The Senkaku Islands[a], also known as the Pinnacle Islands or the Diaoyu Islands[b] in China and as the Tiaoyutai Islands[c] in Taiwan, are a group of uninhabited islands in the East China Sea, administered by Japan.
| Disputed islands | |
|---|---|
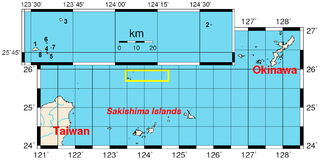 Location of the islands (yellow rectangle and inset) | |
 | |
| Other names | Diaoyu Islands / Diaoyutai Islands / Pinnacle Islands |
| Geography | |
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 25°44′42″N 123°29′06″E / 25.74500°N 123.48500°E |
| Total islands | 5 + 3 rocks (reefs) |
| Major islands |
|
| Area | 7 km2 (2.7 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 383 m (1257 ft) |
| Administration | |
| City | Ishigaki, Okinawa |
| Claimed by | |
| Township | Toucheng Township, Yilan County, Taiwan |
| County | Yilan County, Taiwan |
| Senkaku Islands | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 钓鱼岛及其附属岛屿 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Diaoyu Island and its affiliated islands | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Taiwanese name | |||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 釣魚臺列嶼 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Diaoyutai / Tiaoyutai Islands | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||||
| Kanji | 尖閣諸島 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The islands are located northeast of Taiwan, east of China, west of Okinawa Island, and north of the southwestern end of the Ryukyu Islands.
The islands are the focus of a territorial dispute between Japan and China and between Japan and Taiwan.[9] China claims the discovery and ownership of the islands from the 14th century, while Japan maintained ownership of the islands from 1895 until its surrender at the end of World War II. The United States administered the islands as part of the United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands from 1945 until 1972, when the islands returned to Japanese control under the Okinawa Reversion Agreement between the United States and Japan.[10] The discovery of potential undersea oil reserves in 1968 in the area was a catalyst for further interest in the disputed islands.[11][12][13][14][15] Despite the diplomatic stalemate between China and Taiwan, both governments agree that the islands are part of Taiwan as part of Toucheng Township in Yilan County. Japan administers and controls the Senkaku islands as part of the city of Ishigaki in Okinawa Prefecture. It does not acknowledge the claims of China nor Taiwan, but it has not allowed the Ishigaki administration to develop the islands.
As a result of the dispute, the public is largely barred from approaching the uninhabited islands, which are about a seven-hour boat ride from Ishigaki. Vessels from the Japan Coast Guard pursue Chinese ships crossing the maritime boundary in what one visiting journalist described in 2012 as "an almost cold war-style game of cat-and-mouse", and fishing and other civilian boats are prevented from getting too close to avoid a provocative incident.[16]
The Senkaku Islands are important nesting sites for seabirds, and are one of two remaining nesting sites in the world for the short-tailed albatross, alongside Tori-shima, Izu Islands.[17]
Names
The islands are referred to as the Senkaku Islands (尖閣諸島, Senkaku-shotō, variants: 尖閣群島 Senkaku-guntō[18] and 尖閣列島 Senkaku-rettō[19]) in Japanese. In mainland China, they are known as the Diaoyu Islands (Chinese: 钓鱼岛; pinyin: Diàoyúdǎo) or more fully "Diaoyu Dao and its affiliated islands" (Chinese: 钓鱼岛及其附属岛屿; pinyin: Diàoyúdǎo jí qí fùshǔ dǎoyǔ),[20] while in Taiwan they are called the Diaoyutai Islands[citation needed] or Tiaoyutai Islands[21][22][23][24] (Chinese: 釣魚臺列嶼; pinyin: Diàoyútái liè yǔ).[25][26][27][28] In Western sources, the historical English name Pinnacle Islands is occasionally still used when neutrality among the competing national claims is desirable.[29][30][31][32]
In Okinawan (northern Ryukyu), the islands are known as ʔiyukubajima (魚蒲葵島),[33] while their Yaeyama (southern Ryukyu) name is iigunkubajima.
