgson, 1850 Four subspecies
| Eastern Himalayas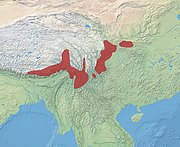 | Size: 170–220 cm (67–87 in) long, plus 15 cm (6 in) tail[153] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[154] Diet: Grass, bamboo shoots, forbs, and leaves[154] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpine ibex | C. ibex Linnaeus, 1758 | The Alps | Size: 130–140 cm (51–55 in) long, plus 12–15 cm (5–6 in) tail[155] Habitat: Grassland, and rocky areas[156] Diet: Grass and herbs, as well as woody plants and cryptogams[156] | LC
|
| East Caucasian tur | C. cylindricornis (Blyth, 1841) | Caucasus Mountains in eastern Europe | Size: 120–165 cm (47–65 in) long, plus 10–14 cm (4–6 in) tail[157] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[158] Diet: Grass, trees, and a variety of other plants[158] | NT
|
| Iberian ibex | C. pyrenaica Schinz, 1838 | Iberian Peninsula | Size: 100–140 cm (39–55 in) long, plus 10–15 cm (4–6 in) tail[159] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and rocky areas[160] Diet: Leaves, acorns, forbs, and grass[159] | LC
|
| Markhor | C. falconeri (Wagner, 1839) Three subspecies
| Central Asia | Size: 140–185 cm (55–73 in) long, plus 8–14 cm (3–6 in) tail[161] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and rocky areas[162] Diet: Grass and leaves[162] | NT
|
| Nubian ibex | C. nubiana F. Cuvier, 1825 | Northern Africa and the Middle East | Size: 105–125 cm (41–49 in) long[163] Habitat: Shrubland, rocky areas, and desert[164] Diet: Wide variety of herbaceous and woody plants[164] | VU
|
| Siberian ibex | C. sibirica (Pallas, 1776) | Central Asia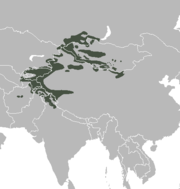 | Size: 130–165 cm (51–65 in) long, plus 10–18 cm (4–7 in) tail[165] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and desert[166] Diet: Grass, as well as herbs and shrubs[166] | NT
|
| Walia ibex | C. walie Rüppell, 1835 | Northeastern Africa | Size: 150–170 cm (59–67 in) long, plus 20–25 cm (8–10 in) tail[167] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[168] Diet: Shrubs, herbs, lichens, and grass[169] | VU
|
| West Caucasian tur | C. caucasica Güldenstädt, Pallas, 1783 Two subspecies
| Caucasus Mountains in eastern Europe | Size: 120–165 cm (47–65 in) long, plus 10–14 cm (4–6 in) tail[170] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[171] Diet: Grass, trees, and a variety of other plants[171] | EN
|
| Wild goat | C. aegagrus Erxleben, 1777 Five subspecies
| Western Asia (worldwide distribution of domestic goat in farming) | Size: 115–170 cm (45–67 in) long[172] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and desert[173] Diet: Grass, herbaceous plants, and shrubs, as well as trees[173] | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese serow | C. crispus (Temminck, 1836) | Japan | Size: Around 130 cm (51 in) long[174] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[175] Diet: Leaves, shoots, and acorns[175] | LC
|
| Mainland serow | C. sumatraensis (Bechstein, 1799) Three subspecies
| The Himalayas and southeastern Asia | Size: 140–155 cm (55–61 in) long, plus 8–16 cm (3–6 in) tail[176] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[177] Diet: Leaves and twigs[177] | VU
|
| Red serow | C. rubidus (Blyth, 1863) | Southeastern Asia | Size: 140–155 cm (55–61 in) long[178] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and rocky areas[179] Diet: Grass, shoots, and leaves[178] | NT
|
| Taiwan serow | C. swinhoei Gray, 1862 | Taiwan | Size: 80–114 cm (31–45 in) long, plus 7–12 cm (3–5 in) tail[180] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[181] Diet: Grass and shrubs[181] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Himalayan tahr | H. jemlahicus (H. Smith, 1826) | Himalayas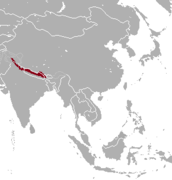 | Size: 90–140 cm (35–55 in) long[182] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[183] Diet: Herbaceous plants and shrubs, grass, and sedges[183] | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese goral | N. griseus (Milne-Edwards, 1874) Two subspecies
