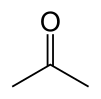
Acetone
chemical compound
Acetone, or propanone, is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3)2CO. This clear, mobile, easy-to-burn liquid is the simplest example of the ketones. Acetone can be mixed with water. It is an important solvent, often to clean things in the laboratory. Common uses of acetone in the home are as the active ingredient in nail polish remover and as paint thinner. It is a common building block in organic chemistry.
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Propan-2-one[7] | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| 3DMet | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 635680 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.602 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 1466 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Acetone | ||
PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1090 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6O | |||
| Molar mass | 58.08 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Pungent, irritating, floral, cucumber like | ||
| Density | 0.7845 g/cm3 (25 °C) | ||
| Melting point | −94.7 °C (−138.5 °F; 178.5 K)[12] | ||
| Boiling point | 56.05 °C (132.89 °F; 329.20 K)[12] | ||
| Miscible | |||
| Solubility | Miscible in benzene, diethyl ether, methanol, chloroform, ethanol[8] | ||
| log P | -0.16[9] | ||
| Vapor pressure |
| ||
| Acidity (pKa) | |||
| −33.78·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD) | 1.3588 (VD = 54.46) | ||
| Viscosity | 0.295 mPa·s (25 °C)[8] | ||
| Structure | |||
| Trigonal planar at C2 | |||
| Dihedral at C2 | |||
| 2.91 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH | (−250.03) – (−248.77) kJ/mol | ||
| Std enthalpy of combustion ΔcH | −1.772 MJ/mol | ||
| Standard molar entropy S | 200.4 J/(mol·K) | ||
| Specific heat capacity, C | 125.45 J/(mol·K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Explosive limits | 2.6–12.8%[13] | ||
| U.S. Permissible exposure limit (PEL) | 1000 ppm (2400 mg/m3)[6] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Sources
🔥 Top keywords: Main PageSpecial:Search0Slash (punctuation)BlackSpecial:RecentChanges4 (number)DavidSOLID (object-oriented design)Wikipedia:AboutFile:Sexual intercourse with internal ejaculation.webmHelp:ContentsHelp:IntroductionLisa Sparxxx2023 UEFA Champions League FinalColour24-hour clockAdolf Hitler UunonaBismillahir Rahmanir Raheem6 (number)T. N. SeshanFile:ASCII-Table-wide.svg20 (number)Poor Things (movie)United StatesCristiano RonaldoList of people who have walked on the MoonAli Malikov50 (number)17 (number)The Valley (2024 TV series)GrassList of mathematical symbolsList of U.S. states and territories by time zone8 (number)List of countries by areaWikipedia:Simple talkList of largest Hindu templesRama