Chinese records of these islands date back to as early as the 15th century when they were referred as Diaoyu in books such as Voyage with a Tail Wind (Chinese: 順風相送; pinyin: Shùnfēng Xiāngsòng) (1403) [34] and Record of the Imperial Envoy's Visit to Ryūkyū (Chinese: 使琉球錄; pinyin: Shǐ Liúqiú Lù) (1534). Adopted by the Chinese Imperial Map of the Ming Dynasty, the Chinese name for the island group (Diaoyu) and the Japanese name for the main island (Uotsuri) both mean "fishing".
History

Early history
Historically, the Chinese had used the uninhabited islands as navigational markers in making the voyage to the Ryukyu Kingdom upon commencement of diplomatic missions to the kingdom, "resetting the compass at a particular isle in order to reach the next one".[35]
The first published description of the islands in Europe appears in a book imported by Isaac Titsingh in 1796. His small library of Japanese books included Sangoku Tsūran Zusetsu (三國通覧圖說, An Illustrated Description of Three Countries) by Hayashi Shihei.[36] This text, which was published in Japan in 1785, described the Ryūkyū Kingdom.[37] Hayashi followed convention in giving the islands their Chinese names in his map in the text, where he coloured them in the same pink as China.[38]
In 1832, the Oriental Translation Fund of Great Britain and Ireland supported the posthumous abridged publication of Titsingh's French translation.[39]
The name, "Pinnacle Isles" was first used by James Colnett, who charted them during his 1789-1791 voyage in the Argonaut.[40] William Robert Broughton sailed past them in November 1797 during his voyage of discovery to the North Pacific in HMS Providence, and referred to Diaoyu Island/Uotsuri Island as "Peaks Island".[41] Reference was made to the islands in Edward Belcher's 1848 account of the voyages of HMS Sammarang.[42] Captain Belcher observed that "the names assigned in this region have been too hastily admitted."[43] Belcher reported anchoring off Pinnacle Island in March 1845.[44]
In the 1870s and 1880s, the English name Pinnacle Islands was used by the British navy for the rocks adjacent to the largest island Uotsuri-shima / Diaoyu Dao (then called 和平嶼; hô-pîng-sū; 'Peace Island in Hokkien'); Kuba-shima / Huangwei Yu (then called Ti-a-usu); and Taishō-tō / Chiwei Yu.[45]
A Japanese navy record issued in 1886 first started to identify the islets using equivalents of the Chinese and English terms employed by the British. The name "Senkaku Retto" is not found in any Japanese historical document before 1900 (the term "Senkaku Gunto" began being used in the late 19th century), and first appeared in print in a geography journal published in 1900. It was derived from a translation of the English name Pinnacle Islands into a Sinicized Japanese term "Sento Shoto" (as opposed to "Senkaku Retto", i.e., the term used by the Japanese today), which has the same meaning.[46]
The collective use of the name "Diaoyutai" to denote the entire group began with the advent of the controversy in the 1970s.[47]
Control of the islands by Japan and the US



As the uninhabited islets were historically used as maritime navigational markers, they were never subjected to administrative control other than the recording of the geographical positions on maps, descriptions in official records of Chinese missions to the Ryukyu Kingdom, etc.[35]
The Japanese central government annexed the islands in early 1895 while still fighting China in the First Sino-Japanese War.[38] Around 1900, Japanese entrepreneur Koga Tatsushirō (古賀 辰四郎) constructed a bonito fish processing plant on the islands, employing over 200 workers. The business failed around 1940 and the islands have remained deserted ever since.[48] In the 1970s, Koga Tatsushirō's son Zenji Koga and Zenji's wife Hanako sold four islets to the Kurihara family of Saitama Prefecture. Kunioki Kurihara[49] owned Uotsuri, Kita-Kojima, and Minami-Kojima. Kunioki's sister owned Kuba.[50]
The islands came under US government occupation in 1945 after the surrender of Japan ended World War II.[48] In 1969, the United Nations Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East (ECAFE) identified potential oil and gas reserves in the vicinity of the Senkaku Islands.[51] In 1971, the Okinawa Reversion Treaty passed the U.S. Senate, returning the islands to Japanese control in 1972.[52] Also in 1972, the Republic of China government and People's Republic of China government officially began to declare ownership of the islands.[53]