| Southeastern Asia 178px|alt=Map of range | Size: 88–118 cm (35–46 in) long, plus 11–20 cm (4–8 in) tail[184] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and rocky areas[185] Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, and nuts[185] | NE
|
| Himalayan goral | N. goral (Hardwicke, 1825) Two subspecies
| Himalayas | Size: 81–130 cm (32–51 in) long[186] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[187] Diet: Grass, leaves, twigs, fruit, and nuts[187] | NT
|
| Long-tailed goral | N. caudatus (H. Milne-Edwards, 1867) | Eastern Asia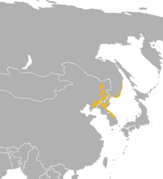 | Size: 81–129 cm (32–51 in) long[188] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[189] Diet: Grass, herbs, shoots, leaves, nuts, as well as fruit[189] | VU
|
| Red goral | N. baileyi Pocock, 1914 | Eastern Asia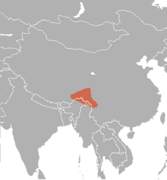 | Size: 93–103 cm (37–41 in) long, plus 7–10 cm (3–4 in) tail[190] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and rocky areas[191] Diet: Lichens, as well as grass, shoots, leaves, and twigs[191] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nilgiri tahr | N. hylocrius (Ogilby, 1838) | Southern India | Size: 90–140 cm (35–55 in) long, plus 9–12 cm (4–5 in) tail[192] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[193] Diet: Grass and forbs[193] | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mountain goat | O. americanus (Blainville, 1816) | Western North America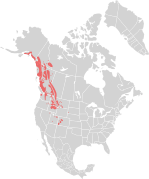 | Size: 120–160 cm (47–63 in) long, plus 8–20 cm (3–8 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[194] Diet: Grass, forbs, sedges, ferns, moss, lichen, twigs, and leaves[194] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muskox | O. moschatus (Zimmermann, 1780) | The Arctic (reintroduced in blue) | Size: 190–270 cm (75–106 in) long, plus 7–12 cm (3–5 in) tail[5] Habitat: Grassland[195] Diet: Sedges and grass, as well as shrubs and some forbs[195] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argali | O. ammon Linnaeus, 1758 Nine subspecies
| Central and eastern Asia | Size: 120–190 cm (47–75 in) long[196] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and desert[197] Diet: Grass, sedges, and some herbs and lichens[197] | NT
|
| Bighorn sheep | O. canadensis Shaw, 1804 Three subspecies
| Western North America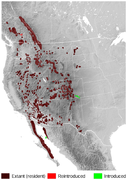 | Size: 160–180 cm (63–71 in) long[198] Habitat: Grassland, and rocky areas[199] Diet: Grass, as well as forbs and shrubs[199] | LC
|
| Dall sheep | O. dalli Nelson, 1884 Two subspecies
| Northwestern North America | Size: 130–180 cm (51–71 in) long, plus 7–12 cm (3–5 in) tail[200] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[201] Diet: Grass and sedges[201] | LC
|
| Mouflon | O. gmelini Blyth, 1841 Four subspecies
| Western Asia | Size: 105–140 cm (41–55 in) long, plus 12–13 cm (5–5 in) tail[202] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[203] Diet: Grass and shrubs[202] | NT
|
| Sheep | O. aries Linnaeus, 1758 | Domesticated worldwide | Size: 120–180 cm (47–71 in) long, plus 7–15 cm (3–6 in) tail[204] Habitat: Savanna, grassland, desert, forest, and rocky areas[204] Diet: Grass, as well as a wide variety of vegetation[204] | NE
|
| Snow sheep | O. nivicola Eschscholtz, 1829 Six subspecies
| Eastern Russia | Size: 126–188 cm (50–74 in) long[206] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[207] Diet: Grass, as well as lichens, mosses, and willow sprouts[207] | LC
|
