Hamas,[d] an acronym of its official name, Harakat al-Muqawama al-Islamiya (Arabic: حركة المقاومة الإسلامية, romanized: Ḥarakat al-Muqāwamah al-ʾIslāmiyyah, lit. 'Islamic Resistance Movement'),[56] is a Palestinian Sunni Islamist[57] political and military movement governing the Israeli-occupied Gaza Strip since 2007.[58]
Islamic Resistance Movement حركة المقاومة الإسلامية | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Chairman of the Political Bureau | Ismail Haniyeh |
| Deputy Chairman | Saleh al-Arouri X |
| Leader in the Gaza Strip | Yahya Sinwar |
| Military commander | Mohammed Deif |
| Deputy military commander | Marwan Issa X |
| Founder | ... and others
|
| Founded | December 10, 1987 |
| Split from | Muslim Brotherhood |
| Headquarters | Gaza City, Gaza Strip |
| Military wing | Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades |
| Ideology | |
| Religion | Sunni Islam |
| Political alliance | Alliance of Palestinian Forces |
| Colours | Green |
| Palestinian Legislative Council | 74 / 132 |
| Flag of Hamas | |
 | |
| Hamas | |
|---|---|
| Dates of operation | 1987–present |
| Headquarters | Gaza City, Gaza Strip |
| Size | 40,000[17] |
| Allies | State allies:
Non-state allies: |
| Opponents | State opponents: Non-state opponents: |
| Battles and wars | |
| Designated as a terrorist group by | |
Hamas was founded by Palestinian imam and activist Ahmed Yassin in 1987, after the outbreak of the First Intifada against the Israeli occupation. It emerged from his 1973 Mujama al-Islamiya Islamic charity affiliated with the Muslim Brotherhood.[59] In 2006, Hamas won the Palestinian legislative election by campaigning on clean government without corruption, combined with affirmation of Palestinians' right to armed struggle against the Israeli occupation, thus winning a majority in the Palestinian Legislative Council.[60] In 2007, Hamas took control of the Gaza Strip from rival Palestinian faction Fatah,[61][62] which it has governed since separately from the Palestinian National Authority. This was followed by an Israeli blockade of the Gaza Strip with Egyptian support, and multiple wars with Israel, including in 2008–09, 2012, 2014, and 2021. The ongoing 2023 war began after Hamas launched a surprise attack on Israel, killing mostly civilians, and taking hostages back to Gaza.[63][64][65] The attack has been described as the biggest military setback for Israel since the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, which Israel has responded to in an ongoing ground invasion of Gaza.[66]
While initially seeking a state in all of Mandatory Palestine that would replace Israel, Hamas began acquiescing to 1967 borders in the agreements it signed with Fatah in 2005, 2006 and 2007.[67][68][69] In 2017, Hamas released a new charter that supported a Palestinian state within the 1967 borders without recognizing Israel.[70][71][72][73] Hamas's repeated offers of a truce (for a period of 10–100 years[74]) based on the 1967 borders are seen by many as being consistent with a two-state solution,[75][76][77][78] while others state that Hamas retains the long-term objective of establishing one state in former Mandatory Palestine.[79][80] While the 1988 Hamas charter was widely described as antisemitic, Hamas's 2017 charter removed the antisemitic language and said Hamas's struggle was with Zionists, not Jews.[81][82][83][84] Hamas has promoted Palestinian nationalism in an Islamic context.[85] In terms of foreign policy, Hamas has historically sought out relations with Egypt,[86] Iran,[86] Qatar,[87] Saudi Arabia,[88] Syria[86] and Turkey[89]; some of its relations have been impacted by the Arab Spring.[90][clarification needed]
Hamas has carried out attacks against Israeli civilians and soldiers, including suicide bombings and indiscriminate rocket attacks.[91] These actions have led human rights groups to accuse it of war crimes. Argentina, Australia, Canada, Israel, Japan, Paraguay, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, the United States and the European Union[48] have designated Hamas as a terrorist organization. In 2018, a motion at the United Nations to condemn Hamas was rejected.[e][93][94]
Etymology
Hamas is an acronym of the Arabic phrase حركة المقاومة الإسلامية or Ḥarakah al-Muqāwamah al-ʾIslāmiyyah, meaning "Islamic Resistance Movement". This acronym, HMS, was glossed in the 1988 Hamas Covenant[95] by the Arabic word ḥamās (حماس) which itself means "zeal", "strength", or "bravery".[96]
History
Hamas was established in 1987, and has its origins in Egypt's Muslim Brotherhood movement, which had been active in the Gaza Strip since the 1950s and gained influence through a network of mosques and various charitable and social organizations. In the 1980s the Brotherhood emerged as a powerful political factor, challenging the influence of the PLO,[97] and in 1987 adopted a more nationalist and activist line under the name of Hamas.[97] During the 1990s and early 2000s, the organization conducted numerous suicide bombings and other attacks against Israel.
In the Palestinian legislative election of January 2006, Hamas gained a large majority of seats in the Palestinian Parliament, defeating the ruling Fatah party. After the elections, conflicts arose between Hamas and Fatah, which they were unable to resolve.[98][99][100] In June 2007, Hamas defeated Fatah in a series of violent clashes, and since that time Hamas has governed the Gaza portion of the Palestinian Territories, while at the same time they were ousted from government positions in the West Bank.[101][102] Israel and Egypt then imposed an economic blockade on Gaza and largely sealed their borders with the territory.[103][104]
After acquiring control of Gaza, Hamas-affiliated and other militias launched rocket attacks upon Israel, which Hamas ceased in June 2008 following an Egyptian-brokered ceasefire.[105] The ceasefire broke down late in 2008, with each side accusing the other of responsibility.[106] In late December 2008, Israel attacked Gaza,[107] withdrawing its forces in mid-January 2009.[108] Since 2009, Hamas has faced multiple military confrontations with Israel, notably the 2012 and 2014 Gaza Wars, leading to substantial casualties. Hamas has maintained control over Gaza, often clashing with the Palestinian Authority led by Fatah. Efforts at reconciliation between Hamas and Fatah have seen limited success. Hamas continued to face international isolation and blockades, while engaging in sporadic rocket attacks and tunnel construction activities against Israel.
2023 Israel–Hamas war


On October 7, 2023, early morning, Hamas launched a barrage of rockets on Israeli towns and cities, followed by an invasion, breaching the Gaza–Israel barrier. For months prior to the attack, Hamas had been leading Israeli intelligence to believe that they were not seeking conflict.[109][110] Hamas militants proceeded to massacre hundreds in Israeli civilian communities, including Kibbutzim, villages and towns, and hundreds of civilians celebrating at the Nova music festival. In total, 1,139 people were killed in Israel, making this the deadliest attack by Palestinian militants since the foundation of Israel in 1948. Approximately 250 Israeli civilians and soldiers were taken as hostages to the Gaza Strip, including 30 children.[111][112][113][114] International human rights groups, medical personnel, and journalists have chronicled the militants' onslaught, detailing the killing, including the decapitation and burning, of women, children, and the elderly, alongside young men and soldiers.[115][114][116][117] There are numerous reports of rapes and sexual assaults by Hamas militants, allegations that Hamas has denied.[118][119][120]
Senior Hamas official Khaled Mashal said that the group was fully aware of the consequences of attack on Israel, stating that Palestinian liberation comes with "sacrifices".[121][122]
Hamas Political Bureau member Ghazi Hamad said that Hamas would repeat the October 7 attack time and again until Israel is annihilated, since Israel constitutes a catastrophe to the Arab and Islamic nation.[123][124]
The Israeli military responded by imposing a total blockade of the Gaza Strip,[125][126][127] followed by an extensive aerial bombardment campaign on Gazan targets. Israel then launched an ongoing large-scale ground invasion of Gaza with the stated goal of destroying Hamas and controlling Gaza afterwards.[128][129][130]
Political and religious positions
Policies and attitudes towards Israel
1988–2005 (first charter)
Hamas in its early days, as social-religious charity center arming themselves for the ongoing resistance against the Israeli occupation of the Palestinian territories, in August 1988 published their first charter in which Hamas stated that "Israel" should be "eliminated" through a "clash with the enemies", a "struggle against Zionism" and "conflict with Israel".[131] 'Palestine', that is all of the territory that belonged to the British Mandate for Palestine (that is, from the Jordan River to the Mediterranean Sea),[132] should be "liberated" from "Zionism"[133] and transformed into an Islamic Waqf (Islamic charitable endowment) in which "followers of all religions can coexist in security and safety".[134][135] Practically speaking though, Hamas is at war with Israel's army (later also attacking Israeli civilians) since the spring of 1989, initially as part of the First Intifada, a protest movement gradually turning more riotous and violent.
Sheikh Ahmed Yassin, founder of Hamas, who died in 2004 (killed by Israel), has at unreported date offered Israel a ten-year hudna (truce, armistice) in return for establishment of a Palestinian state in the West Bank and Gaza. Yassin later added, the hudna could be renewed, even for longer periods, but would never signal a recognition of Israel.[74]
In 2005, Hamas signed the Palestinian Cairo Declaration, which confirms "the right of the Palestinian people to resistance in order to end the occupation, establish a Palestinian state with full sovereignty with Jerusalem as its capital" (etc.), aiming to reconcile several Palestinian factions but not describing specific steps or strategies towards Israel.
2006–2007 (ambiguity)
In March 2006, after winning an absolute majority in the 2006 Palestinian legislative elections, Hamas published its government program in which Hamas claimed sovereignty for the Palestinian territories but did not repeat its claim to all of mandatory Palestine, instead declared their willingness to have contacts with Israel "in all mundane affairs: business, trade, health, and labor".[136] The program further stated: "The question of recognizing Israel is not the jurisdiction of one faction, nor the government, but a decision for the Palestinian people."[137]Since then until today, spokesmen of Hamas seem to disagree about their attitudes towards Israel, and debates are running as to whether the original 1988 Hamas charter has since March 2006 become obsolete and irrelevant or on the contrary still spells out Hamas's genuine and ultimate goals (see: 1988 Hamas charter, § Relevance).
The March 2006 Hamas legislative program was further explained on 6 June 2006 by Hamas' MP Riad Mustafa: "Hamas will never recognize Israel", but if a popular Palestinian referendum would endorse a peace agreement including recognition of Israel, "we would of course accept their verdict".[137]
Also on 6 June 2006, Ismail Haniyeh, senior political leader of Hamas and at that time Prime Minister of the Palestinian National Authority, sent a letter to US President George W. Bush (via University of Maryland's Jerome Segal), stating: "We are so concerned about stability and security in the area that we don't mind having a Palestinian state in the 1967 borders and offering a truce for many years", and asking Bush for a dialogue with the Hamas government. A similar message he sent to Israel's leaders.[138][139] Haniyeh had reportedly proposed a fifty-year armistice.[140] Neither Washington nor Israel replied.[138][139] Nuancing sheikh Ahmed Yassin's statements before 2004 about a hudna (truce) with Israel (see above), Hamas's (former) senior adviser Ahmed Yousef has said (at unknown date) that a "hudna" (truce, armistice) is more than a ceasefire and "obliges parties to use the period to seek a permanent, non-violent resolution to their differences."[141]
On 28 June 2006, Hamas signed the second version of (originally) 'the Palestinians' Prisoners Document' which supports the quest for a Palestinian state "on all territories occupied in 1967".[68][142][143] This document also recognized the PLO as "the sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people", and states that "the negotiations" should be conducted by PLO and President of the Palestinian National Authority and eventual agreements must be ratified by either the Palestinian National Council or a general referendum "held in the homeland and the Diaspora".
