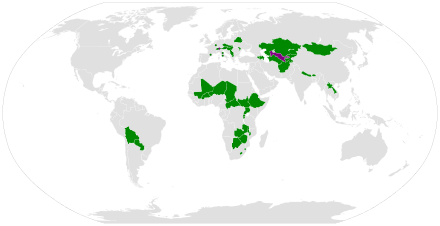
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie solely on endorheic basins. Currently, there are 44 landlocked countries, two of them doubly landlocked (Liechtenstein and Uzbekistan), and three landlocked de facto states in the world. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country, while Ethiopia is the world's most populous landlocked country.[1][2]
Generally, being landlocked creates political and economic disadvantages that having access to international waters would avoid. For this reason, nations large and small throughout history have fought to gain access to open waters, even at great expense in wealth, bloodshed, and political capital.
The economic disadvantages of being landlocked can be alleviated or aggravated depending on degree of development, surrounding trade routes and freedom of trade, language barriers, and other considerations. Some landlocked countries in Europe are affluent, such as Andorra, Austria, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, San Marino, Switzerland, and Vatican City, all of which, excluding Luxembourg (a founding member of NATO), frequently employ neutrality in global political issues.
However, 32 out of the 44 landlocked countries, including those in Africa, Asia, and South America, have been classified as Landlocked Developing Countries (LLDCs) by the United Nations.[3] Nine of the twelve countries with the lowest Human Development Indices (HDI) are landlocked.[4] International initiatives are aimed at reducing inequalities resulting from issues such as these, such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 10, which aims to reduce inequality substantially by 2030.[5]
History
In 1990, there were only 30 landlocked countries in the world. However, the dissolutions of the Soviet Union and Czechoslovakia; the breakup of Yugoslavia; the independence referendums of South Ossetia (de facto state), Eritrea, Montenegro, South Sudan, and the Luhansk People's Republic (de facto state); and the unilateral declaration of independence of Kosovo (de facto state) created 15 new landlocked countries and five landlocked de facto states while the former landlocked country of Czechoslovakia ceased to exist on 1 January 1993.[6]
On 30 September 2022, the Luhansk People's Republic (de facto state) was annexed by Russia and ceased to exist as a landlocked de facto state.[7]
On 19 September 2023, Azerbaijan launched a new offensive against the Republic of Artsakh (de facto state) and achieved a decisive victory.[8] The Government of Artsakh was officially dissolved on 1 January 2024. As a result, Artsakh ceased to exist as a landlocked de facto state and the Nagorno-Karabakh region was reintegrated into Azerbaijan.[9]
As of 1 April 2024, there were 44 landlocked countries and three landlocked de facto states (Kosovo, South Ossetia, and Transnistria) in the world.
Significance

Historically, being landlocked has been disadvantageous to a country's development. It cuts a nation off from important sea resources such as fishing, and impedes or prevents direct access to maritime trade, a crucial component of economic and social advance. As such, coastal regions, or inland regions that have access to the World Ocean, tended to be wealthier and more heavily populated than inland regions that have no access to the World Ocean. Paul Collier in his book The Bottom Billion argues that being landlocked in a poor geographical neighbourhood is one of four major development "traps" by which a country can be held back. In general, he found that when a neighbouring country experiences better growth, it tends to spill over into favorable development for the country itself. For landlocked countries, the effect is particularly strong, as they are limited in their trading activity with the rest of the world. He states, "If you are coastal, you serve the world; if you are landlocked, you serve your neighbors."[10] Others have argued that being landlocked has an advantage as it creates a "natural tariff barrier" that protects the country from cheap imports. In some instances, this has led to more robust local food systems.[11][12]
Landlocked developing countries have significantly higher costs of international cargo transportation compared to coastal developing countries (in Asia the ratio is 3:1).[13]
Historically, traveling between a landlocked country and a country which did not border said country required the traveler to pass border controls twice or more. In recent times the advent of air travel has largely negated this impediment.
Actions to avoid being landlocked
Countries have acted to overcome being landlocked by acquiring land that reaches the sea:
- The Republic of Ragusa, in 1699, gave the town of Neum to the Ottoman Empire because it did not want to have a land border with the Republic of Venice.[14] This small municipality was inherited by Bosnia and Herzegovina and now provides limited sea access, splitting the Croatian part of the Adriatic coast in two. Since Bosnia and Herzegovina is a new country, railways and ports have not been built for its need. There is no freight port along its short coastline at Neum, making it effectively landlocked, although there are plans to change this. Instead the Port of Ploče in Croatia is used.