| Urial | O. vignei Blyth, 1841 | Central and southern Asia | Size: 120–160 cm (47–63 in) long, plus 11–13 cm (4–5 in) tail[208] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[209] Diet: Grass and shrubs[208] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibetan antelope | P. hodgsonii (Abel, 1826) | Tibetan Plateau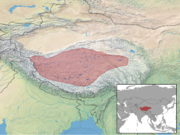 | Size: 120–130 cm (47–51 in) long[210] Habitat: Grassland[211] Diet: Grass and herbs[210] | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bharal | P. nayaur (Hodgson, 1833) | Himalayas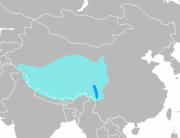 | Size: 120–140 cm (47–55 in) long[212] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and desert[213] Diet: Grass, alpine herbs, and lichens[213] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chamois | R. rupicapra (Linnaeus, 1758) Seven subspecies
| Europe and western Asia (former range in gray)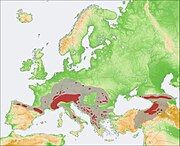 | Size: 110–135 cm (43–53 in) long[214] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[215] Diet: Grass, herbs, tree leaves, buds, shoots, and fungi[215] | LC
|
| Pyrenean chamois | R. pyrenaica Bonaparte, 1845 Three subspecies
| Southern Europe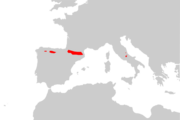 | Size: 90–130 cm (35–51 in) long, plus 3–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[216] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[217] Diet: Herbs and flowers, as well as lichen, moss, and young pine shoots[216] | LC
|
Subfamily Cephalophinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbott's duiker | C. spadix True, 1890 | Tanzania | Size: 97–140 cm (38–55 in) long, plus 8–13 cm (3–5 in) tail[218] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[219] Diet: Leaves, fruit, flowers and moss[218] | EN
|
| Aders's duiker | C. adersi (Thomas, 1918) | Eastern Africa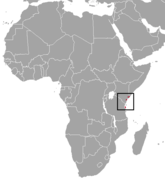 | Size: 66–72 cm (26–28 in) long, plus 9–12 cm (4–5 in) tail[220] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[221] Diet: Leaves, seeds, sprouts, buds, and fruit[221] | VU
|
| Bay duiker | C. dorsalis Gray, 1846 Two subspecies
| Western and southern Africa | Size: 70–100 cm (28–39 in) long[222] Habitat: Forest[223] Diet: Fruit and leaves, as well as birds[222] | NT
|
| Black duiker | C. niger (Gray, 1846) | Western Africa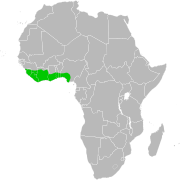 | Size: 80–90 cm (31–35 in) long, plus 12–14 cm (5–6 in) tail[224] Habitat: Forest[225] Diet: Flowers, leaves, shrubs, grass, fruit, insects, and eggs[225] | LC
|
| Black-fronted duiker | C. nigrifrons (Gray, 1871) Six subspecies
| Central Africa | Size: 80–170 cm (31–67 in) long, plus 7–15 cm (3–6 in) tail[226] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[227] Diet: Fruit and leaves[228] | LC
|
| Brooke's duiker | C. brookei (Thomas, 1903) | Western Africa | Size: About 100 cm (39 in) long, plus 12 cm (5 in) tail[229] Habitat: Forest[229] Diet: Fruit and leaves[229] | NE
|
| Jentink's duiker | C. jentinki Thomas, 1892 | Western Africa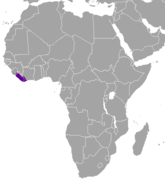 | Size: 130–150 cm (51–59 in) long, plus 12–16 cm (5–6 in) tail[230] Habitat: Forest[231] Diet: Fruit, nuts, and tree stems[231] | EN
|
| Ogilby's duiker | C. ogilbyi (Waterhouse, 1838) | Western Africa | Size: 85–115 cm (33–45 in) long, plus 12–15 cm (5–6 in) tail[232] Habitat: Forest[233] Diet: Fruit and leaves[232] | LC
|
| Peters's duiker | C. callipygus (Peters, 1876) | Western central Africa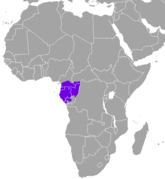 | Size: 94–109 cm (37–43 in) long, plus 8–15 cm (3–6 in) tail[234] Habitat: Forest[235] Diet: Fruit and leaves[234] | LC
|
| Red forest duiker | C. natalensis (Smith, 1834) Two subspecies
| Southeastern Africa | Size: 75–87 cm (30–34 in) long, plus 9–14 cm (4–6 in) tail[236] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[237] Diet: Fruit and leaves[236] | LC
|
| Red-flanked duiker | C. rufilatus (Gray, 1846) | Western and central Africa | Size: 60–80 cm (24–31 in) long[238] Habitat: Forest and savanna[239] Diet: Leaves and fruit, as well as flowers and twigs[238] | LC
|
| Weyns's duiker | C. weynsi (Thomas, 1901) Three subspecies
