सीजः
थ्व छगु तत्त्व (एलेमेन्ट) ख:|
| Copper | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
29Cu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| रुप | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
red-orange metallic luster Native copper (~4 cm in size) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| साधारण गुण | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| नां, चिं, ल्या | copper, Cu, 29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| उच्चारण | /ˈkɒpər/ KOP-ər | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| धातुया वर्ग | transition metal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ग्रुप, पिरियद, ब्लक | 11, 4, d | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight | 63.546(3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
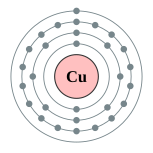
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s1 2, 8, 18, 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Middle East (9000 BC) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 8.96 g·cm−3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Liquid density at m.p. | 8.02 g·cm−3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 1357.77 K, 1084.62 °C, 1984.32 °F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 2835 K, 2562 °C, 4643 °F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 13.26 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 300.4 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 24.440 J·mol−1·K−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | +1, +2, +3, +4 (mildly basic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | 1.90 (Pauling scale) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies (more) | 1st: 745.5 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2nd: 1957.9 kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd: 3555 kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | 128 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 132±4 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 140 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellanea | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic[१] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | (20 °C) 16.78 nΩ·m | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 401 W·m−1·K−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | (25 °C) 16.5 µm·m−1·K−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound (thin rod) | (r.t.) (annealed) 3810 m·s−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 110–128 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 48 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 140 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 3.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vickers hardness | 369 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 35 HB = 874 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS registry number | 7440-50-8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most stable isotopes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
लिधंसा
🔥 Top keywords: मू पौब्राह्मणश्री हनुमान चालीसाराजपूतबंगाली भाषाविकिपिडिया:सतः फल्चातःहताः २ग्वाहालि:धलःपौविकिपिडिया:हलिम बुखँ (ग्रेगोरियन पात्रो)कर्णवालबुद्धपूजा पालीजयमंगल गाथाअंग्रेजी भाषाविकिपिडियाविशेष:MyTalkग्रीसप्रशान्त महासागरकर्नाटकविशेष:RecentChangesभारत१००००विकिपिडिया:सामाजिक दबूप्रविधिसम्प्रतिसहसवानविशेष:Searchआलापुर तहसीलसौर्य शक्तिसंयुक्त अधिराज्यसंयुक्त राज्य अमेरिकाTemplate:Cite webजर्मन लिपिइच्छाप्रकृतिएच टी एम् एल्नक्षत्रबूटज्याक, क्यालिफोर्नियाऔराई् तहसीलभवन