- The International Congo Society, which owned the territory now constituting the Democratic Republic of the Congo, was awarded a narrow piece of land cutting through Angola to connect it to the sea by the Conference of Berlin in 1885.
- After World War I, in the Treaty of Versailles, a part of Germany designated "the Polish corridor" was given to the new Second Polish Republic, for access to the Baltic Sea. This gave Poland a short coastline, but without a large harbour. This was also the pretext for making Danzig (now Gdańsk) with its harbour the Free City of Danzig, to which Poland was given free access. However, the Germans placed obstacles to this free access, especially when it came to military material. In response, the small fishing harbour of Gdynia was soon greatly enlarged.
- As a result of a 2005 territorial exchange with Ukraine, Moldova received a 600-metre (650-yard) long bank of the Danube (which is an international waterway),[15] subsequently building its Port of Giurgiulești there.
Trade agreements
Countries can make agreements on getting free transport of goods through neighbouring countries:
- The Treaty of Versailles required Germany to offer Czechoslovakia a lease for 99 years of parts of the ports in Hamburg and Stettin, allowing Czechoslovakia sea trade via the Elbe and Oder rivers. Stettin was annexed[16] by Poland after World War II, but Hamburg continued the contract so that part of the port (now called Moldauhafen) until 2028 [17] could be used for sea trade by a successor of Czechoslovakia, the Czech Republic.
- The Danube is an international waterway, and thus landlocked Austria, Hungary, Moldova, Serbia, and Slovakia have secure access to the Black Sea (the same access is given to inland parts of Germany and Croatia, though Germany and Croatia are not landlocked). However, oceangoing ships cannot use the Danube, so cargo must be transloaded anyway, and many overseas imports into Austria and Hungary use land transport from Atlantic and Mediterranean ports. A similar situation exists for the Rhine river where Switzerland has boat access, but not oceangoing ships. Luxembourg has such through the Moselle, but Liechtenstein has no boat access, even though it is located along the Rhine, as the Rhine is not navigable that far upstream.
- The Mekong is an international waterway so that landlocked Laos has access to the South China Sea (since Laos became independent from French Indochina). However, it is not navigable above the Khone Phapheng Falls.
- Free ports allow transshipment to short-distance ships or river vessels.
- The TIR Convention allows sealed road transport without customs checks and charges, mostly in Europe.[18]
Political repercussions
Losing access to the sea is generally a great loss to a nation, politically, militarily, and economically. The following are examples of countries becoming landlocked.
- The independence of Eritrea, brought about by the 30-year Eritrean War of Independence,[19] caused Ethiopia to become landlocked in 1991: the Ethiopian Navy operated from foreign ports in Djibouti and Yemen before being dissolved in 1996.
- Montenegro's decision to abandon the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro caused the federal unit of Serbia to become a landlocked current independent state.
- Bolivia lost its coastline to Chile in the War of the Pacific and accepted it in treaties signed in 1884 and 1904. The last treaty gives port storage facilities and special treatment for the transit of goods from and to Bolivia through Chilean ports and territory. Peru and Argentina have also given special treatment for the transit of goods. A fluvial Bolivian Navy, which did not exist at the time of the War of the Pacific, was created later and both trains and operates in Lake Titicaca and rivers. The Bolivian people annually celebrate a patriotic "Dia del Mar" (Day of the Sea) to remember its territorial loss, which included both the coastal city of Antofagasta and what has proven to be one of the most significant and lucrative copper deposits in the world. Early in the 21st century, the selection of the route of gas pipes from Bolivia to the sea fueled popular uprisings, as people were against the option of laying the pipes through Chilean territory.
- Austria and Hungary also lost their access to the sea as a consequence of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919) and the Treaty of Trianon (1920) respectively. Previously, although Croatia had a limited constitutional autonomy within the Kingdom of Hungary, the City of Fiume/Rijeka on the Croatian coast was governed directly from Budapest by an appointed governor as a corpus separatum, to provide Hungary with its only international port in the periods 1779–1813, 1822–1848 and 1868–1918. The most important ports in Austria were Trieste and Pula, now in Italy and Croatia.
- By 1801, the Nizam's dominion of Hyderabad State assumed the shape it is now remembered for: that of a landlocked princely state with territories in central Deccan, bounded on all sides by British India, whereas 150 years earlier it had had a considerable coastline on the Bay of Bengal that was annexed by the British.[20]
- It is possible that one of the causes of the Paraguayan War was Paraguay's lack of direct ocean access (although this is disputed; see the linked article).