| Central Africa | Size: 80–115 cm (31–45 in) long, plus 8–16 cm (3–6 in) tail[240] Habitat: Forest[241] Diet: Fruit and leaves[240] | LC
|
| White-bellied duiker | C. leucogaster (Gray, 1873) Two subspecies
| Central Africa | Size: 78–100 cm (31–39 in) long, plus 8–15 cm (3–6 in) tail[242] Habitat: Forest[243] Diet: Fruit, leaves, and flowers[242] | NT
|
| White-legged duiker | C. crusalbum Grubb, 1978 | Western Africa | Size: 85–115 cm (33–45 in) long, plus 12–15 cm (5–6 in) tail[232] Habitat: Forest[244] Diet: Fruit and leaves[232] | NT
|
| Yellow-backed duiker | C. silvicultor (Afzelius, 1815) Four subspecies
| Central and western Africa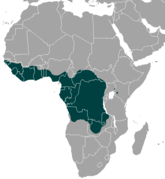 | Size: 115–145 cm (45–57 in) long, plus 11–18 cm (4–7 in) tail[245] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[246] Diet: Fruit, as well as leaves, seeds, buds, bark, and shoots[245] | NT
|
| Zebra duiker | C. zebra (Gray, 1838) | Western Africa | Size: 70–90 cm (28–35 in) long, plus 10–15 cm (4–6 in) tail[247] Habitat: Forest[248] Diet: Fruit and leaves[247] | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue duiker | P. monticola (Thunberg, 1789) Twelve subspecies
| Central and southern Africa | Size: 55–72 cm (22–28 in) long, plus 7–13 cm (3–5 in) tail[249] Habitat: Forest[250] Diet: Fruit, seeds, flowers, and fungi[249] | LC
|
| Maxwell's duiker | P. maxwellii (H. Smith, 1827) Two subspecies
| Western Africa | Size: 36–40 cm (14–16 in) long[251] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[252] Diet: Leaves and fruit[252] | LC
|
| Walter's duiker | P. walteri Colyn, Huselman, Sonet, Oudé, Winters, Natta, Nagy, Verheyen, 2010 | Western Africa | Size: Similar to Maxwell's duiker[251] Habitat: Shrubland[253] Diet: Leaves and fruit[251] | DD
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common duiker | S. grimmia (Linnaeus, 1758) Thirteen subspecies
| Sub-Saharan Africa | Size: 70–105 cm (28–41 in) long, plus 10–20 cm (4–8 in) tail[254] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[255] Diet: Variety of foliage, herbs, fruit, seeds, and cultivated crops[255] | LC
|
Subfamily Hippotraginae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Addax | A. nasomaculatus (Blainville, 1816) | Scattered western Africa | Size: 150–170 cm (59–67 in) long, plus 25–35 cm (10–14 in) tail[256] Habitat: Savanna, grassland, and desert[257] Diet: Grass and shrubs[256] | CR
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bluebuck† | H. leucophaeus (Pallas, 1766) | Southern tip of Africa (former range) | Size: 230–300 cm (91–118 in) long[258] Habitat: Grassland[259] Diet: Grass[258] | EX
|
| Roan antelope | H. equinus (Desmarest, 1804) Six subspecies
| Sub-Saharan Africa | Size: 190–240 cm (75–94 in) long, plus 37–48 cm (15–19 in) tail[260] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[261] Diet: Grass[260] | LC
|
| Sable antelope | H. niger (Harris, 1838) Four subspecies
| Southeastern Africa | Size: 190–255 cm (75–100 in) long, plus 40–75 cm (16–30 in) tail[262] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[263] Diet: Grass, as well as forbs and leaves[263] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabian oryx | O. leucoryx (Pallas, 1777) | Arabian Peninsula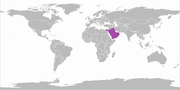 | Size: 153–235 cm (60–93 in) long, plus 45–90 cm (18–35 in) tail[264] Habitat: Desert[265] Diet: Grass and shrubs[265] | VU
|
| East African oryx | O. beisa (Rüppell, 1835) Two subspecies
| Eastern Africa | Size: 153–170 cm (60–67 in) long, plus 45–50 cm (18–20 in) tail[266] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[267] Diet: Grass and shrubs, as well as melons, roots, bulbs, and tubers[267] | EN
|
| Gemsbok | O. gazella (Linnaeus, 1758) | Southern Africa | Size: 180–195 cm (71–77 in) long[268] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[269] Diet: Grass and shrubs, as well as melons, roots, bulbs, and tubers[269] | LC