Since 1972, when the islands reverted to Japanese government control, the mayor of Ishigaki has been given civic authority over the territory. The Japanese central government, however, has prohibited Ishigaki from surveying or developing the islands.[48][54]
In 1978, a Japanese political group constructed the first lighthouse on Uotsuri island and grazed two goats. Goats have since proliferated and affected the island's vegetation.[55]
In 1979 an official delegation from the Japanese government composed of 50 academics, government officials from the Foreign and Transport ministries, officials from the now-defunct Okinawa Development Agency, and Hiroyuki Kurihara, visited the islands and camped on Uotsuri for about four weeks. The delegation surveyed the local ecosystem, finding moles and sheep, studied the local marine life, and examined whether the islands would support human habitation.[50]
In 1988, a Japanese political group reconstructed a lighthouse on Uotsuri Island.[56]
In 2005, a Japanese fisherman who owned a lighthouse at Uotsuri Island expressed his intention to relinquish the ownership of the lighthouse, and the lighthouse became a national property pursuant to the provisions of the Civil Code of Japan. Since then, the Japan Coast Guard has maintained and managed the Uotsuri lighthouse.[56]
From 2002 to 2012, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications paid the Kurihara family ¥25 million a year to rent Uotsuri, Minami-Kojima and Kita-Kojima. Japan's Ministry of Defense rents Kuba island for an undisclosed amount. Kuba is used by the U.S. military as a practice aircraft bombing range. Japan's central government completely owns Taisho island.[50][57]
The reaction of the Kan Cabinet to the September 2010 Senkaku boat collision incident was seen by former Prime Minister Shinzo Abe as "a very foolish move" and "frighteningly naive".[58][59]
On December 17, 2010, Ishigaki declared January 14 as "Pioneering Day" to commemorate Japan's 1895 annexation of the Senkaku Islands. China condemned Ishigaki's actions.[60]
In May 2012, both the Tokyo Metropolitan and Japanese central governments announced plans to negotiate purchase of Uotsuri, Kita-Kojima, and Minami-Kojima from the Kurihara family,[50] and on September 11, 2012, the Japanese government nationalized its control over Minami-kojima, Kita-kojima, and Uotsuri islands by purchasing them from the Kurihara family for ¥2.05 billion.[61] China's Foreign Ministry objected saying Beijing would not "sit back and watch its territorial sovereignty violated."[62]
In 2014, Japan constructed a lighthouse and wharf featuring Japanese flag insignia on the islets.[63]
Geography


The island group are known to consist of five uninhabited islets and three barren rocks.[64] China has identified and named as many as 71 islets that belong to this group after the Japanese Cabinet released names of 39 uninhabited islands.[65][66]
These minor features in the East China Sea are located approximately 120 nautical miles northeast of Taiwan, 200 nautical miles east of the Chinese mainland and 200 nautical miles southwest of the Japanese island of Okinawa.[67]
According to one visitor, Uotsuri-shima, the largest of the islands, consists of a pair of rocky gray mountains with steep, boulder-strewn slopes rising almost straight from the water's edge. Other, nearby islands were described as large rocks covered by low vegetation.[16]
In ascending order of distances, the island cluster is located:
- 140 km (76 nmi; 87 mi) east of Pengjia Islet, Republic of China (Taiwan)[68]
- 170 km (92 nmi; 110 mi) north of Ishigaki Island, Japan
- 186 km (100 nmi; 116 mi) northeast of Keelung, Republic of China (Taiwan)
- 410 km (220 nmi; 250 mi) west of Okinawa Island, Japan
| No. | Japanese name[69] | Republic of China name[70][71] | China (PRC) name[72][73] | Coordinates | Area (km2)[71] | Highest elevation (m) | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Uotsuri Island (魚釣島)[74] | 釣魚臺[75] / 釣魚台 Diaoyutai POJ: Tiò-hî-tâi[76] | Diaoyu Dao (钓鱼岛/釣魚島) | 25°44′36″N 123°28′33″E / 25.74333°N 123.47583°E | 4.32 | 383 |  |
| 2 | Taisho Island (大正島)[77] | 赤尾嶼 Chiwei Isle | Chiwei Yu (赤尾屿/赤尾嶼) | 25°55′21″N 124°33′31″E / 25.92250°N 124.55861°E | 0.0609 | 75 |  |
| 3 | Kuba Island (久場島)[78] | 黃尾嶼 Huangwei Isle | Huangwei Yu (黄尾屿/黄尾嶼) | 25°55′26″N 123°40′55″E / 25.92389°N 123.68194°E | 1.08 | 117 |  |
| 4 | Kitakojima Island (北小島)[79] | 北小島 Beixiao Island | Beixiao Dao (北小岛/北小島) | 25°43′47″N 123°32′29″E / 25.72972°N 123.54139°E | 0.3267 | 135 |  |