In an August 2006 interview with The New York Times, Ismail Haniyeh, senior political leader of Hamas and then Prime Minister of the Palestinian National Authority, said: "We have no problem with a sovereign Palestinian state over all our lands within the 1967 borders, living in calm."[144]
In February 2007, Hamas signed the Fatah–Hamas Mecca Agreement, stressing "the importance of national unity as basis for (…) confronting the occupation" and "activate and reform the PLO", but without further details about how to confront or deal with Israel.[145] At the time of signing that 2007 agreement, Mousa Abu Marzook, Deputy Chairman of the Hamas Political Bureau, underlined his view of the Hamas position: "I can recognize the presence of Israel as a fait accompli (amr wâqi') or, as the French say, a de facto recognition, but this does not mean that I recognize Israel as a state".[146] More Hamas leaders, through the years, have made similar statements.[73][147]
In June 2007, Hamas ousted the Fatah movement from the Gaza Strip, took control there, and since then Hamas occasionally fired rockets from the Gaza Strip on Israel, purportedly to retaliate Israeli aggression against the people of Gaza.[148]
2008–2012 (two spokesmen, four stances)
In April 2008, former US President Jimmy Carter met with Khaled Mashal, the recognized Hamas leader since 2004. Mashal said to Carter, Hamas would "accept a Palestinian state on the 1967 borders" and accept the right of Israel "to live as a neighbour" if such a deal would be approved by a referendum among the "Palestinians". Nevertheless, Mashal did not offer a unilateral ceasefire (as Carter had suggested him to do). The US State Department showed utter indifference for Mashal's new stance; Israel's Prime Minister Ehud Olmert even refused to meet with Carter in Jerusalem, not to mention paying attention to the new Hamas stance.[148]
On 19 June 2008, Hamas and Israel agreed to a six-month cease-fire,[149] which Hamas declared finished at 18 December[150] amidst mutual accusations of breaching the agreed conditions.[149]
Meanwhile, in November 2008, in a meeting with 11 European members of parliaments, Hamas senior official Ismail Haniyeh repeated what he had written in June 2006 to U.S. President George W. Bush but with one extra condition: Hamas was willing to accept a Palestinian state "in the territories of 1967" and offered Israel a long-term truce if Israel recognized the Palestinians' national rights – which he said Israel had declined.[151]
In September 2009, Ismail Haniyeh, head of the Hamas government in the Gaza Strip, wrote to UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon – like he had told the New York Times in August 2006: "We would never thwart efforts to create an independent Palestinian state with borders [from] June 4, 1967, with Jerusalem as its capital."[152]
In May 2010, Khaled Mashal, chairman of the Hamas Political Bureau (thus Hamas' highest leader), again stated that a state "Israel" living nextto "a Palestinian state on the borders of 1967" would be acceptable for Hamas – but only if a referendum among "the Palestinian people" would endorse this arrangement. In November 2010, Ismail Haniyeh,[f] also proposed a Palestinian state on 1967 borders, though added three further conditions: "resolution of the issue of refugees", "the release of Palestinian prisoners", and "Jerusalem as its capital"; and he made the same reservation as Mashal in May 2010 had made, that a Palestinian referendum needed to endorse this arrangement.[154][155]
On December 1, 2010, Ismail Haniyeh (senior Hamas leader, see above), in a news conference in Gaza, repeated his November 2010 message: "We accept a Palestinian state on the borders of 1967, with Jerusalem as its capital, the release of Palestinian prisoners, and the resolution of the issue of refugees," but only if such arrangement would be endorsed by "a referendum" held among all Palestinians: in Gaza, West Bank, and the diaspora.[156]
In May 2011, Hamas and Fatah signed an agreement in Cairo, agreeing to form a ('national unity') government and appoint the Ministers "in consensus between them", but it contained no remarks about how to confront or deal with Israel.[157] In February 2012, Hamas and Fatah signed the Fatah–Hamas Doha Agreement, agreeing (again) to form an interim national consensus government, which (again) did not materialize.
Still in February 2012, according to the Palestinian authority (either the Fatah branch in West Bank or the Hamas branch in Gaza), Hamas forswore the use of violence against Israel ("ceasefire", an Israeli news website called it), followed by a few weeks without violence between Hamas and Israel.[158][159] But violence between Israel and Palestinian militant groups, in the Gaza Strip and southern Israel, also involving Hamas, would soon resume.
2017–2022 (new charter)
On 1 May 2017, in a press conference in Doha (Qatar) presenting a new charter, Khaled Mashal, chief of the Hamas Political Bureau (thus acknowledged as to be highest Hamas leader), declared that, though Hamas considered the establishment of a Palestinian state "on the basis of June 4, 1967" (West Bank, Gaza Strip and East Jerusalem being not under Israeli reign) acceptable, Hamas would in that case still not recognise the statehood of Israel and not relinquish their goal of liberating all of Palestine from "the Zionist project".[73][160]
Around 2018, a Hamas finance minister has suggested that a "long-term ceasefire as understood by Hamas [hudna] and a two-state settlement are the same".[76] Meanwhile, reports are that in the early 2020s, Hamas leaders occasionally still called for the annihilation of the state of Israel.[161] In 2021 Hamas organized and financed a conference among 250 Gaza citizens about the future management of the State of Palestine following the takeover of Israel which was predicted to come soon. According to the conclusions of the conference, the Jewish Israeli fighters would be killed, while the peaceful individuals could be integrated or be allowed to leave. At the same time the highly skilled and educated would be prevented from leaving.[162][163]
2023 – present (all-out war)
On 7 October 2023, a major war between Hamas and Israel broke out, the severest military clash on the territories of Israel and Palestine since the 1973 Yom Kippur War. A number of conflicting statements were made by Hamas senior leaders regarding the policy towards Israel.
On 24 October, Ghazi Hamad—member of the decison-making Hamas Political Bureau[164]—explained the 7 October attack: "Israel is a country that has no place on our land. We must remove that country because it constitutes a security, military and political catastrophe to the Arab and Islamic nation". "We are called a nation of martyrs and we are proud to sacrifice martyrs". Hamad called the creation of the Jewish state "illogical": "(…) We are the victims of the occupation. Therefore, nobody should blame us for the things we do".[165][166]
On 1 November 2023, Ismail Haniyeh, incumbent highest Hamas leader, stated that if Israel agreed to a ceasefire in the 2023 Israel–Hamas war, if humanitarian corridors would be opened, and aid would be allowed into Gaza,Hamas would be "ready for political negotiations for a two-state solution with Jerusalem as the capital of Palestine". Haniyeh also praised the support of movements in Yemen, Iraq, Syria and Lebanon for the Palestinian struggle.[167]
In January 2024, Khaled Mashal, top Hamas leader until 2017 and now heading the Hamas diaspora office – in contradiction with Haniyeh's proclamation from November 2023 – repeated his stance from 1 May 2017: a (preliminary) Palestinian state "on the 1967 borders", that is "21 per cent of Palestine", would be accepted by Hamas but not as the permanent "two-state solution" which "The West" since a long time envisions and promotes; "our Palestinian project" remains "our right in Palestine from the sea to the river", which Hamas will not give up, therefore Hamas will not recognise the legitimacy of "the usurping entity [Israel]".[168]
Hamas political official Khalil al-Hayya told the press in April 2024 that Hamas "is willing to agree to a truce of five years or more with Israel and that it would lay down its weapons and convert into a political party if an independent Palestinian state is established along pre-1967 borders"; the suggestion was considered a "significant concession".[169]
Comments from non-Hamas-members
The vision that Hamas has unfolded in its original 1988 charter – as several author have noted – seems similar to, and (partly) the mirror image of, the vision of certain Zionist groups concerning nearly the same territory, and might even have been derived from, or inspired by, those Zionist views.[g][171][172][173][174][175]
Several (other) authors have interpreted the 1988 Hamas charter as a call for "armed struggle against Israel".[132]
Through all the years of Hamas' existence, authors and scientists like Tibi (1997), Khaled Hroub (2000), Mkhaimer Abusada (2009),[176] N.Faeq and D.Jahnata (2020) and I.Alsoos (2021) have warned – notwithstanding Hamas's rhetoric especially since 2006 about long-term hudna's, "live as a neighbour" next to Israel, etc. – that, if Israel would accept a so-called hudna (truce, armistice) proposal from Hamas (a Palestinian state "in the territories of 1967" combined with a long-term truce), this would not imply peace or reconciliation with Israel: Hamas's long-term goal would remain "winning back all of historic [mandatory] Palestine" and create an Islamic state in all former Mandatory Palestine in which Jews could live as citizens, not "a sovereign Jewish entity";[79][80] they warn that Hamas believes, over time they will be strong enough to liberate all historic Palestine.[176] Establishing a Palestinian state in the West Bank and Gaza (as part of a hudna deal) would only be Hamas's interim solution, during which Israel would not be recognized, these authors argue.[79][80]
In mid-2006, University of Maryland's Jerome Segal suggested that a Palestinian state within the 1967 borders and a truce for many years could be considered Hamas's de facto recognition of Israel.[138]
As of January 2007, Israeli, American and European news media considered Hamas to be the "dominant political force" within the Palestinian territories.[65][177][178]
Journalist Zaki Chehab wrote in 2007 that Hamas's public concessions following the 2006 elections were "window-dressing" and that the organisation would never recognise Israel's right to exist.[179]
As to the question whether Hamas would be capable to enter into a long-term non-aggression treaty with Israel without being disloyal to their understanding of Islamic law and God's word, the Atlantic magazine columnist Jeffrey Goldberg in January 2009 stated: "I tend to think not, though I've noticed over the years a certain plasticity of belief among some Hamas ideologues. Also, this is the Middle East, so anything is possible".[180]
Religious policy
In the Gaza Strip
The gender ideology outlined in the Hamas charter, the importance of women in the religious-nationalist project of liberation is asserted as no lesser than that of males. Their role was defined primarily as one of manufacturing males and caring for their upbringing and rearing, though the charter recognized they could fight for liberation without obtaining their husband's permission and in 2002 their participation in jihad was permitted.[181] The doctrinal emphasis on childbearing and rearing as woman's primary duty is not so different from Fatah's view of women in the First Intifada and it also resembles the outlook of Jewish settlers, and over time it has been subjected to change.[182][183]
In 1989, during the First Intifada, a small number of Hamas followers[184] campaigned for the wearing of the hijab, which is not a part of traditional women's attire in Palestine,[citation needed] for polygamy, and also insisted women stay at home and be segregated from men. In the course of this campaign, women who chose not to wear the hijab were verbally and physically harassed, with the result that the hijab was being worn 'just to avoid problems on the streets'.[185] The harassment dropped drastically when, after 18 months UNLU condemned it,[186] though similar campaigns reoccurred.