|
| Scimitar oryx | O. dammah (Cretzschmar, 1827) | Reservation in Chad | Size: 190–220 cm (75–87 in) long, plus 45–60 cm (18–24 in) tail[270] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and desert[271] Diet: Grass, herbs, roots, and buds, as well as fruit and vegetables[272] | EN
|
Subfamily Nesotraginae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bates's pygmy antelope | N. batesi (Winton, 1903) | Central Africa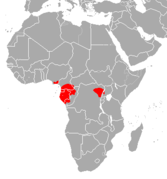 | Size: 50–58 cm (20–23 in) long, plus 4–5 cm (2–2 in) tail[273] Habitat: Forest[274] Diet: Leaves[274] | LC
|
| Suni | N. moschatus von Dueben, 1846 Four subspecies
| Eastern Africa | Size: 57–62 cm (22–24 in) long[275] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[276] Diet: Leaves[275] | LC
|
Subfamily Reduncinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kob | K. kob (Erxleben, 1777) Three subspecies
| Central and western Africa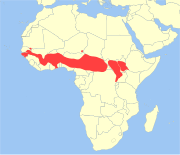 | Size: 160–180 cm (63–71 in) long, plus 10–15 cm (4–6 in) tail[277] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[278] Diet: Grass[278] | LC
|
| Lechwe | K. leche Gray, 1850 Four subspecies
| Scattered southern Africa | Size: 130–180 cm (51–71 in) long, plus 30–45 cm (12–18 in) tail[279] Habitat: Forest, grassland, and inland wetlands[280] Diet: Floodplain and aquatic grass[280] | NT
|
| Nile lechwe | K. megaceros (Fitzinger, 1855) | South Sudan and Ethiopia | Size: 130–180 cm (51–71 in) long, plus 45–50 cm (18–20 in) tail[281] Habitat: Grassland and inland wetlands[282] Diet: Grass and water plants[283] | EN
|
| Puku | K. vardonii (Livingstone, 1857) Two subspecies
| Scattered south-central Africa | Size: 126–142 cm (50–56 in) long[284] Habitat: Savanna, grassland, and inland wetlands[285] Diet: Grass[284] | NT
|
| Waterbuck | K. ellipsiprymnus (Ogilby, 1833) Thirteen subspecies
| Sub-Saharan Africa (ellipsiprymnus, kondensis, pallidus, and thikae in yellow)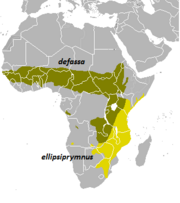 | Size: 177–235 cm (70–93 in) long[286] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[287] Diet: Grass and shrubs[287] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grey rhebok | P. capreolus (Forster, 1790) | Southern Africa | Size: 115–125 cm (45–49 in) long[288] Habitat: Savanna and grassland[289] Diet: Shrubs and forbs[289] | NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bohor reedbuck | R. redunca (Pallas, 1767) Seven subspecies
| Central Africa | Size: 100–135 cm (39–53 in) long[290] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[291] Diet: Grass[291] | LC
|
| Mountain reedbuck | R. fulvorufula (Afzelius, 1815) Three subspecies
| Separated central, eastern, and southern Africa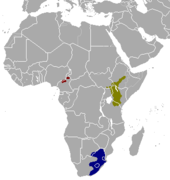 | Size: 100–124 cm (39–49 in) long, plus 13–20 cm (5–8 in) tail[292] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[293] Diet: Grass[293] | EN
|
| Southern reedbuck | R. arundinum (Boddaert, 1785) | Southern Africa | Size: 134–167 cm (53–66 in) long[294] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[295] Diet: Grass, as well as herbs and shrubs[295] | LC
|
Notes
References
Sources
- Castelló, José R. (2016). Bovids of the World: Antelopes, Gazelles, Cattle, Goats, Sheep, and Relatives. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-16717-6.
- Harris, Tim (2018). The Encyclopedia of Animals. Chartwell Books. ISBN 978-0-7858-3646-9.
- Kingdon, Jonathan (2013). The Kingdon Field Guide to African Mammals (1st ed.). Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4081-7481-4.
- Kingdon, Jonathan (2020). The Kingdon Pocket Guide to African Mammals (2nd ed.). Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4729-8320-6.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan, eds. (2013). Mammals of China. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-4688-7.