| 5 | Minamikojima Island (南小島)[80] | 南小島 Nanxiao Island | Nanxiao Dao (南小岛/南小島) | 25°43′25″N 123°33′00″E / 25.72361°N 123.55000°E | 0.4592 | 149 | |
| 6 | Okinokitaiwa Island (沖ノ北岩)[81] | 沖北岩 Chongbeiyan | Bei Yu (北屿/大北小岛/大北小島) | 25°46′45″N 123°32′30″E / 25.77917°N 123.54167°E | 0.0183 | nominal |  |
| 7 | Okinominamiiwa Island (沖ノ南岩)[82] | 沖南岩 Chongnanyan | Nan Yu (南屿/大南小岛/大南小島/南岩) | 25°45′19″N 123°34′01″E / 25.75528°N 123.56694°E | 0.0048 | nominal |  |
| 8 | Tobise Island (飛瀬)[83] | 飛瀨 Feilai | Fei Yu (飞屿/飞礁岩/飛礁岩) | 25°44′08″N 123°30′22″E / 25.73556°N 123.50611°E | 0.0008 | nominal |  |

The depth of the surrounding waters of the continental shelf is approximately 100–150 metres (330–490 ft) except for the Okinawa Trough on the south.[84] The shelf is shallow enough that the western islands were likely connected to the mainland during the Last Glacial Period.[85]
Geology

Uotsuri, Kitakojima, Minamikojima and surrounding islets are sedimentary in origin, predominantly consisting of probably Miocene aged sandstone and sandstone-conglomerate, with subordinate conglomerate, coal seams up to 10 centimetres thick, and rare siltstone beds. The sedimentary strata have around 300 metres of exposed thickness at Uotsuri, and have SW-NE, EW and NW-SE strikes, with a general inclination of a dip of less than 20 degrees towards the North.[86] These strata are intruded by sheets of Mio-Pliocene porphyritic hornblende diorite, and are fringed by recent coral outcrops and surface talus deposits. Kuba and Taisho are volcanic in origin, with Kuba comprising "pyroxene andesite, lava, volcanic bombs, pumice, limestone, and other rocky material" and Taisho is thought to be consist of "andesite, tuff breccia, and tuffaceous sandstone".[87]
Wildlife
Plants
Permission for collecting herbs on three of the islands was recorded in an Imperial Chinese edict of 1893.[88]
Several floral surveys have been conducted on the Senkaku islands,[89][90] with a 1980 survey finding that Uotsuri had 339 species of plants. These ecological communities varied based on altitude, with the communities being divided into windswept mountaintop vegetation with Podocarpus macrophyllus trees, with the understory including Liriope muscari and Rhaphiolepis umbellata, inclined high forest including the palms Livistona chinensis and Arenga engleri, lowland windswept shrub forest including Ficus microcarpa and Planchonella obovata, and seashore plants. Minamikojima was much less diverse, and dominated by grasses, while Kitakojima only had sparse plant life.[91] Kuba has a forest near the crater, which includes a variety of flora including Ceodes umbellifera, Macaranga tanarius, Ficus benjamina, Diospyros maritima, Trema orientalis, Machilus thunbergii, and Livistona subglobosa, with forest floor plants being sparse.[90]
Animals
In an account by Hisashi Kuroiwa in 1900, it was noted the large number of birds present on the islands, tens of thousands of short-tailed and black-footed albatross would flock on Uotsuri-shima, in the colder months, while hundreds of thousands of sooty tern and brown noddy would descend on Kitakojima and Minamikojima in the warmer months. He also described the air of Uotsuri as swarming with bluebottle flies and mosquitoes. In the same year, an account by Miyajima Mikinosuke, surveying Kuba Island, noted the presence of whimbrel, Von Schrenck's bittern, the streaked shearwater, and the brown booby. Mikinosuke also noted the large number of chickens and feral cats on the island, with dozens of cats descending on the seabirds at night.[92] Kitakojima and Minamikojima are one of only two significant breeding places of the rare short-tailed albatross (Phoebastria albatrus).[17] The islands have been recognised as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.[93]
Uotsuri-shima, the largest island, has a number of endemic species such as the Senkaku mole (Mogera uchidai) and Okinawa-kuro-oo-ari ant. Due to the introduction of domestic goats to the island in 1978, the Senkaku mole is now an endangered species.[94] The striped field mouse (Apodemus agrarius) has also been noted to be present on Uotsuri. Surveys from 1900 to 1953 and noted the presence of the Asian house shrew, black rats and fruit bats but these were not noted in more recent surveys.[89][91]
Six species of reptile have been recorded from the islands, including Gekko hokouensis (Uotsuri, Minami) Eumeces elegans (Uotsuri, Minami), an indeterminate species of Scincella (Uotsuri) Ramphotyphlops braminus (Uotsuri) Elaphe carinata (Uotsuri) and Dinodon rufozonatus (Uotsuri).[85]