Since Hamas took control of the Gaza Strip in 2007, some of its members have attempted to impose Islamic dress or the hijab head covering on women.[176][187] The government's "Islamic Endowment Ministry" has deployed Virtue Committee members to warn citizens of the dangers of immodest dress, card playing, and dating.[188] There are no government laws imposing dress and other moral standards, and the Hamas education ministry reversed one effort to impose Islamic dress on students.[176] There has also been successful resistance to attempts by local Hamas officials to impose Islamic dress on women.[189] Hamas officials deny having any plans to impose Islamic law, one legislator stating that "What you are seeing are incidents, not policy," and that Islamic law is the desired standard "but we believe in persuasion".[188]
In 2013, UNRWA canceled its annual marathon in Gaza after Hamas prohibited women from participating in the race.[190]
In the West Bank
In 2005, the human rights organization Freemuse released a report titled "Palestine: Taliban-like attempts to censor music", which said that Palestinian musicians feared that harsh religious laws against music and concerts will be imposed since Hamas group scored political gains in the Palestinian Authority local elections of 2005.[191]
The attempt by Hamas to dictate a cultural code of conduct in the 1980s and early 1990s led to a violent fighting between different Palestinian sectors. Hamas members reportedly burned down stores that stocked videos they deemed indecent and destroyed books they described as "heretical".[192]
In 2005, an outdoor music-and-dance performance in Qalqiliya was suddenly banned by the Hamas-led municipality, for the reason that such an event would be "haram", i.e. forbidden by Islam.[193] The municipality also ordered that music no longer be played in the Qalqiliya zoo, and mufti Akrameh Sabri issued a religious edict affirming the municipality decision.[192] In response, the Palestinian national poet Mahmoud Darwish warned that "There are Taliban-type elements in our society, and this is a very dangerous sign."[191][192][194][195]
The Palestinian columnist Mohammed Abd Al-Hamid, a resident of Ramallah, wrote that this religious coercion could cause the migration of artists, and said "The religious fanatics in Algeria destroyed every cultural symbol, shattered statues and rare works of art and liquidated intellectuals and artists, reporters and authors, ballet dancers and singers—are we going to imitate the Algerian and Afghani examples?"[192]
Erdoğan's Turkey as a role model
Some Hamas members have stated that the model of Islamic government that Hamas seeks to emulate is that of Turkey under the rule of Recep Tayyip Erdoğan. The foremost members to distance Hamas from the practices of the Taliban and to publicly support the Erdoğan model were Ahmed Yousef and Ghazi Hamad, advisers to Prime Minister Hanieh.[196][197] Yusuf, the Hamas deputy foreign minister, reflected this goal in an interview with a Turkish newspaper, stating that while foreign public opinion equates Hamas with the Taliban or al-Qaeda, the analogy is inaccurate. Yusuf described the Taliban as "opposed to everything", including education and women's rights, while Hamas wants to establish good relations between the religious and secular elements of society and strives for human rights, democracy and an open society.[198] According to professor Yezid Sayigh of King's College in London, how influential this view is within Hamas is uncertain, since both Ahmad Yousef and Ghazi Hamad were dismissed from their posts as advisers to Hamas Prime Minister Ismail Hanieh in October 2007.[196] Both have since been appointed to other prominent positions within the Hamas government. Khaled al-Hroub of the West Bank-based and anti-Hamas[199] Palestinian daily Al Ayyam added that despite claims by Hamas leaders that it wants to repeat the Turkish model of Islam, "what is happening on the ground in reality is a replica of the Taliban model of Islam."[200][201]
1988 Hamas Charter
Hamas published its charter in August 1988, wherein it defined itself as a chapter of the Muslim Brotherhood and its desire to establish "an Islamic state throughout Palestine".[202] The foundational document was, according to Khaled Hroub, written by a single individual and made public without going through the usual prior consultation process.[h] It was then signed on August 18, 1988. It contains characterizations of Israeli society as Nazi-like in its cruelty,[204] and irredentist claims.[205][206][207] It declares all of Palestine a waqf, an unalienable religious property consisting of land endowed to Muslims in perpetuity by God,[208][i][210] with religious coexistence under Islam's rule.[211] The charter rejects a two-state solution, stating that the conflict cannot be resolved "except through jihad".[212][213]
Article 6 states that the movement's aim is to "raise the banner of Allah over every inch of Palestine, for under the wing of Islam followers of all religions can coexist in security and safety where their lives, possessions and rights are concerned".[214][215] It adds that, "when our enemies usurp some Islamic lands, jihad becomes a duty binding on all Muslims".[216] Many scholars have pointed out that both the 1988 Hamas's charter and the Likud party platform sought full control of the land, thus denouncing the two-state solution.[217][218][171][172][173][174][219][175] For Hamas, to concede territory is seen as equivalent to renouncing Islam itself.[citation needed]
The 1988 Hamas charter is said, November 2023, to "mandate(s) the killing of Jews".[220] The "governing" 1988 charter of Hamas was said, in 2018, to "openly dedicate(s) Hamas to genocide against the Jewish people", referring to the Hamas 1988 charter, article 7.[221] More authors have characterized the violent language against all Jews in the original Hamas charter as genocidal,[222][223] incitement to genocide,[224][225] or antisemitic.[222][226] The charter attributes collective responsibility to Jews, not just Israelis, for various global issues, including both World Wars.[227]
The charter is said to echoe Nazi propaganda in claiming that Jews profited during World War II.[228] Jeffrey Goldberg, editor-in-chief of The Atlantic magazine, has compared these to those that appear in The Protocols of the Elders of Zion.[225]
On the other hand, Ahmed Yassin, the founder of Hamas, has said in a 1988 interview—apparently reacting on accusations that 'Hamas hate Jews':
"We don't hate Jews and fight Jews because they are Jewish. They are a people of faith and we are a people of faith, and we love all people of faith. If my brother, from my own mother and father and my own faith takes my home and expels me from it, I will fight him. I will fight my cousin if he takes my home and expels me from it. So when a Jew takes my home and expels me from it, I will fight him. I don't fight other countries because I want to be at peace with them, I love all people and wish peace for them, even the Jews. The Jews lived with us all of our lives and we never assaulted them, and they held high positions in government and ministries. But if they take my home and make me a refugee like 4 million Palestinians in exile? Who has more right to this land? The Russian immigrant who left this land 2000 years ago or the one who left 40 years ago? We don't hate the Jews, we only ask for them to give us our rights."[229]
2017 charter
In May 2017, Hamas unveiled a rewritten charter, titled "A Document of General Principles and Policies". The charter accepts a Palestinian state in the 1967 borders, without recognizing Israel. The charter clarifies that Hamas's struggle is not against the Jewish people but against Zionists.[230] The charter argues that armed resistance to occupation is supported by international law.[231][232][233] It also claims to support democracy.[234][160] Hamas has described these changes as adaptation within a specific context, as opposed to abandonment of its principles.[235]
The 2017 Hamas charter or document—without referring to their own 1988 charter though—denies and rejects the idea that Hamas would "struggle against Jews because they are Jewish": Hamas's "conflict is with the Zionist project not (…) the Jews because they are Jewish".[236] But some sources maintain Hamas's condemnation of Zionists is antisemitic too.[234][237] The 2017 charter describes Zionism as the enemy of all Muslims, and a danger to international security, what author J.S. Spoerl in 2020 has disqualified as "hardly (...) a serious repudiation of anti-Semitism".[238]
Organization
Leadership and structure

Hamas inherited from its predecessor a tripartite structure that consisted in the provision of social services, of religious training and military operations under a Shura Council. Traditionally it had four distinct functions: (a) a charitable social welfare division (dawah); (b) a military division for procuring weapons and undertaking operations (al-Mujahideen al Filastinun); (c) a security service (Jehaz Aman); and (d) a media branch (A'alam).[239] Hamas has both an internal leadership within the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, and an external leadership, split between a Gaza group directed by Mousa Mohammed Abu Marzook from his exile first in Damascus and then in Egypt, and a Kuwaiti group (Kuwaidia) under Khaled Mashal.[240] The Kuwaiti group of Palestinian exiles began to receive extensive funding from the Gulf States after its leader Mashal broke with Yasser Arafat's decision to side with Saddam Hussein in the Invasion of Kuwait, with Mashal insisting that Iraq withdraw.[241] On May 6, 2017, Hamas' Shura Council chose Ismail Haniya to become the new leader, to replace Mashal.[242]
The exact structure of the organization is unclear as it is shrouded in a veil of secrecy in order to conceal operational activities. Formally, Hamas maintains the wings are separate and independent, but this has been questioned. It has been argued that its wings are both separate and combined for reasons of internal and external political necessity. Communication between the political and military wings of Hamas is made difficult by the thoroughness of Israeli intelligence surveillance and the existence of an extensive base of informants. After the assassination of Abdel Aziz al-Rantisi the political direction of the militant wing was diminished and field commanders were given wider discretional autonomy over operations.[243]
Political Bureau
Hamas's overarching governing body is the Majlis al-Shura (Shura Council), based on the Qur'anic concept of consultation and popular assembly (shura), which Hamas leaders argue provides for democracy within an Islamic framework.[244] As the organization grew more complex and Israeli pressure increased, the Shura Council was renamed the General Consultative Council, with members elected from local council groups. The council elects the 15-member Political Bureau (al-Maktab al-Siyasi)[245] that makes decisions for Hamas. Representatives come from Gaza, the West Bank, leaders in exile and Israeli prisons.[246] The Political Bureau was based in Damascus until the Syrian Civil War until Hamas's support for the civil opposition to Bashar al-Assad led to the office's relocation to Qatar in January 2012, .[246][247]
Finances and funding
Hamas, like its predecessor the Muslim Brotherhood, assumed the administration of Gaza's waqf properties, endowments which extend over 10% of all real estate in the Gaza Strip, with 2,000 acres of agricultural land held in religious trusts, together with numerous shops, rentable apartments and public buildings.[248]
In the first five years of the 1st Intifada, the Gaza economy, 50% of which depended on external sources of income, plummeted by 30–50% as Israel closed its labour market and remittances from the Palestinian expatriates in the Gulf countries dried up following the 1991–1992 Gulf War.[249] At the 1993 Philadelphia conference, Hamas leaders' statements indicated that they read George H. W. Bush's outline of a New World Order as embodying a tacit aim to destroy Islam, and that therefore funding should focus on enhancing the Islamic roots of Palestinian society and promoting jihad, which also means zeal for social justice, in the occupied territories.[250] Hamas became particularly fastidious about maintaining separate resourcing for its respective branches of activity—military, political and social services.[251] It has had a holding company in East Jerusalem (Beit al-Mal), a 20% stake in Al Aqsa International Bank which served as its financial arm, the Sunuqrut Global Group and al-Ajouli money-changing firm.[252]
