రేచుకుక్కలు
ఇవి అడవి జంతువులు, క్రూర జంతువులు. అడవిలో ఎన్నో జంతువులుంటాయి. కాని వీటికి ఒక ప్రత్యేకత వున్నది. వీటి ఆకారం చూడడానికి కుక్కల్లాగె వున్నా ఇంకా అందంగా అన్ని ఒకే రంగులో వుండి కుక్కల కన్నా కొంచెం పెద్దగా వుంటాయి. మూతి కొంచెం పొడుగ్గా మూతి కొన నల్లగా కుచ్చు తోక కలిగి వుంటాయి. ఇవి ఎప్పుడు గుంపులు గుంపులుగా వుంటాయి. ఒంటరిగా మాత్రం వుండవు. ఇవి మనుషులకు గాని జంతువులకు గాని ఎంతమాత్రం భయపడవు. వేటాడె సమయంలో ఇవి చాల చురుగ్గా నిర్బయంగా ప్రవర్తిస్తాయి. మేకలు, గొర్రెలు మందమీద పడి గొర్రెలను చంపి తింటాయి. మనుషులకు ఇవి ఏమాత్రం హాని చేయవు. ఇవి గొర్రెల మందలో పడ్డాయంటే తప్పనిసరిగా రెండు మూడు గొర్రెలు చావల్సిందే. ఎంతమంది కాపలా దారులున్నా అందరు కలిసి బెదిరించినా అవి తమ దాడిని మాత్రం ఆపవు. అవి ముందుగా గొర్రె గొంతును పట్టి రక్తం పీల్సి పడవేస్తాయి. మిగతావి పొట్టను చీల్సి తింటాయి. కాపలాదారు పక్కనే వున్న వాటికి భయం లేదు. తమ పని తాము కానిస్తాయి. కాపరులకు కూడా వాటి సంగతి తెలుసు గాన వాటి బారిన పడిన దాన్ని వదిలి మిగతా వాటిని దూరంగా తోలుకొని పోతారు. మిగతా గొర్రెలను దూరంగా తీసుకెళ్లి అక్కడ బద్రంగా వదిలి చచ్చిన గొర్రె మిగిలిన భాగానైనా తీసుకొద్దామని వెళ్లగా అప్పటికి ఆ రేసుకుక్కలు తృప్తిగా గొర్రెను తినేసి మూతులను న్నాక్కుంటూ వస్తున్నతన్ని చూసి తాపీగా వెళ్లుతాయి. అవి అల్లంత దూరంలోనె భుక్తాయసం తీసుకుంటుండగా గొర్రెల కాపరి అక్కడ మిగిలిన గొర్రె తోలుని తీసి బుజాన వేసుకొని తిరుగు ముఖం పడ్తాడు. ఈ రోజుకి అవి ఎటువంటి దాడి చేయవు. ఇక గొర్రెల కాపరులు ఈ రోజుకి తాపీగా గొర్రెలను మేపు కుంటారు. ఈ రేసు కుక్కలు కేవలం ఒక మంద మాత్రమే వస్తాయి. అవి ఎప్పుడు ఒకే ప్రాంతాన్ని అంటి పెట్టుకొని వుండవు. ఆ తర్వాత ఎప్పుడొ ఈ ప్రాంతానికి వస్తాయి. అంత వరకు గొర్రెల కాపరులకు నిచ్చింతే. విశేషమేమిటంటే మనుషులు ఎవ్వరూ వాటికి హాని చేయరు, అవి కూడా మనుషులకు హాని చేయవు. అవి దేవతా కుక్కలని వీరి నమ్మకం. వాటిని కొట్ట కూడదని వీరి నియమం. ఈ సంగతి వాటికి తెలిసి నట్టుంది. అడవి జంతువుల గురించి తెలిసినవారు చూసిన వారు చెప్పే దాన్ని బట్టి అడవి పందిని వేటాడ్డం పులలకు కూడ చాల కష్టమట. అలాంటి అడవి పందిని కూడ ఈ రేసు కుక్కలు అతి సునాయసంగా వేటాడతాయట. చూసిన వారు చెప్తారు. వింతైన విషయమేమిటంటే పులులు కూడ వీటికి భయపడతాయట...