- When the Entente Powers divided the former Ottoman Empire under the Treaty of Sèvres at the close of World War I, Armenia was promised part of the Trebizond vilayet (roughly corresponding to the modern Trabzon and Rize provinces in Turkey). This would have given Armenia access to the Black Sea. However, the Sèvres treaty collapsed with the Turkish War of Independence and was superseded by the Treaty of Lausanne (1923), which firmly established Turkish rule over the area.
- In 2011, South Sudan broke off from the Sudan, causing the former to become landlocked. There still remains conflict over the oil fields in South Sudan between the two countries.[21]
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea now gives a landlocked country a right of access to and from the sea without taxation of traffic through transit states. The United Nations has a programme of action to assist landlocked developing countries,[22] and the current responsible Undersecretary-General is Anwarul Karim Chowdhury.
Some countries have a long coastline, but much of it may not be readily usable for trade and commerce. For instance, in its early history, Russia's only ports were on the Arctic Ocean and frozen shut for much of the year. The wish to gain control of a warm-water port was a major motivator of Russian expansion towards the Baltic Sea, Black Sea, and Pacific Ocean. On the other hand, some landlocked countries can have access to the ocean along wide navigable rivers. For instance, Paraguay (and Bolivia to a lesser extent) have access to the ocean through the Paraguay and Paraná rivers.
Several countries have coastlines on landlocked bodies of water, such as the Caspian Sea and the Dead Sea. Since these seas are in effect lakes without access to wider seaborne trade, countries such as Kazakhstan are still considered landlocked. Although the Caspian Sea is connected to the Black Sea via the man-made Volga–Don Canal, large oceangoing ships are unable to traverse it.
By degree
Landlocked countries may be bordered by a single country having direct access to the high seas, two or more such countries, or be surrounded by other landlocked countries, making a country doubly landlocked.
Landlocked by a single country
Three countries are landlocked by a single country (enclaved countries):
- Lesotho, a state surrounded by South Africa.
- San Marino, a state surrounded by Italy.
- Vatican City (a.k.a. the Holy See), a city-state surrounded by Italy, specifically Rome.
Landlocked by two countries
Seven landlocked countries are surrounded by only two mutually bordering neighbours (semi-enclaved countries):
- Andorra (between France and Spain)
- Bhutan (between China and India)
- Eswatini (between Mozambique and South Africa)
- Liechtenstein (between Austria and Switzerland) – one of the only two "doubly landlocked countries" in the world
- Moldova (between Romania and Ukraine) – ignoring Pridnestrovie (Transnistria), a de facto state
- Mongolia (between China and Russia)
- Nepal (between China and India)
To this group could be added three landlocked territories, two of them are de facto states with limited or no international recognition:
- Pridnestrovie (Transnistria) (between Moldova and Ukraine) – de facto state
- South Ossetia (between Georgia and Russia) – de facto state
- West Bank (between Israel and Jordan) – Israeli-occupied territory partly administered by the State of Palestine[23][24][25][26]
Doubly landlocked
A country is "doubly landlocked" or "double-landlocked" when it is surrounded only by landlocked countries (i.e. requiring the crossing of at least two national borders to reach a coastline).[27][28] There are two such countries:
- Liechtenstein in Western Europe, surrounded by Austria and Switzerland.[29]
- Uzbekistan in Central Asia, surrounded by Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan.[30]
After the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Württemberg became a doubly landlocked state, bordering Bavaria, Baden, Switzerland, the Grand Duchy of Hesse (Wimpfen exclave), Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, and Hohenzollern-Hechingen. The latter two were themselves landlocked between each other, Württemberg and Baden. In 1866 they became an exclave of Prussia, giving Württemberg a border with a coastal country but any path to a coast would still lead across at least two borders. The Free City of Frankfurt which was independent between 1815 and 1866 was doubly landlocked as it bordered the Electorate of Hesse, the Grand Duchy of Hesse, Hesse-Homburg, and Nassau. In the German Confederation there were several other landlocked states that only bordered landlocked states and landlocked exclaves of coastal states: the Grand Duchy of Hesse, Hesse-Homburg, Nassau (all until 1866), Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, Saxe-Hildburghausen (both until 1826), and Reuss, elder line (until 1871). All of these bordered Prussia but not the main territory with sea access.