By 2011, Hamas's budget, calculated to be roughly US$70 million, derived even more substantially (85%) from foreign, rather than internal Palestinian, sources.[252] Only two Israeli-Palestinian sources figure in a list seized in 2004, while the other contributors were donor bodies located in Jordan, Qatar, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Britain, Germany, the United States, United Arab Emirates, Italy and France. Much of the money raised comes from sources that direct their assistance to what Hamas describes as its charitable work for Palestinians, but investments in support of its ideological position are also relevant, with Persian Gulf States and Saudi Arabia prominent in the latter. Matthew Levitt claims that Hamas also taps money from corporations, criminal organizations and financial networks that support terror.[253] It is also alleged that it engages in cigarette and drug smuggling, multimedia copyright infringement and credit card fraud.[252] The United States, Israel and the EU have shut down many charities and organs that channel money to Hamas, such as the Holy Land Foundation for Relief.[254] Between 1992 and 2001, this group is said to have provided $6.8 million to Palestinian charities of the $57 million collected. By 2001, it was alleged to have given Hamas $13 million, and was shut down shortly afterwards.[255]
About half of Hamas's funding came from states in the Persian Gulf down to the mid-2000s. Saudi Arabia supplied half of the Hamas budget of $50 million in the early 2000s,[256] but, under US pressure, began to cut its funding by cracking down on Islamic charities and private donor transfers to Hamas in 2004,[257] which by 2006 drastically reduced the flow of money from that area. Iran and Syria, in the aftermath of Hamas's 2006 electoral victory, stepped in to fill the shortfall.[258][259] Saudi funding, negotiated with third parties including Egypt, remained supportive of Hamas as a Sunni group but chose to provide more assistance to the PNA, the electoral loser, when the EU responded to the outcome by suspending its monetary aid.[260] During the 1980s, Iran began to provide 10% of Hamas's funding, which it increased annually until by the 1990s it supplied $30 million.[256] It accounted for $22 million, over a quarter of Hamas's budget, by the late 2000s.[257] According to Matthew Levitt, Iran preferred direct financing to operative groups rather than charities, requiring video proof of attacks.[257][261] Much of the Iran funding is said to be channeled through Hezbollah.[257] After 2006, Iran's willingness to take over the burden of the shortfall created by the drying up of Saudi funding also reflected the geopolitical tensions between the two, since, though Shiite, Iran was supporting a Sunni group traditionally closely linked with the Saudi kingdom.[262] The US imposed sanctions on Iran's Bank Saderat, alleging it had funneled hundreds of millions to Hamas.[263] The US has expressed concerns that Hamas obtains funds through Palestinian and Lebanese sympathizers of Arab descent in the Foz do Iguaçu area of the tri-border region of Latin America, an area long associated with arms trading, drug trafficking, contraband, the manufacture of counterfeit goods, money-laundering and currency fraud. The State Department adds that confirmatory information of a Hamas operational presence there is lacking.[264]
After 2009, sanctions on Iran made funding difficult, forcing Hamas to rely on religious donations by individuals in the West Bank, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia. Funds amounting to tens of millions of dollars raised in the Gulf states were transferred through the Rafah Border Crossing. These were not sufficient to cover the costs of governing the Strip and running the al Qassam Brigades, and when tensions arose with Iran over support of President Assad in Syria, Iran dropped its financial assistance to the government, restricting its funding to the military wing, which meant a drop from $150 million in 2012 to $60 million the following year. A further drop occurred in 2015 when Hamas expressed its criticisms of Iran's role in the Yemeni Civil War.[265]
In 2017, the PA government imposed its own sanctions against Gaza, including, among other things, cutting off salaries to thousands of PA employees, as well as financial assistance to hundreds of families in the Gaza Strip. The PA initially said it would stop paying for the electricity and fuel that Israel supplies to the Gaza Strip, but after a year partially backtracked.[266] The Israeli government has allowed millions of dollars from Qatar to be funneled on a regular basis through Israel to Hamas, to replace the millions of dollars the PA had stopped transferring to Hamas. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu explained that letting the money go through Israel meant that it could not be used for terrorism, saying: "Now that we are supervising, we know it's going to humanitarian causes."[267]
According to U.S. officials, as of 2023 Hamas has an investment portfolio that is worth anywhere from 500 million to US$1 billion, including assets in Sudan, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, Algeria and the United Arab Emirates.[268] Hamas has denied such allegations.[269]
Social services wing
Hamas developed its social welfare programme by replicating the model established by Egypt's Muslim Brotherhood. For Hamas, charity and the development of one's community are both prescribed by religion and to be understood as forms of resistance.[270] In Islamic tradition, dawah (lit. transl. "the call to God") obliges the faithful to reach out to others by both proselytising and by charitable works, and typically the latter centre on the mosques which make use of both waqf endowment resources and charitable donations (zakat, one of the five pillars of Islam) to fund grassroots services such as nurseries, schools, orphanages, soup kitchens, women's activities, library services and even sporting clubs within a larger context of preaching and political discussions.[271] In the 1990s, some 85% of its budget was allocated to the provision of social services.[272] Hamas has been called perhaps the most significant social services actor in Palestine. By 2000, Hamas or its affiliated charities ran roughly 40% of the social institutions in the West Bank and Gaza and, with other Islamic charities, by 2005, was supporting 120,000 individuals with monthly financial support in Gaza.[273] Part of the appeal of these institutions is that they fill a vacuum in the administration by the PLO of the Palestinian territories, which had failed to cater to the demand for jobs and broad social services, and is widely viewed as corrupt.[274] As late as 2005, the budget of Hamas, drawing on global charity contributions, was mostly tied up in covering running expenses for its social programmes, which extended from the supply of housing, food and water for the needy to more general functions such as financial aid, medical assistance, educational development and religious instruction. A certain accounting flexibility allowed these funds to cover both charitable causes and military operations, permitting transfer from one to the other.[275]
The dawah infrastructure itself was understood, within the Palestinian context, as providing the soil from which a militant opposition to the occupation would flower.[j] In this regard it differs from the rival Palestinian Islamic Jihad which lacks any social welfare network, and relies on spectacular terrorist attacks to recruit adherents.[277] In 2007, through funding from Iran, Hamas managed to allocate at a cost of $60 million, monthly stipends of $100 for 100,000 workers, and a similar sum for 3,000 fishermen laid idle by Israel's imposition of restrictions on fishing offshore, plus grants totalling $45 million to detainees and their families.[278] Matthew Levitt argues that Hamas grants to people are subject to a rigorous cost-benefit analysis of how beneficiaries will support Hamas, with those linked to terrorist activities receiving more than others.[279] Israel holds the families of suicide bombers accountable and bulldozes their homes, whereas the families of Hamas activists who have been killed or wounded during militant operations are given an initial, one-time grant varying between $500–$5,000, together with a $100 monthly allowance. Rent assistance is also given to families whose homes have been destroyed by Israeli bombing though families unaffiliated with Hamas are said to receive less.[183][280]
Until 2007, these activities extended to the West Bank, but, after a PLO crackdown, now continue exclusively in the Gaza Strip.[281] After the 2013 Egyptian coup d'état deposed the elected Muslim Brotherhood government of Mohamed Morsi in 2013, Hamas found itself in a financial straitjacket and has since endeavoured to throw the burden of responsibility for public works infrastructure in the Gaza Strip back onto the Palestinian National Authority, but without success.[282]
Military wing

The Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades is Hamas's military wing.[283] While the number of members is known only to the Brigades leadership, Israel estimates the Brigades have a core of several hundred members who receive military style training, including training in Iran and in Syria (before the Syrian Civil War).[284] Additionally, the brigades have an estimated 10,000–17,000 operatives,[273][285] forming a backup force whenever circumstances call for reinforcements for the Brigade. Recruitment training lasts for two years.[284] The group's ideology outlines its aim as the liberation of Palestine and the restoration of Palestinian rights under the dispensations set forth in the Qur'an, and this translates into three policy priorities:
To evoke the spirit of Jihad (Resistance) among Palestinians, Arabs, and Muslims; to defend Palestinians and their land against the Zionist occupation and its manifestations; to liberate Palestinians and their land that was usurped by the Zionist occupation forces and settlers.[286]
According to its official stipulations, the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades' military operations are to be restricted to operating only inside Palestine, engaging with Israeli soldiers,[k] and in exercising the right of self-defense against armed settlers. They are to avoid civilian targets, to respect the enemy's humanity by refraining from mutilation, defacement or excessive killing, and to avoid targeting Westerners either in the occupied zones or beyond.[287]

Down to 2007, the Brigades are estimated to have lost some 800 operatives in conflicts with Israeli forces. The leadership has been consistently undermined by targeted assassinations. Aside from Yahya Ayyash (January 5, 1996), it has lost Emad Akel (November 24, 1993), Salah Shehade (July 23, 2002), Ibrahim al-Makadmeh (March 8, 2003), Ismail Abu Shanab (August 21, 2003), Ahmed Yassin (March 22, 2004), and Abdel Aziz al-Rantisi (April 17, 2004).[288][289]
The Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades groups its fighters in 4–5 man cells, which in turn are integrated into companies and battalions. Unlike the political section, which is split between an internal and external structure, the Brigades are under a local Palestinian leadership, and disobedience with the decisions taken by the political leadership have been relatively rare.[290]
Although the Izz al-Din al-Qassam Brigades are an integral part of Hamas, the exact nature of the relationship is hotly debated. They appear to operate at times independently of Hamas, exercising a certain autonomy.[291][292][293][294][295] Some cells have independent links with the external leadership, enabling them to bypass the hierarchical command chain and political leadership in Gaza.[296] Ilana Kass and Bard O'Neill, likening Hamas's relationship with the Brigades to the political party Sinn Féin's relationship to the military arm of the Irish Republican Army, quote a senior Hamas official as stating: "The Izz al-Din al-Qassam Brigade is a separate armed military wing, which has its own leaders who do not take their orders from Hamas and do not tell us of their plans in advance."[297][l]
Gaza forces, October 2023