| రేచుకుక్క (Dhole) కాల విస్తరణ: Post-Pleistocene-Recent | |
|---|---|
 | |
Conservation status | |
| శాస్త్రీయ వర్గీకరణ | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Subfamily: | Caninae |
| Genus: | Cuon Hodgson, 1838 |
| Species: | C. alpinus |
| Binomial name | |
| Cuon alpinus (Pallas, 1811) | |
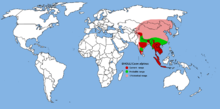 | |
| Dhole range | |
ఉపజాతులు
| Subspecies | Trinomial authority | Description | Range | Synonyms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indian dhole Cuon a. dukhunensis[1] | Sykes, 1831 | Peninsular India, south of Ganges River | ||
| Himalayan dhole Cuon a. primaevus[1] | Hodgson, 1833 | Gentically distinct[2] | Himalaya and northern regions of the Indian subcontinent: Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve, Sikkim, India[2] | |
| Kashmir dhole Cuon a. laniger[1] | Pocock, 1936 | Kashmir, Lhasa | ||
| Kiangsi dhole Cuon a. lepturus[1] | Heude, 1892 | Southern China | grayiformis (Hodgson, 1863) clamitans (Heude, 1892)rutilans (Müller, 1839) | |
| Indochinese dhole Cuon a. infuscus[1] | Pocock, 1936 | Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam | adustus (Pocock, 1941) | |
| Sumatran dhole Cuon a. sumatrensis[1] | Hardwicke, 1821 | A small subspecies, it measures only two feet in length, and stands 360 mm (14 in) high at the shoulder. It has a pointed, black, fox-like muzzle with long, dark whiskers. The nose and lips are foxy brown mixed with black. The general colour is foxy ferraginous red, with lighter shades on the belly and inner sides of the legs.[3] | Sumatra, Indonesia | |
| Javan dhole Cuon a. javanicus[1] | Desmarest, 1820 | Java, Indonesia | ||
| Eastern[4] or Ussuri dhole[5] Cuon a. alpinus దస్త్రం:Ussuridhole.JPG | Pallas, 1811 | This is the largest subspecies, with a long, narrow face and a skull measuring 189 mm long on average. The winter fur's general tone is intense rusty-red. The top of the head and the outer ears are brownish-rusty with black-brown highlights. The shoulders and upper surface of the back is brownish-rusty with black-brown highlights. The outer sides of the legs are rusty brown, while the inner sides of the legs and lower sides of the body are yellowish.[5] | Russian Far East, China, Tibet, Mongolia | fumosus (Pocock, 1936) |
| Western[4] or Tien Shan dhole[6] Cuon a. hesperius దస్త్రం:Tien shan dhole.jpg | Afanasjev and Zolotarev, 1935 | A small subspecies, it has a short, wide face and a skull measuring 180 mm long on average. The general tone of the winter fur is lighter-coloured than C. a. alpinus, with weakly developed rusty-red tints. The top of the head and outer sides of the ears are reddish-straw coloured. The upper surface of the neck is dirty-white, with a narrow, sandy-yellow-coloured band running along the upper surface of the back from the ears to the shoulders. The outer surfaces of the limbs are sandy-yellow, while the flanks and inner sides of the limbs have little to no yellowish tint.[6] | Transoxiana, Eastern Russia and China | jason (Pocock, 1936) |
| †Late Pleistocene dhole Cuon a. europaeus | Bourguignat, 1875 | The earliest form to evolve a singlely cusped, sharply trenchant tooth in place of the lower tubercular molar[7] | Czech Republic, Hungary, Austria, Switzerland and French Riviera | |
| †Late Middle Pleistocene dhole Cuon a. fossilis | Nehring, 1890 | An intermediate form between Cuon a. priscus and Cuon a. europaeus[7] | Heppenloch, Germany | |
| †Early Middle Pleistocene dhole Cuon a. priscus | Thenius, 1954 |