There were no doubly landlocked countries from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the end of World War I. Liechtenstein bordered the Austro-Hungarian Empire, which had an Adriatic coastline, and Uzbekistan was then part of the Russian Empire, which had both ocean and sea access.
With the dissolution of Austria-Hungary in 1918 and creation of an independent, landlocked Austria, Liechtenstein became the sole doubly landlocked country until 1938. In the Anschluss that year, Austria was absorbed into Nazi Germany, which possessed a border on the Baltic Sea and the North Sea. After World War II, Austria regained its independence and Liechtenstein once again became doubly landlocked.
Uzbekistan, which had been part of the Russian Empire and then the Soviet Union, gained its independence with the dissolution of the latter in 1991 and became the second doubly landlocked country.
However, Uzbekistan's doubly landlocked status depends on the Caspian Sea's status dispute: some countries, especially Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan, claim that the Caspian Sea should be considered as a real sea (mainly because this way they would have larger oil and gas fields), which would make Uzbekistan only a simple landlocked country since its neighbours Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan have access to the Caspian Sea.
List of landlocked countries and landlocked de facto states
Notes:
- a Has a coastline on the inland saltwater Caspian Sea
- b De facto state
- c Landlocked by a single country
- d Doubly landlocked country
Groupings
The landlocked countries and de facto states can be grouped in contiguous groups as follows:[31]
- Eastern, Middle, and Western African cluster (10): Burkina Faso, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, Ethiopia, Mali, the Niger, Rwanda, South Sudan, and Uganda[32]
- Eastern, Southern, and Western European cluster (9): Austria, Czechia, Hungary, Kosovo (de facto state), Liechtenstein, North Macedonia, Serbia, Slovakia, and Switzerland[33]
- Central and Southern Asian cluster (6): Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan[34]
- Eastern and Southern African cluster (4): Botswana, Malawi, Zambia, and Zimbabwe[32]
- Eastern European group (2): Moldova and Transnistria (de facto state)[33]
- South American group (2): Bolivia and Paraguay[35]
- Western Asian group (2): Armenia and Azerbaijan[34]
Notes:
- If it were not for the 40 km (25 mi) of coastline at Moanda, DR Congo would join the two African clusters into one, making it the biggest contiguous cluster in the world instead.
- The Central and Southern Asian cluster and the Western Asian group can be considered contiguous, joined by the landlocked Caspian Sea. Mongolia is almost a part of this cluster too, being separated from Kazakhstan by only 30 km (19 mi), across Chinese or Russian territory.
- Before the Annexation of Sikkim by India, the Himalayan states of Bhutan, Nepal, and Sikkim form their own Southern Asian group.
"Single" landlocked countries
There are the following 12 "single" landlocked countries (each of them borders no other landlocked country or de facto state):
- Asia (5): Bhutan, Laos, Mongolia, Nepal, and South Ossetia (de facto state)[34]
- Europe (5): Andorra, Belarus, Luxembourg, San Marino, and Vatican City (the Holy See)[33]
- Africa (2): Eswatini and Lesotho[32]
Landlocked countries by continent
According to the United Nations geoscheme (excluding the de facto states), Africa has the most landlocked countries, at 16, followed by Europe (14), Asia (12), and South America (2). However, if Armenia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, and South Ossetia (de facto state) are counted as parts of Europe, then Europe has the most landlocked countries, at 20 (including all three landlocked de facto states). If these transcontinental or culturally European countries are included in Asia, then both Africa and Europe (including Kosovo and Transnistria) have the most, at 16. Depending on the status of Kazakhstan and the South Caucasian countries, Asia has between 9 and 13 (including South Ossetia). South America only has two landlocked countries: Bolivia and Paraguay.
Australia and North America have no landlocked countries, while Antarctica has no countries at all. Oceania (which is usually not considered a continent but a geographical region by the English-speaking countries) also has no landlocked countries.
All landlocked countries, except Bolivia and Paraguay, are located on the continental mainland of Afro-Eurasia.
See also
- Convention on Transit Trade of Land-locked States
- Declaration recognising the Right to a Flag of States having no Sea-coast
- Enclave and exclave
- Island country
- List of countries and territories by land and maritime borders
- List of countries that border only one other country
- Navies of landlocked countries
- List of countries bordering on two or more oceans















