During the 2023 Gaza war, the IDF published its intelligence about the Hamas military in the Strip.[300] They put the strength of the Qassam Brigades there at the start of the war at 30,000 fighters, organised by area in five brigades, consisting in total of 24 battalions and c. 140 companies.[300] Each regional brigade had a number of strongholds and outposts, and included specialised arrays for rocket firing, anti-tank missiles, air defenses, snipers, and engineering.[300]
Media
Al-Aqsa TV
Al-Aqsa TV is a television channel founded by Hamas.[301] The station began broadcasting in the Gaza Strip on January 9, 2006,[302][303] less than three weeks before the Palestinian legislative elections. It has shown television programs, including some children's television, which deliver antisemitic messages.[304] Hamas has stated that the television station is "an independent media institution that often does not express the views of the Palestinian government headed by Ismail Haniyeh or of the Hamas movement", and that Hamas does not hold antisemitic views.[305] The programming includes ideologically tinged children's shows, news talk, and religiously inspired entertainment.[306] According to the Anti-Defamation League, the station promotes terrorist activity and incites hatred of Jews and Israelis.[303] Al-Aqsa TV is headed by the controversial Fathi Ahmad Hammad, chairman of al-Ribat Communications and Artistic Productions—a Hamas-run company that also produces Hamas's radio station, Voice of al-Aqsa, and its biweekly newspaper, The Message.[307] Hamad has made a number of controversial comments, including a speech in which he reportedly stated: 'you have Jews everywhere and we must attack every Jew on the globe by way of slaughtering and killing' [308]
Al-Fateh magazine
Al-Fateh ("the conqueror") is the Hamas children's magazine, published biweekly in London, and also posted in an online website. It began publication in September 2002, and its 108th issue was released in mid-September 2007. The magazine features stories, poems, riddles, and puzzles, and states it is for "the young builders of the future".[309]
According to the Anti-Defamation League, al-Fateh promotes violence and antisemitism, with praise for and encouragement to become suicide bombers, and that it "regularly includes photos of children it claims have been detained, injured or killed by Israeli police, images of children firing slingshots or throwing rocks at Israelis and children holding automatic weapons and firebombs."[310]
Social media
Hamas has traditionally presented itself as a voice of suffering of the Palestinian people. According to Time magazine, a new social media strategy was employed in the wake of the October 7 attack: Hamas asserted itself as the dominant resistance force in the Middle East by recording and broadcasting the brutality of their attacks.[311]
According to Dr. Harel Horev, historian and researcher of Palestinian affairs at Tel Aviv University, Hamas has used social media to dehumanize Israelis/Jews. According to his research, Hamas took over the most popular accounts on Palestinian networks in a covert manner that did not reveal its involvement. This control gave it the ability to significantly influence the Palestinian discourse online through content that denies the humanity and right to life of Israelis. These included posters, songs and videos glorifying threats; computer games that encourage the murder of Jews; training videos for carrying out effective and indiscriminate stabbing and shooting attacks; and anti-Semitic cartoons as a central means of dehumanizing the Israeli/Jew in the Palestinian online discourse.[312][313]
Internal security
The General Security Service, formally part of the Hamas political party, operates akin to a governmental body within Gaza. Under the direct oversight of Hamas leader Yahya Sinwar, it conducts extensive surveillance on Palestinians, compiling files on various individuals including journalists and government critics. This secret police force relies on a network of informants and employs tactics such as censorship and surveillance to maintain control. Before the conflict with Israel, the unit reportedly had a monthly budget of $120,000 and consisted of 856 personnel, including more than 160 individuals paid to spread Hamas propaganda and conduct online attacks against opponents.[314]
Other powerful internal security bodies in Gaza include Military Intelligence, which focuses on Israel, and the Internal Security Service, an arm of the Interior Ministry.[314]
Violence
Hamas has used both political activities and violence in pursuit of its goals. For example, while politically engaged in the 2006 Palestinian Territories parliamentary election campaign, Hamas stated in its election manifesto that it was prepared to use "armed resistance to end the occupation".[315]
From 2000 to 2004, Hamas was responsible for killing nearly 400 Israelis and wounding more than 2,000 in 425 attacks, according to the Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs. From 2001 through May 2008, Hamas launched more than 3,000 Qassam rockets and 2,500 mortar attacks into Israel.[316]
Attacks on civilians

Hamas have committed massacres targeting Israeli civilians. Hamas's most deadly suicide bombing was an attack on a Netanya hotel on March 27, 2002, in which 30 people were killed and 140 were wounded. The attack has also been referred to as the Passover massacre since it took place on the first night of the Jewish festival of Passover at a Seder.
Hamas has defended suicide attacks as a legitimate aspect of its asymmetric warfare against Israel. In 2003, according to Stephen Atkins, Hamas resumed suicide bombings in Israel as a retaliatory measure after the failure of peace talks and an Israeli campaign targeting members of the upper echelon of the Hamas leadership.[m] but they are considered as crimes against humanity under international law.[318][319] In a 2002 report, Human Rights Watch stated that Hamas leaders "should be held accountable" for "war crimes and crimes against humanity" committed by the al-Qassam Brigades.[320][321][322]
In May 2006, Israel arrested a top Hamas official, Ibrahim Hamed, who Israeli security officials alleged was responsible for dozens of suicide bombings and other attacks on Israelis.[323] Hamed's trial on those charges has not yet concluded.[324] In 2008, Hamas explosives engineer Shihab al-Natsheh organized a deadly suicide bombing in Dimona.[325][326]
Since 2002, militants of al-Qassam Brigades and other groups have used homemade Qassam rockets to hit Israeli towns in the Negev, such as Sderot. Al-Qassam Brigades was estimated in 2007 to have launched 22% of the rocket and mortar attacks,[327] which killed fifteen people between the years 2000 and 2009.[328] The introduction of the Qassam-2 rocket in 2008 enabled Palestinian paramilitary groups to reach, from Gaza, such Israeli cities such as Ashkelon.[329]
In 2008, Hamas leader Khaled Mashal, offered that Hamas would attack only military targets if the IDF would stop causing the deaths of Palestinian civilians.[330] Following a June 19, 2008, ceasefire, the al-Qassam Brigades ended its rocket attacks and arrested Fatah militants in Gaza who had continued sporadic rocket and mortar attacks against Israel. The al-Qassam Brigades resumed the attacks after the November 4 Israeli incursion into Gaza.[105][331]
On June 15, 2014, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu accused Hamas of involvement in the kidnapping of three Israeli teenagers (including one who held American citizenship), saying "This has severe repercussions."[332] On July 20, 2014, nearly two weeks into Operation Protective Edge, Netanyahu in an interview with CNN described Hamas as "genocidal terrorists."[333]
On August 5, 2014, Israel announced that Israeli security forces arrested Hussam Kawasme, in Shuafat, in connection with the murders of the teens.[334] During interrogation, Kawasme admitted to being the mastermind behind the attack, in addition to securing the funding from Hamas.[335] Officials have stated that additional people arrested in connection with the murders are still being held, but no names have been released.[336]
On August 20, Saleh al-Arouri, a Hamas leader then in exile in Turkey, claimed responsibility for the kidnapping of the three Israeli teens. He delivered an address on behalf of Khaled Mashal at the conference of the International Union of Muslim Scholars in Istanbul, a move that might reflect a desire by Hamas to gain leverage.[337] In it he said:
Our goal was to ignite an intifada in the West Bank and Jerusalem, as well as within the 1948 borders. ... Your brothers in the Al-Qassam Brigades carried out this operation to support their imprisoned brothers, who were on a hunger strike. ... The mujahideen captured these settlers in order to have a swap deal.[338][better source needed]
Hamas political leader Khaled Mashal accepted that members of Hamas were responsible, stating that he knew nothing of it in advance and that what the leadership knew of the details came from reading Israeli reports.[339] Mashal, who had headed Hamas's exiled political wing since 2004, has denied being involved in the "details" of Hamas's "military issues," but "justified the killings as a legitimate action against Israelis on 'occupied' lands."[340]

During the 2023 Hamas attack on Israel, Hamas infiltrated homes, shot civilians en masse, and took scores of Israeli civilians and soldiers as hostages into Gaza.[63][64] According to Human Rights Watch, the deliberate targeting of civilians, indiscriminate attacks, and taking of civilians as hostages amount to war crimes under international humanitarian law.[341] During its October 2023 offensive against Israel, Hamas massacred 364 people at the Re'im music festival, while abucting others.[342][343] During the same offensive, it also was reported that Hamas had massacred the population of the Kfar Aza kibbutz.[344] About 10 percent of the residents of the Be'eri kibbutz were killed.[345] Hamas militants attacked the Psyduck festival, that took place near kibutz Nir Oz, killing 17 Israeli partygoers.[346] Video footage shows children being deliberately killed during the kibbutz attacks,[347] as well as what appears to be an attempt to decapitate a living person using a garden hoe.[348] Forensic teams who have examined bodies of victims said many bodies showed signs of torture as well as rape.[349][350][351] Testimonies from witnesses to acts of gang rapes committed by Hamas militants were collected by the police.[352]
Rocket attacks on Israel
Hamas and other Palestinian armed groups have launched thousands of rockets into Israel since 2001, killing 15 civilians, wounding many more, and posing an ongoing threat to the nearly 800,000 Israeli civilians who live and work in the weapons' range. Hamas officials have said that the rockets were aimed only at military targets, saying that civilian casualties were the "accidental result" of the weapons' poor quality. According to Human Rights Watch, statements by Hamas leaders suggest that the purpose of the rocket attacks was indeed to strike civilians and civilian objects. From January 2009, following Operation Cast Lead, Hamas largely stopped launching rocket attacks on Israel and has on at least two occasions arrested members of other groups who have launched rockets, "showing that it has the ability to impose the law when it wants".[353] In February 2010, Hamas issued a statement regretting any harm that may have befallen Israeli civilians as a result of Palestinian rocket attacks during the Gaza war. It maintained that its rocket attacks had been aimed at Israeli military targets but lacked accuracy and hence sometimes hit civilian areas. Israel responded that Hamas had boasted repeatedly of targeting and murdering civilians in the media.[354]
According to one report, commenting on the 2014 conflict, "nearly all the 2,500–3,000 rockets and mortars Hamas has fired at Israel since the start of the war seem to have been aimed at towns", including an attack on "a kibbutz collective farm close to the Gaza border", in which an Israeli child was killed.[355] Former Israeli Lt. Col. Jonathan D. Halevi stated that "Hamas has expressed pride in aiming long-range rockets at strategic targets in Israel including the nuclear reactor in Dimona, the chemical plants in Haifa, and Ben-Gurion Airport", which "could have caused thousands" of Israeli casualties "if successful".[356]