Rich marine biodiversity adjacent to the islands has been recognized but poorly studied. Seemingly, varieties of larger fish and animals inhabit or migrate through the area, including tunas, sharks, marlins, critically endangered hawksbill sea turtles, dolphins, pilot whales, sperm whales, and humpback whales.[95]
Sovereignty dispute
Territorial sovereignty over the islands and the maritime boundaries around them are disputed between the People's Republic of China, the Republic of China, and Japan.
The People's Republic and Republic of China claim that the islands have been a part of Chinese territory since at least 1534. China acknowledges that Japan took control of the islands in 1894–1895 during the first Sino-Japanese War, through the signature of the Treaty of Shimonoseki. China asserts that the Potsdam Declaration required that Japan relinquish control of all islands except for "the islands of Honshū, Hokkaidō, Kyūshū, Shikoku and such minor islands as we determine", and China states that this means control of the islands should pass to Republic of China, which was part of China at the time of the first Sino-Japanese War as well as of the San Francisco Peace Treaty. Both the People's Republic of China (PRC)[96] and the Republic of China (ROC)[97] respectively separately claim sovereignty based on arguments that include the following points:
- Discovery and early recording in maps and travelogues.[98]
- The islands being China's frontier off-shore defence against wokou (Japanese pirates) during the Ming and Qing dynasties (1368–1911).
- A Chinese map of Asia, as well as the Sangoku Tsūran Zusetsu map[97] compiled by Japanese cartographer Hayashi Shihei[99] in the 18th century,[98] showing the islands as a part of China.[98][100]
- Japan taking control of the islands in 1895 at the same time as the First Sino-Japanese War was happening. Furthermore, correspondence between Foreign Minister Inoue and Interior Minister Yamagata in 1885, warned against the erection of national markers and developing their land to avoid Qing Dynasty suspicions.[98][100][101]
- The Potsdam Declaration stating that "Japanese sovereignty shall be limited to the islands of Honshū, Hokkaidō, Kyūshū, Shikoku and such minor islands as we determine", and "we" referred to the victors of the Second World War who met at Potsdam and Japan's acceptance of the terms of the Declaration when it surrendered.[100][102][103]
- China's formal protest of the 1971 US transfer of control to Japan.[104]
Japan does not accept that there is a dispute, asserting that the islands are an integral part of Japan.[105] Japan has rejected claims that the islands were under China's control prior to 1895, and that these islands were contemplated by the Potsdam Declaration or affected by the San Francisco Peace Treaty.[106]
The existence of the back-arc basin complicates descriptive issues. According to Professor Ji Guoxing of the Asia-Pacific Department at Shanghai Institute for International Studies,

- China's interpretation of the geography is that
...the Okinawa Trough proves that the continental shelves of China and Japan are not connected, that the Trough serves as the boundary between them, and that the Trough should not be ignored ....[107]
- Japan's interpretation of the geography is that
...the trough is just an incidental depression in a continuous continental margin between the two countries ... [and] the trough should be ignored ....[107]

The stance given by the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs is that the Senkaku Islands are clearly an inherent territory of Japan, in light of historical facts and based upon international law, and the Senkaku Islands are under the valid control of Japan. They also state "there exists no issue of territorial sovereignty to be resolved concerning the Senkaku Islands."[108][109] The following points are given:
- The islands had been uninhabited and showed no trace of having been under the control of China prior to 1895.[110]
- The islands were neither part of Republic of China nor part of the Pescadores Islands, which were ceded to Japan by the Qing Dynasty of China in Article II of the May 1895 Treaty of Shimonoseki,[110] thus were not later renounced by Japan under Article II of the San Francisco Peace Treaty.[111]
