Theta variant, also known as lineage P.3,[a] is one of the variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. The variant was first identified in the Philippines on February 18, 2021, when two mutations of concern were detected in Central Visayas.[1] It was detected in Japan on March 12, 2021, when a traveler from the Philippines arrived at Narita International Airport in Tokyo.[2]
It is distinct from those first discovered in the United Kingdom, South Africa, and Brazil, and is thought to pose a similar threat. The variant is more resistant to neutralizing antibodies, including those gained through vaccination, like how the South African and Brazilian variants appear to be.[3]
Under the simplified naming scheme proposed by the World Health Organization, P.3 has been labeled Theta variant, and was considered a variant of interest (VOI), but not a variant of concern.[4]
As of July 2021, Theta is no longer considered as a variant of interest by the WHO.[4]
Classification
Naming
On March 17, 2021, Public Health England (PHE) named Lineage P.3 VUI-21MAR-02.[5]
On June 1, 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) named lineage P.3 as Theta variant.[6]
Mutations
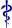
- Amino acid mutations of SARS-CoV-2 Theta variant plotted on a genome map of SARS-CoV-2 with a focus on the spike.[7]
A total of 14 amino acid replacements were observed in all samples (labeled in red below), including seven spike protein mutations. Among the spike protein mutations, four have been previously associated with lineages of concern (i.e., E484K, N501Y, D614G, and P681H) while three additional replacements were observed towards the C-terminal region of the protein (i.e., E1092K, H1101Y, and V1176F). A single amino acid replacement at the N-terminus of ORF8 (i.e., K2Q) was also found in all samples. Three other mutations were seen in 32 of the 33 samples (labeled in green) including a three-amino acid deletion at the spike protein positions 141 to 143. Lastly, five synonymous mutations (labeled in gray) were also detected in all of the cases.[8]
| Gene | Amino acid |
|---|---|
| ORF1ab | F924F |
| D1554G | |
| S2433S | |
| L3201P | |
| D3681E | |
| N3928N | |
| L3930F | |
| P4715L | |
| A5692V | |
| S | LGV141_143del |
| E484K | |
| N501Y | |
| G593G | |
| D614G | |
| P681H | |
| S875S | |
| E1092K | |
| H1101Y | |
| V1176F | |
| ORF8 | K2Q |
| N | R203K |
| G204R |
| Gene | Amino acid |
|---|---|
| ORF1a | D1554G |
| S2625F | |
| D2980N | |
| L3201P | |
| D3681E | |
| L3930F | |
| ORF1b | P314L |
| L1203F | |
| A1291V | |
| S | LGV141_143del |
| E484K | |
| N501Y | |
| G593G | |
| D614G | |
| P681H | |
| S875S | |
| E1092K | |
| H1101Y | |
| V1176F | |
| ORF8 | K2Q |
| N | R203K |
| G204R |
History
On February 18, 2021, the Department of Health of the Philippines confirmed the detection of two mutations of COVID-19 in Central Visayas after samples from patients were sent to undergo genome sequencing. The mutations were later named as E484K and N501Y, which were detected in 37 out of 50 samples, with both mutations co-occurrent in 29 out of these. There were no official names for the variants and the full sequence was yet to be identified.[1]
On March 12, 2021, Japan detected the variant on a traveler from the Philippines.[2]
On March 13, 2021, the Department of Health confirmed the mutations constituted a new variant, which was designated as lineage P.3. On the same day, it also confirmed its first case of lineage P.1 in the country. Although the lineages P.1 and P.3 stem from the same lineage B.1.1.28, the department said that the impact of lineage P.3 on vaccine efficacy and transmissibility is yet to be ascertained.[10]
On March 17, 2021, the United Kingdom confirmed its first two cases, where Public Health England (PHE) termed it VUI-21MAR-02.[11]
On April 30, 2021, Malaysia detected 8 cases of lineage P.3 in Sarawak.[12]
Statistics
| Country | PANGOLIN[13] | outbreak.info[9] | Regeneron[14] | Other sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Philippines Philippines | 455 | 513 | 516 | 461[15] |
 USA USA | 17 | 20 | 17 | |
 Germany Germany | 11 | 11 | 11 | |
 Malaysia Malaysia | 10 | 10 | 10 | 13[16] |
 United Kingdom United Kingdom | 9 | 9 | 9 | 10[17] |
 Japan Japan | 7 | 8 | 8 | |
 Netherlands Netherlands | 7 | 7 | 7 | 4[18] |
 Canada Canada | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
 Australia Australia | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
 Belgium Belgium | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
 China[b] China[b] | 3 | 14 | 14 | |
 Guam Guam | 3 | – | 3 | |
 New Zealand New Zealand | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
 Norway Norway | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
 Singapore Singapore | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
 Angola Angola | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
 South Korea South Korea | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
 Sweden Sweden | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
 Brazil Brazil | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
 Finland Finland | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 550 | 620 | 624 | 488 |