In July 2008, Barack Obama, then the Democratic presidential candidate, said: "If somebody was sending rockets into my house, where my two daughters sleep at night, I'm going to do everything in my power to stop that, and I would expect Israelis to do the same thing."[357] On December 28, 2008, Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice said in a statement: "the United States strongly condemns the repeated rocket and mortar attacks against Israel."[358] On March 2, 2009, Secretary of State Hillary Clinton condemned the attacks.[359]
On October 7, 2023, Hamas claimed responsibility for a barrage of missile attacks originating from the Gaza Strip.[360]
Attempts to derail 2010 peace talks
In 2010, Hamas, who have been actively sidelined from the peace talks by Israel, spearheaded a coordinated effort by 13 Palestinian militant groups, in attempt to derail the stalled peace talks between Israel and Mahmoud Abbas, President of the Palestinian Authority. According to the Israeli Coordinator of Government Activities in the Territories Major Gen. Eitan Dangot, Israel seeks to work with Salam Fayyad, to help revive the Palestinian economy, and hopes to ease restrictions on the Gaza Strip further, "while somehow preventing the Islamic militants who rule it from getting credit for any progress". According to Dangot, Hamas must not be seen as ruling successfully or be allowed to "get credit for a policy that would improve the lives of people".[361] The campaign consists of attacks against Israelis in which, according to a Hamas declaration in early September, "all options are open".[362][363][364][365] The participating groups also include Palestinian Islamic Jihad, the Popular Resistance Committees and an unnamed splinter group of Fatah.[366]
As part of the campaign, on August 31, 2010, 4 Israeli settlers, including a pregnant woman, were killed by Hamas militants while driving on Route 60 near the settlement Kiryat Arba, in the West bank. According to witnesses, militants opened fire on the moving vehicle, but then "approached the car" and shot the occupants in their seats at "close range". The attack was described by Israeli sources as one of the "worst" terrorist acts in years.[367][368][369] A senior Hamas official said that Israeli settlers in the West Bank are legitimate targets since "they are an army in every sense of the word".[370][371]
Guerrilla warfare

Hamas has made great use of guerrilla tactics in the Gaza Strip and to a lesser degree the West Bank.[372] It has successfully adapted these techniques over the years since its inception. According to a 2006 report by rival Fatah party, Hamas had smuggled between several hundred and 1,300 tons of advanced rockets, along with other weaponry, into Gaza.[372]
Hamas has used IEDs and anti-tank rockets against the IDF in Gaza. The latter include standard RPG-7 warheads and home-made rockets such as the Al-Bana, Al-Batar and Al-Yasin. The IDF has a difficult, if not impossible, time trying to find hidden weapons caches in Palestinian areas—this is due to the high local support base Hamas enjoys.[373]
Extrajudicial killings of rivals
In addition to killing Israeli civilians and armed forces, Hamas has also murdered suspected Palestinian Israel collaborators and Fatah rivals.[374][375] According to the Associated Press, collaborating with Israel is a crime punishable by death in Gaza.[376] Hundreds of Palestinians were executed by both Hamas and Fatah during the First Intifada.[377] In the wake of the 2006 Israeli conflict with Gaza, Hamas was accused of systematically rounding up, torturing and summarily executing Fatah supporters suspected of supplying information to Israel. Human Rights Watch estimates several hundred Gazans were "maimed" and tortured in the aftermath of the conflict. Seventy-three Gazan men accused of "collaborating" had their arms and legs broken by "unidentified perpetrators", and 18 Palestinians accused of helping Israel were executed by Hamas security officials in the first days of the conflict.[378][379][380] In November 2012, Hamas's Izzedine al-Qassam brigade publicly executed six Gaza residents accused of collaborating with Israel. According to the witnesses, six alleged informers were shot dead one by one in Gaza City, while the corpse of the sixth victim was tied by a cable to the back of a motorcycle and dragged through the streets.[381] In 2013, Human Rights Watch issued a statement condemning Hamas for not investigating and giving a proper trial to the six men. Their statement was released the day before Hamas issued a deadline for "collaborators" to turn themselves in, or they will be pursued "without mercy".[382] During the 2014 Israel-Gaza conflict, Hamas executed at least 23 accused collaborators after three of its commanders were assassinated by Israeli forces, with Amnesty International also reporting instances of torture used by Hamas forces.[383][384] An Israeli source denied that any of the commanders had been targeted on the basis of human intelligence.[385]
Frequent killings of unarmed people have also occurred during Hamas-Fatah clashes.[386][387] NGOs have cited a number of summary executions as particular examples of violations of the rules of warfare, including the case of Muhammad Swairki, 28, a cook for Palestinian Authority Chairman Mahmoud Abbas's presidential guard, who was thrown to his death, with his hands and legs tied, from a 15-story apartment building in Gaza City.[388] Hamas security forces reportedly shoot and torture Palestinians who opposed Hamas rule in Gaza.[389] In one case, a Palestinian had criticized Hamas in a conversation on the street with some friends. Later that day, more than a dozen armed men with black masks and red kaffiyeh took the man from his home, and brought him to a solitary area where they shot him three times in the lower legs and ankles. The man told Human Rights Watch that he was not politically active.[378]
On August 14, 2009, Hamas fighters stormed the Mosque of cleric Abdel-Latif Moussa.[390] The cleric was protected by at least 100 fighters from Jund Ansar Allah ("Army of the Helpers of God"), an Islamist group with links to Al-Qaeda. The resulting battle left at least 13 people dead, including Moussa and six Hamas fighters, and 120 people injured.[391] According to Palestinian president Mahmoud Abbas, during 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict, Hamas killed more than 120 Palestinian youths for defying house arrest imposed on them by Hamas, in addition to 30–40 Palestinians killed by Hamas in extrajudicial executions after accusing them of being collaborators with Israel.[392] Referring to the killing of suspected collaborators, a Shin Bet official stated that "not even one" of those executed by Hamas provided any intelligence to Israel, while the Shin Bet officially "confirmed that those executed during Operation Protective Edge had all been held in prison in Gaza in the course of the hostilities".[385]
2011–2013 Sinai insurgency
Hamas has been accused of providing weapons, training and fighters for Sinai-based insurgent attacks,[393][394] although Hamas strongly denies the allegations, calling them a smear campaign aiming to harm relations with Egypt.[393] According to the Egyptian Army, since the ouster of Egypt's Muslim-Brotherhood president Mohamed Morsi, over 600 Hamas members have entered the Sinai Peninsula through smuggling tunnels.[395] In addition, several weapons used in Sinai's insurgent attacks are being traced back to Hamas in the Gaza Strip, according to the army.[395] The four leading insurgent groups in the Sinai have all reportedly maintained close ties with the Gaza Strip.[396] Hamas called the accusation a "dangerous development".[397] Egyptian authorities stated that the 2011 Alexandria bombing was carried out by the Gaza-based Army of Islam, which has received sanctuary from Hamas and earlier collaborated in the capture of Gilad Shalit.[396][398][399][400] Army of Islam members linked to the August 2012 Sinai attack have reportedly sought refuge in the Gaza Strip.[396] Egypt stated that Hamas directly provided logistical support to the Muslim Brotherhood militants who carried out the December 2013 Mansoura bombing.[401]
Terrorist designation
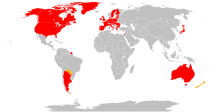
The United States designated Hamas as a terrorist organisation in 1995, as did Canada in November 2002,[402] and the United Kingdom in November 2021.[52] The European Union so designated Hamas's military wing in 2001 and, under US pressure,[403] designated Hamas in 2003.[404] Hamas challenged this decision,[405] which was upheld by the European Court of Justice in July 2017.[406] Japan[407] and New Zealand[408] have designated the military wing of Hamas as a terrorist organization.[409] The organization is banned in Jordan.[410] In late February 2024, New Zealand re-designated the entire Hamas organization as a terror entity.[411]
Hamas is not regarded as a terrorist organization by Afghanistan, Algeria, Iran,[412] Russia,[413] Norway,[n] Turkey, China,[415] Egypt, Syria, and Brazil.[416][417][418] "Many other states, including Russia, China, Syria, Turkey and Iran consider the (armed) struggle waged by Hamas to be legitimate."[419]
According to Tobias Buck, Hamas is "listed as a terrorist organisation by Israel, the US and the EU, but few dare to treat it that way now" and in the Arab and Muslim world it has lost its pariah status and its emissaries are welcomed in capitals of Islamic countries.[420] While Hamas is considered a terrorist group by several governments and some academics, others regard Hamas as a complex organization, with terrorism as only one component.[421][422]
| Country | Designated as terrorist org. | Comments |
|---|---|---|
 Australia Australia | Yes | Australia announced they would designate Hamas as a terrorist organization in its entirety in 2022. Prior to that, Hamas's military wing, the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades, were recognized as one but the political branch were not.[423][424][425][426] |
 Brazil Brazil | No | Brazil does not designate Hamas as a terrorist organization.[416][427] The Brazilian government only classifies organizations as terrorists when the United Nations does so.[428] |
 Canada Canada | Yes | Under the Anti-Terrorism Act, the Government of Canada has listed Hamas as a terrorist entity, thus establishing it as a terrorist group, since 2002.[429][430] |
 China China | No | As of 2006, China does not designate Hamas to be a terrorist organization and acknowledges Hamas to be the legitimately elected political entity in the Gaza Strip that represents the Palestinian people. In June 2006, a spokesperson for the Chinese Foreign Ministry stated: "We believe that the Palestinian government is legally elected by the people there and it should be respected."[431][432] |
 Egypt Egypt | No | In March 2014, as part of a crackdown on the Muslim Brotherhood organization following the July 2013 overthrow of Mohamed Morsi, Cairo's Urgent Matters Court outlawed Hamas's activities in Egypt, ordered the closure of its offices and to arrest any Hamas member found in the country.[433][434] In February 2015, the aforementioned court designated Hamas as a terrorist organization, accusing Hamas of carrying terrorist attacks in Egypt through tunnels linking the Sinai Peninsula to the Gaza Strip.[435] In June 2015, Egypt's appeals court overturned the prior ruling that listed Hamas as a terrorist organization,[436] and Egypt (as of 2023) no longer officially regards Hamas to be a terrorist organization. |
 European Union European Union | Yes | The EU designated Hamas as a terrorist group from 2003. In December 2014, the General Court of the European Union ordered that Hamas be removed from the register. The court stated that the move was technical and was not a reassessment of Hamas's classification as a terrorist group. In March 2015, EU decided to keep Hamas on its terrorism blacklist "despite a controversial court decision", appealing the court's judgment.[437][438][439][440][441][442][443][444] In July 2017, this appeal was upheld by the European Court of Justice.[445][446] |
 India India | No | Hamas is not regarded as a terrorist organization by India,[447] though individual Indian leaders have condemned certain Hamas' attacks as terrorist. |
 Iran Iran | No | Hamas is not regarded as a terrorist organization by Iran.[412][419] |