- A resident of Okinawa Prefecture who had been engaging in activities such as fishery around the Senkaku Islands since around 1884 made an application for the lease of the islands, and approval was granted by the Meiji Government in 1896. After this approval, he sent a total of 248 workers to those islands and ran the following businesses: constructing piers,[112] collecting bird feathers, manufacturing dried bonito, collecting coral, raising cattle, manufacturing canned goods and collecting mineral phosphate guano (bird manure for fuel use). The fact that the Meiji Government gave approval concerning the use of the Senkaku Islands to an individual, who in turn was able to openly run these businesses mentioned above based on the approval, demonstrates Japan's valid control over the Islands.[113]
- Though the islands were controlled by the United States as an occupying power between 1945 and 1972, Japan has since 1972 exercised administration over the islands.
- Japanese allege that Republic of China and China only started claiming ownership of the islands in 1971, following a May 1969 United Nations report that a large oil and gas reserve may exist under the seabed near the islands.[114][115]
In 2012 the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs created a website in support of its claims;[116] in late 2014 the National Marine Data and Information Service, a department under the State Oceanic Administration of People's Republic of China created a website of its own to support its claims.[117][118] In 2016, Chinese fishing, Coast Guard and other vessels were entering the territorial waters around the islands almost daily and in August 2016 the Japanese foreign minister Fumio Kishida reportedly told China's foreign minister Wang Yi "that the activity represented an escalation of tensions" according to Japanese sources. It was the first meeting of the top diplomats since the Permanent Court of Arbitration ruling against China's South China Sea claims[119][120] and was coincident with a three-party meeting (including South Korea) relative to a North Korean submarine-launched missile in the Sea of Japan.[121]
On 22 June 2020, the Ishigaki City Council voted to change the name of the area containing the Senkaku Islands from "Tonoshiro" to "Tonoshiro Senkaku".[122] Republic of China's Ministry of Foreign Affairs responded that the islands belong to Republic of China, and any moves to deny this fact are invalid.[123] The Taiwanese government and the opposition KMT party also condemned the council's move, saying the Islands are ROC territory and the nation would not give up even "an inch" of its sovereignty.[124]
In popular culture
Diaoyu Islands: The Truth is a documentary film produced by Chris D. Nebe and J.J. Osbun of Monarex Hollywood Corporation and directed by Chris D. Nebe. Nebe calls on the Japanese Government to cede the islands to China, asserting that Japan has no justifiable claim to the islands, and that the United States of America has turned a blind eye in Japan's favor due to the need of the United States to have a strong ally between it and China. Reception of the film was positive in Chinese media, while the Australian Broadcasting Corporation's Correspondents Report called Nebe a 'Chinese propagandist' in 2014.[125]
In 2018 the National Museum of Territory and Sovereignty (currently located in the Toranomon Mitsui Building, Chiyoda, Tokyo) was established by the Japanese government to raise public awareness of Japanese territorial rights issues concerning the Senkaku Islands, as well as issues concerning territorial claims to Takeshima and southernmost Kuril Islands.[126]
See also
Notes
Footnotes
References
- Belcher, Edward and Arthur Adams. (1848). Narrative of the Voyage of H.M.S. Samarang, During the Years 1843–46: Employed Surveying the Islands of the Eastern Archipelago. London : Reeve, Benham, and Reeve. OCLC 192154
- Charney, Jonathan I., David A. Colson, Robert W. Smith. (2005). International Maritime Boundaries, 5 vols. Hotei Publishing: Leiden. ISBN 9780792311874; ISBN 9789041119544; ISBN 9789041103451; ISBN 9789004144613; ISBN 9789004144798; OCLC 23254092
- Findlay, Alexander George. (1889). A Directory for the Navigation of the Indian Archipelago and the Coast of China. London: R. H. Laurie. OCLC 55548028
- Hagström, Linus. (2005). Japan's China Policy: A Relational Power Analysis. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-34679-5; OCLC 475020946
- Inoue, Kiyoshi. (1972) Senkaku Letto /Diaoyu Islands The Historical Treatise. Kyoto: Daisan Publisher (出版社: 第三書館) (1996/10)「尖閣」列島―釣魚諸島の史的解明 [単行本]. ISBN 978-4-8074-9612-9; also hosted in here [2] for online reading (set to Shift-JIS character code), with English synopsis here. Chinese translation by Ying Hui, Published by Commercial Press Hong Kong (1973) 釣魚列島的歷史和主權問題 / 井上清著 ; 英慧譯, ISBN 9622574734.