 Israel Israel | Yes | The Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs states, "Hamas maintains a terrorist infrastructure in Gaza and the West Bank, and acts to carry out terrorist attacks in the territories and Israel."[448] |
 Japan Japan | Yes | As of 2005, Japan had frozen the assets of 472 terrorists and terrorist organizations including those of Hamas.[449] In 2006 it publicly acknowledged that Hamas had won the 2006 Palestinian legislative elections democratically.[450] |
 Jordan Jordan | No | Hamas was banned in 1999, reportedly in part at the request of the United States, Israel, and the Palestinian Authority.[451] In 2019, Jordanian sources are said to have revealed "that the Kingdom refused a request from the General Secretariat of the Arab League in late March to ban Hamas and list it as a terrorist organization."[452][better source needed] |
 New Zealand New Zealand | Yes | The military wing of Hamas, the Izz al-Din al-Qassam Brigades, has been listed as a terrorist entity since 2010.[453] New Zealand PM Chris Hipkins reiterated in October 2023 that "Hamas is recognised by New Zealand as a terrorist organisation".[454] In February 2024, the Government designated the entire Hamas organisation as a terrorist entity.[411] |
 Norway Norway | No | Norway does not list Hamas as a terrorist organization.[455] Norway distanced itself from the European Union in 2006, claiming that its listing was causing problems for its role as a 'neutral facilitator.'[414] After Progress Party leader Sylvi Listhaug criticized PM Jonas Gahr Støre at the start of the 2023 Israel-Hamas war for not calling Hamas a terrorist organization, Støre said that it was an organization that carried out terrorist acts but he would not change Norway's listing.[456] |
 Americas Americas | Yes | In 2021, the Organization of American States published a statement in which it designated Hamas a terrorist organization. The statement did not receive full support from Argentina, Bolivia, Mexico, and Venezuela.[457] |
 Paraguay Paraguay | Partial | The military wing of Hamas, the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades, is listed as a terrorist organization.[citation needed] |
 Philippines Philippines | No | Hamas is not considered as a terrorist organization by the Philippines. The National Security Council has proposed considering Hamas as a terrorist group as a response to the 2023 Israel–Hamas war.[458][459] |
 Qatar Qatar | No | The Qatari government has a designated terrorist list. As of 2014, the list contained no names, according to The Daily Telegraph.[460] In September 2020, Qatar brokered a ceasefire between Israel and Hamas that is reported to include "plans to build a power station operated by Qatar, the provision of $34 million for humanitarian aid, provision of 20,000 COVID-19 testing kits by Qatar to the Health Ministry, and a number of initiatives to reduce unemployment in the Gaza Strip."[461] |
 Russia Russia | No | Russia does not designate Hamas a terrorist organisation, and held direct talks with Hamas in 2006, after Hamas won the Palestine elections, stating that it did so to press Hamas to reject violence and recognise Israel.[462] |
 Saudi Arabia Saudi Arabia | No | Saudi Arabia banned the Muslim Brotherhood in 2014 and branded it a terrorist organization. While Hamas is not specifically listed, a non-official Saudi source stated that the decision also encompasses its branches in other countries, including Hamas.[463][464] As of January 2020, ties between Saudi Arabia and Hamas remain strained despite attempts at a rapprochement. Wesam Afifa, director general of Al-Aqsa TV is quoted as saying that "Saudi Arabia did not sever ties with Hamas, and even when Riyadh made public its list of terrorists in 2017, Hamas was not added to the list."[465] In 2020, Saudi Arabia arrested 68 Palestinian and Jordanian citizens associated with Hamas in a special terrorism court. In 2022, Saudi Arabia released a number of those detainees in recent months, including senior member Mohammad Al-Khodary, who was set free in October, following statements by Hamas leaders expressing their desire for improved relations with the country.[466] In 2023, during Ramadan, senior members of Hamas, including Ismail Haniyeh, Mousa Marzook, Khalil al-Hayya and Khaled Meshaal arrived in Saudi Arabia to mend Hamas's relationship with Saudi Arabia. They were spotted performing Umrah in Mecca, Saudi Arabia.[467] |
 Switzerland Switzerland | Partial | Before the Hamas-led attack on Israel, Switzerland had not designated it as a terrorist organization and had direct contacts with all major stakeholders in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, including Hamas.[468] After the attack, the Federal Council classified Hamas as a terrorist organization[469][470] and stated that it would recommend Swiss parliament to pass a new law by the end of February 2024 to ban "Hamas activities" or "support" for the group.[471] The Security Policy Commission of the National Council on 10 October had voted to ban Hamas and declare it terrorist[472] with the Swiss parliament's upper house, the Council of States, following suit.[473] The Federal Council proposed a five-year ban on Hamas which still needs to be ratified by both houses of parliament to take effect.[470] |
 Syria Syria | No | Syria does not designate Hamas as a terrorist organization. Syria is among other countries that consider Hamas' armed struggle to be legitimate.[419] |
 Turkey Turkey | No | The Turkish government met with Hamas leaders in February 2006, after the organization's victory in the Palestinian elections. In 2010, Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdoğan described Hamas as "resistance fighters who are struggling to defend their land".[474][475] |
 United Kingdom United Kingdom | Yes | Hamas in its entirety is proscribed as a terrorist group and banned under the Terrorism Act 2000. "The government now assess that the approach of distinguishing between the various parts of Hamas is artificial. Hamas is a complex but single terrorist organisation."[52] |
 United Nations United Nations | No | The list of United Nations designated terrorist groups does not include Hamas.[476] On December 5, 2018, the UN rejected a US resolution aimed at unilaterally condemning Hamas for Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel and other violence.[477][478][92][479] |
 United States United States | Yes | Lists Hamas as a "Foreign Terrorist Organization".[480] The State Department decided to add Hamas to its US State Department list of Foreign Terrorist Organizations in April 1993.[481] As of 2023[update], it is still listed.[482] |
Criticism
Aside from its use of political violence in pursuit of its goals, Hamas has been widely criticised for a variety of reasons, including the use of antisemitic hate speech by its representatives, frequent calls for the military destruction of Israel, its specific use of human shields[483] and child combatants as part of its military operations, its restriction of political freedoms within the Gaza Strip, and human rights abuses.
After starting the 2023 war, the European Parliament passed a motion stating the need for Hamas to be eliminated, with US President Biden having expressed the same sentiment.[484][485] Hamas was accused of having committed genocide against Israelis on 7 October 2023 by 240 legal experts, including jurists and academics, Raoul Wallenberg Centre for Human Rights, chaired by former Canadian Justice Minister Irwin Cotler, and Genocide Watch.[486][487][488][489][490]
Support
Israeli policy towards Hamas
Benjamin Netanyahu had been Israel's prime minister for most of the two decades preceding the 2023 Israel–Hamas war, and was criticized for having championed a policy of empowering Hamas in Gaza.[491][492][493][494] This policy was part of a strategy to sabotage a two-state solution by confining the Palestinian Authority to the West Bank and weakening it, and to demonstrate to the Israeli public and western governments that Israel has no partner for peace.[495][496] This criticism was leveled by several Israeli officials, including former prime minister Ehud Barak, and former head of Shin Bet security services Yuval Diskin.[495] Saudi Arabia and the Palestinian Authority were also critical of Israel under Netanyahu allowing suitcases of Qatari money to be given to Hamas,[495] in exchange for maintaining the ceasefire.[491] The Times of Israel reported after the Hamas attack that Netanyahu's policy to treat the Palestinian Authority as a burden and Hamas as an asset had "blown up in our faces".[491]
Public support
A poll conducted in 2021 found that 53% of Palestinians believed Hamas was "most deserving of representing and leading the Palestinian people". Only 14% preferred Abbas's Fatah party.[497] At the same time, a majority of Gazans saw Hamas as corrupt as well, but were frightened to criticize the group.[498] Polls conducted in September 2023 found that support for Hamas among Palestinians was around 27–31%.[499]
Public opinions of Hamas deteriorated after it took control of the Gaza Strip in 2007. Prior to the takeover, 62% of Palestinians had held a favorable view of the group, while a third had negative views. According to a 2014 Pew Research just prior to the 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict, only about a third had positive opinions and more than half viewed Hamas negatively. Furthermore, 68% of Israeli Arabs viewed Hamas negatively.[500] In July 2014, 65% of Lebanese viewed Hamas negatively. In Jordan and Egypt, roughly 60% viewed Hamas negatively, and in Turkey, 80% had a negative view of Hamas. In Tunisia, 42% had a negative view of Hamas, while 56% of Bangladeshis and 44% of Indonesians had a negative opinion of Hamas.[500]
Hamas popularity surged after the war in July–August 2014 with polls reporting that 81 percent of Palestinians felt that Hamas had "won" that war.[501][502] A June 2021 opinion poll found that 46% of respondents in Saudi Arabia supported rocket attacks on Israel by Hamas during the 2021 Israel–Palestine crisis.[503] A March/April 2023 poll found that 60% of Jordanians viewed Hamas firing rockets at Israel at least somewhat positively.[504]
In November 2023, during Israel's bombing and blockade of the Gaza Strip, Hamas's popularity among Palestinians in Gaza and the West Bank increased significantly.[505][506] Support for Hamas also increased among the people of Jordan.[507] According to the poll conducted by The Washington Institute for Near East Policy from November 14 to December 6, 2023, 40% of Saudi participants expressed a positive view of Hamas, 95% of Saudis did not believe that Hamas killed civilians in its attack on Israel, and only 16% of Saudis said Hamas should accept a two-state solution.[508]

Foreign relations

After winning the Palestinian elections, Hamas leaders made multi-national diplomatic tours abroad. In April 2006, Mahmoud al-Zahar (then foreign minister) visited Saudi Arabia, Syria, Kuwait, Bahrein, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Yemen, Libya, Algeria, Sudan and Egypt.[509] He met the Saudi foreign minister Prince Faysal. In Syria he held talks on the issue of Palestinians stuck on the Syrian-Iraqi border.[clarification needed] He also stated that he unofficially met officials from Western Europe in Qatar who did not wish to be named.[509] In May 2006, Hamas foreign minister visited Indonesia, Malaysia, the Sultanate of Brunei, Pakistan, China, Sri Lanka and Iran.[509] The minister also participated in China–Arab States Cooperation Forum.[510] Ismail Haniyeh in 2006 visited Egypt, Syria, Kuwait, Iran, Lebanon, Qatar and Saudi Arabia.[511]
Hamas has always maintained leadership abroad. The movement is deliberately fragmented to ensure that Israel cannot kill its top political and military leaders.[512] Hamas used to be strongly allied with both Iran and Syria. Iran gave Hamas an estimated $13–15 million in 2011 as well as access to long-range missiles. Hamas's political bureau was once located in the Syrian capital of Damascus before the start of the Syrian civil war. Relations between Hamas, Iran, and Syria began to turn cold when Hamas refused to back the government of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. Instead, Hamas backed the Sunni rebels fighting against Assad. As a result, Iran cut funding to Hamas, and Iranian ally Hezbollah ordered Hamas members out of Lebanon.[24] Hamas was then forced out of Syria, and subsequently has tried to mend fences with Iran and Hezbollah.[24] Hamas contacted Jordan and Sudan to see if either would open up its borders to its political bureau, but both countries refused, although they welcomed many Hamas members leaving Syria.[513]