- Jarrad, Frederick W. (1873). The China Sea Directory, Vol. IV. Comprising the Coasts of Korea, Russian Tartary, the Japan Islands, Gulfs of Tartary and Amúr, and the Sea of Okhotsk. London: Hydrographic Office, Admiralty. OCLC 557221949
- Lai, Yew Meng (2013), Nationalism and Power Politics in Japan's Relations with China: A Neoclassical Realist Interpretation, Routledge, p. 208, ISBN 978-1-136-22977-0
- Lee, Seokwoo, Shelagh Furness and Clive Schofield. (2002). Territorial disputes among Japan, China and Republic of China concerning the Senkaku Islands. Durham: University of Durham, International Boundaries Research Unit (IBRU). ISBN 978-1-897643-50-1; of China-concerning-the-senkaku-islands/oclc/249501645?referer=di&ht=edition OCLC 249501645
- Suganuma, Unryu. (2000). Sovereign Rights and Territorial Space in Sino-Japanese Relations. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-2159-3; OCLC 170955369
- Valencia, Mark J. (2001). Maritime Regime Building: Lessons Learned and Their Relevance for Northeast Asia. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff. ISBN 9789041115805; OCLC 174100966
Further reading
- Donaldson, John and Alison Williams. "Understanding Maritime Jurisdictional Disputes: The East China Sea and Beyond", Journal of International Affairs, Vol. 59, No. 1. JSTOR 24358237 .
- Dzurek, Daniel. "The Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands Dispute", International Boundaries Research Unit (IBRU). October 18, 1996.
- Helflin, William B. "Daiyou/Senkaku Islands Dispute: Japan and China, Oceans Apart", 1 Asian-Pacific Law & Policy Journal, pp. 1–22 (2000).
- O'Hanlon, Michael E. The Senkaku Paradox: Risking Great Power War Over Small Stakes (Brookings Institution, 2019) online review
- Peterson, Alexander M. "Sino-Japanese Cooperation in the East China Sea: A Lasting Arrangement?" 42 Cornell International Law Journal, pp. 441–474 (2009).
- Ramos-Mrosovsky, Carlos. "International Law's Unhelpful Role in the Senkaku Islands" Archived February 20, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, 29 University of Pennsylvania Journal of International Law, pp. 903–946 (2008).
- Sunohara, Tsuyoshi. Fencing in the Dark: Japan, China, and the Senkakus (Japan Publishing Industry Foundation for Culture, 2020) [3]
External links

- Cabinet Secretariat (Japan), Japan's Response Respecting Law and Order in the International Community / The Senkaku Islands
- Cabinet Secretariat (Japan), Senkaku Islands Research and Commentary Site
- Google Maps: Senkaku Islands
- "Q&A China Japan island row", BBC News Asia-Pacific. September 24, 2010.
- GlobalSecurity.org: "Senkaku/Diaoyutai Islands"; References and links
- Inventory of Conflict and Environment (ICE), Diaoyu Islands Dispute
- Hayashi Shihei (1785). 三国通覧図説 (Sangoku Tsuran Zusetsu). Waseda University,
- Senkaku Islands Bibliographical Materials Society Bibliography of primary source material about Senkaku Islands
- "Notes from central Taiwan: Some 'damn foolish thing' in the Senkakus", Taipei Times