From 2012 to 2013, under the short-lived leadership of Muslim Brotherhood President Mohamed Morsi, Hamas had the support of Egypt. After Morsi was removed from office, his successor Abdul Fattah al-Sisi outlawed the Muslim Brotherhood and destroyed the tunnels Hamas built into Egypt. In 2015, Egypt declared Hamas a terrorist organization. But this decision was overturned by Egypt in June of the same year.[514] There was a rapprochement between Hamas and Egypt, when a Hamas delegation visited Cairo on 12 March 2016.[515] Hamas has assisted Egypt in controlling the insurgency in Sinai.[515] Hamas denied Egypt's request to deploy its own militants in the Sinai leading to tensions between the two.[515]
Egypt has occasionally served as mediator between Hamas and Fatah, seeking to unify the two factions. In 2017, Yahya Sinwar visited Cairo for 5 weeks and convinced the Egyptian government to open the Rafah crossing, letting in cement and fuel in exchange for Hamas committing to better relations with Fatah; this subsequently led to the signing of the 2017 Fatah–Hamas Agreement.[516]
The United Arab Emirates has been hostile to Hamas designating the Brotherhood as a terrorist organization and Hamas was at the time viewed as the Brotherhood's Palestinian equivalent.[24]
Hamas enjoyed close relations with Saudi Arabia in its early years.[517] Saudi Arabia funded most of its operations from 2000 to 2004, but reduced its support due to US pressure.[88] In 2020, many Hamas members in Saudi Arabia were arrested. In 2022, Saudi Arabia began releasing Hamas members from prison. In April 2023, Ismail Haniyeh visited Riyadh, a sign of improving relations.[517] Haniyeh had long sought to visit Saudi Arabia, and his requests to do so had been long ignored up until then.[518]
Despite its Sunni Islamist ideology, Hamas has been flexible and pragmatic in its foreign policy, moderating and toning down its religious rhetoric when expedient;[519] it has developed strong ties with Iran,[520] and has also established relations with constitutionally secular states such as Syria and Russia.[520][519]
North Korea supplies Hamas with weaponry.[521] Ali Barakeh, a Hamas official living in Lebanon, claimed the two are allies.[522][523]
Hamas leaders reportedly re-established relations with Kuwait, Libya and Oman, all of which reportedly have not had warm relations with Fatah.[524] The cool relationship between Fatah and Kuwait owed to Arafat's support for Saddam during the First Gulf War, which lead to the Palestinian exodus from Kuwait (1990–91).[524] This rapproachment is in part due to Hamas's policy of non-interference in the internal affairs of Arab countries.[524] Mahmoud Al-Zahar stated that Hamas does not "play the game" of siding with one Arab nation against another (e.g. in the Gulf War).[525] When Al-Qaradawi, and other Sunni ulema, called for an uprising against Assad's regime in Syria, Mahmoud Al-Zahar maintained that taking sides would harm the Palestinian cause.[526][clarification needed]
Qatar and Turkey
According to Middle East experts, now Hamas has two firm allies: Qatar and Turkey. Both give Hamas public and financial assistance estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars.[24] Qatar has transferred more than $1.8 billion to Hamas.[527] Shashank Joshi, senior research fellow at the Royal United Services Institute, says that "Qatar also hosts Hamas's political bureau which includes Hamas leader Khaled Meshaal." Meshaal also visits Turkey frequently to meet with Turkish Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdoğan.[24] Erdogan has dedicated himself to breaking Hamas out of its political and economic seclusion. On US television, Erdogan said in 2012 that "I don't see Hamas as a terror organization. Hamas is a political party."[512]
Qatar has been called Hamas' most important financial backer and foreign ally.[528][529] In 2007, Qatar was, with Turkey, the only country to back Hamas after the group ousted the Palestinian Authority from the Gaza Strip.[24] The relationship between Hamas and Qatar strengthened in 2008 and 2009 when Khaled Meshaal was invited to attend the Doha Summit where he was seated next to the then Qatari Emir Hamad bin Khalifa al-Thani, who pledged $250 million to repair the damage caused by Israel in the Israeli war on Gaza.[513] These events caused Qatar to become the main player in the "Palestinian issue". Qatar called Gaza's blockade unjust and immoral, which prompted the Hamas government in Gaza, including former Prime Minister Ismail Haniyeh, to thank Qatar for their "unconditional" support. Qatar then began regularly handing out political, material, humanitarian and charitable support for Hamas.[513]

In 2011, U.S. President Barack Obama personally requested that Qatar, one of the U.S.'s most important Arab allies, provide a base for the Hamas leadership. At the time, the U.S. were seeking to establish communications with Hamas and believed that a Hamas office in Qatar would be easier to access than a Hamas bureau in Iran, the group's main backer.[530][531]
In 2012, Qatar's former Emir, Hamad bin Khalifa al-Thani, became the first head of state to visit Gaza under Hamas rule. He pledged to raise $400 million for reconstruction.[532] Sources say that advocating for Hamas is politically beneficial to Turkey and Qatar because the Palestinian cause draws popular support amongst their citizens at home.[533]
Speaking in reference to Qatar's support for Hamas, during a 2015 visit to Palestine, Qatari official Mohammad al-Emadi, said Qatar is using the money not to help Hamas but rather the Palestinian people as a whole. He acknowledges that giving to the Palestinian people means using Hamas as the local contact. Emadi said, "You have to support them. You don't like them, don't like them. But they control the country, you know."[534] Some argue that Hamas's relations with Qatar are putting Hamas in an awkward position because Qatar has become part of the regional Arab problem. Hamas says that having contacts with various Arab countries establishes positive relations which will encourage Arab countries to do their duty toward the Palestinians and support their cause by influencing public opinion in the Arab world.[513] In March 2015, Hamas has announced its support of the Saudi Arabian-led military intervention in Yemen against the Shia Houthis and forces loyal to former President Ali Abdullah Saleh.[535] In a controversial deal, Israel's government under Benjamin Netanyahu supported Qatar's payments to Hamas for many years, in the hope that it would turn Hamas into an effective counterweight to the Palestinian Authority and prevent the establishment of a Palestinian state.[536][531]
In May 2018, Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan tweeted to the Prime Minister of Israel Benjamin Netanyahu that Hamas is not a terrorist organization but a resistance movement that defends the Palestinian homeland against an occupying power. During that period there were conflicts between Israeli troops and Palestinian protestors in the Gaza Strip, due to the decision of the United States to move their embassy to Jerusalem.[537] Also in 2018 the Israel Security Agency accused SADAT International Defense Consultancy (a Turkish private military company with connections to the Turkish government) of transferring funds to Hamas.[538]
In February 2020, Hamas leader Ismail Haniyeh met with Turkish President Erdoğan.[539] On 26 July 2023, Haniyeh met with Erdoğan and Palestinian Authority President Mahmoud Abbas. Behind the meeting was Turkey's effort to reconcile Fatah with Hamas.[540] On 7 October 2023, the day of the Hamas attack on Israel, Haniyeh was in Istanbul, Turkey.[541] On 21 October 2023, Haniyeh spoke with Erdoğan about the latest developments in the Israel–Hamas war and the current situation in Gaza.[542] On 25 October 2023, Erdoğan said that Hamas was not a terrorist organisation but a liberation group fighting to protect Palestinian lands and people.[543]
Lawsuits
In the United States
The charitable trust Holy Land Foundation for Relief and Development was accused in December 2001 of funding Hamas.[544][545][546] The US Justice Department filed 200 charges against the foundation. The case first ended in a mistrial, in which jurors acquitted on some counts and were deadlocked on charges ranging from tax violations to providing material support for terrorists. In a retrial, on November 24, 2008, the five leaders of the Foundation were convicted on 108 counts.[547]
Several US organizations were either shut down or held liable for financing Hamas in early 2001, groups that have origins from the mid-1990s, among them the Holy Land Foundation (HLF), Islamic Association for Palestine (IAP), and Kind Hearts. The US Treasury Department specially designated the HLF in 2001 for terror ties because from 1995 to 2001 the HLF transferred "approximately $12.4 million outside of the United States with the intent to contribute funds, goods, and services to Hamas." According to the Treasury Department, Khaled Meshal identified one of HLF's officers, Mohammed El-Mezain as "the Hamas leader for the US". In 2003, IAP was found liable for financially supporting Hamas, and in 2006, Kind Hearts had their assets frozen for supporting Hamas.[548]
In 2004, a federal court in the United States found Hamas liable in a civil lawsuit for the 1996 murders of Yaron and Efrat Ungar near Bet Shemesh, Israel. Hamas was ordered to pay the families of the Ungars $116 million.[549] The Palestinian Authority settled the lawsuit in 2011. The settlement terms were not disclosed.[550] On August 20, 2004, three Palestinians, one a naturalized American citizen, were charged with a "lengthy racketeering conspiracy to provide money for terrorist acts in Israel".[551] The indicted included Mousa Mohammed Abu Marzook, who had left the US in 1997.[552] On February 1, 2007, two men were acquitted of contravening United States law by supporting Hamas. Both men argued that they helped move money for Palestinian causes aimed at helping the Palestinian people and not to promote terrorism.[553]
In January 2009, a Federal prosecutor accused the Council on American-Islamic Relations (CAIR) of having links to a charity designated as a support network for Hamas.[554] The Justice Department identified CAIR as an "un-indicted co-conspirator" in the Holy Land Foundation case.[555] Later, a federal appeals court removed that label for all parties and instead, named them "joint venturers".[556] CAIR was never charged with any crime, and it complained that the designation had tarnished its reputation.[557][better source needed]
In Germany
A German federal court ruled in 2004 that Hamas was a unified organization whose humanitarian aid work could not be separated from its "terrorist and political activities".[558] In July 2010, Germany outlawed Frankfurt-based International Humanitarian Aid Organization (IHH e.V.), saying it had used donations to support Hamas-affiliated relief projects in Gaza.[559][560] German Interior Minister Thomas de Maiziere said that while presenting their activities to donors as humanitarian assistance, IHH e.V. had "exploited trusting donors' willingness to help by using money that was given for a good purpose for supporting what is, in the final analysis, a terrorist organization".[559][560][561]
See also
Notes
References
Sources
Books
Journal articles
Other
External links
- Official website
 (in Arabic)
(in Arabic) - Official website (in English)
- Hamas leaders CFR
- Hamas Charter of 1988
- Hamas 2017 Document of General Principles & Policies (English translation published by Hamas, via Internet Archive)
- The Covenant of the Islamic Resistance Movement (Hamas) (includes interpretation)
- Hamas Shifts From Rockets to Public Relations The New York Times, July 23, 2009
- 22 years on the start of Hamas Al-Qassam Brigades' Information Office
- Sherifa Zuhur, Hamas and Israel: Conflicting Strategies of Group-Based Politics (PDF file) December 2008
- Fatah and Hamas Human Rights Violations in the Palestinian Occupied Territories in 2007 by Elizabeth Freed of Palestinian Human Rights Monitoring Group
- "Hamas threatens attacks on US: Terrorist warns 'Middle East is full of American targets'" Ynetnews. December 24, 2006. Accessed July 20, 2014.